Question
The aircraft for a particular flight has 72 seats. The airline’s records show that historically
for this flight only 90% of the people who purchase a ticket arrive to board the flight.
They assume this trend will continue and decide to sell extra tickets and hope that no
more than 72 passengers will arrive.
The number of passengers that arrive to board this flight is assumed to follow a binomial
distribution with a probability of 0.9.
(a) The airline sells 74 tickets for this flight. Find the probability that more than 72
passengers arrive to board the flight. [3]
(b) (i) Write down the expected number of passengers who will arrive to board the
flight if 72 tickets are sold. [2]
(ii) Find the maximum number of tickets that could be sold if the expected number
of passengers who arrive to board the flight must be less than or equal to 72. [2]
Each passenger pays $150 for a ticket. If too many passengers arrive, then the airline will
give $300 in compensation to each passenger that cannot board.
(c) Find, to the nearest integer, the expected increase or decrease in the money made
by the airline if they decide to sell 74 tickets rather than 72. [8]
Answer/Explanation
Ans
5. (a) (let T be the number of passengers who arrive)
(P = ( T > 72) =) P = ( T ≥ 73 ) OR 1 – P ( T ≤ 72) (A1)
T ~ B (74, 0.9) OR n = 74 (M1)
= 0.00379 (0.00379124…) A1
Note: Using the distribution B(74, 0.1) , to work with the 10% that do not arrive
for the flight, here and throughout this question, is a valid approach.
[3 marks]
(b) (i) 72 × 0.9 (M1)
64.8 A1
(ii) n × 0.9 = 72 (M1)
80 A1
[4 marks]
(c) METHOD 1
EITHER
when selling 74 tickets
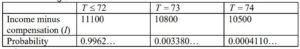
top row A1A1
bottom row A1A1
Note: Award A1A1 for each row correct. Award A1 for one correct
entry and A1 for the remaining entries correct.
E(I) = 11100 × 0.9962… + 10800 × 0.00338… + 10500 × 0.000411 ≈ 11099 (M1)A1
OR
income is 74 × 150 = 11100 (A1)
expected compensation is
0.003380…× 300 + 0.0004110… × 600 ( = 1.26070…) (M1)A1A1
expected income when selling 74 tickets is 11100 − 1.26070… (M1)
=11098.73.. (= $11099) A1
THEN
income for 72 tickets = 72 × 150 = 10800 (A1)
so expected gain ≈11099 − 10800 = $299 A1
Question 5 continued
METHOD 2
for 74 tickets sold, let C be the compensation paid out
P (T = 73) = 0.00338014 …, P= (T=74 ) = 0.000411098 A1A1
E(C) = 0.003380… × 300 + 0.0004110… × 600 (= 1.26070) (M1)A1A1
extra expected revenue = 300 –1.01404… – 0.246658… (300 −1.26070…)
(A1)(M1)
Note: Award A1 for the 300 and M1 for the subtraction.
= $299 (to the nearest dollar) A1
METHOD 3
let D be the change in income when selling 74 tickets
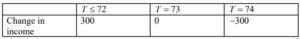
(A1)(A1)
Note: Award A1 for one error, however award A1A1 if there is no explicit mention that
T = 73 would result in D = 0 and the other two are correct.
P (T ≤ 73) 0.9962…, P (T = 74) = 0.000411098 A1A1
E(D) = 300 × 0.9962…+ 0 × 0.003380… − 300 × 0.0004110 (M1)A1A1
= $299 A1
[8 marks]
[Total 15 marks]
Question
A discrete random variable X has the following probability distribution.
x | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
P(X = x) | q | 4 p2 | p | 0.7 – 4 p2 |
Find an expression for q in terms of p . [2]
(i) Find the value of p which gives the largest value of E(X).
(ii) Hence, find the largest value of E(X). [4]
Answer/Explanation
Ans

Question
The following table shows the probability distribution of a discrete random variable X.
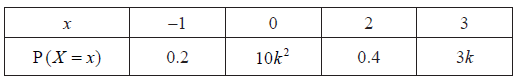
Find the value of k.
Find the expected value of X.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
evidence of using \(\sum {{p_i} = 1} \) (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g. \(10{k^2} + 3k + 0.6 = 1\) , \(10{k^2} + 3k – 0.4 = 0\)
\(k = 0.1\) A2 N2
[4 marks]
evidence of using \({\rm{E}}(X) = \sum {{p_i}{x_i}} \) (M1)
correct substitution (A1)
e.g. \( – 1 \times 0.2 + 2 \times 0.4 + 3 \times 0.3\)
\({\rm{E}}(X) = 1.5\) A1 N2
[3 marks]
Question
A test has five questions. To pass the test, at least three of the questions must be answered correctly.
The probability that Mark answers a question correctly is \(\frac{1}{5}\) . Let X be the number of questions that Mark answers correctly.
Bill also takes the test. Let Y be the number of questions that Bill answers correctly.
The following table is the probability distribution for Y .
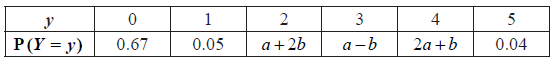
(i) Find E(X ) .
(ii) Find the probability that Mark passes the test.
(i) Show that \(4a + 2b = 0.24\) .
(ii) Given that \({\rm{E}}(Y) = 1\) , find a and b .
Find which student is more likely to pass the test.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
(i) valid approach (M1)
e.g. \(np\) , \(5 \times \frac{1}{5}\)
\({\rm{E}}(X) = 1\) A1 N2
(ii) evidence of appropriate approach involving binomial (M1)
e.g. \(X \sim B\left( {5,\frac{1}{5}} \right)\)
recognizing that Mark needs to answer 3 or more questions correctly (A1)
e.g. \({\rm{P}}(X \ge 3)\)
valid approach M1
e.g. \(1 – {\rm{P}}(X \le 2)\) , \({\rm{P}}(X = 3) + {\rm{P}}(X = 4) + {\rm{P}}(X = 5)\)
\({\text{P(pass)}} = 0.0579\) A1 N3
[6 marks]
(i) evidence of summing probabilities to 1 (M1)
e.g. \(0.67 + 0.05 + (a + 2b) + \ldots + 0.04 = 1\)
some simplification that clearly leads to required answer
e.g. \(0.76 + 4a + 2b = 1\) A1
\(4a + 2b = 0.24\) AG N0
(ii) correct substitution into the formula for expected value (A1)
e.g. \(0(0.67) + 1(0.05) + \ldots + 5(0.04)\)
some simplification (A1)
e.g. \(0.05 + 2a + 4b + \ldots + 5(0.04) = 1\)
correct equation A1
e.g. \(13a + 5b = 0.75\)
evidence of solving (M1)
\(a = 0.05\) , \(b = 0.02\) A1A1 N4
[8 marks]
attempt to find probability Bill passes (M1)
e.g. \({\rm{P}}(Y \ge 3)\)
correct value 0.19 A1
Bill (is more likely to pass) A1 N0
[3 marks]
Question
Two fair 4-sided dice, one red and one green, are thrown. For each die, the faces are labelled 1, 2, 3, 4. The score for each die is the number which lands face down.
List the pairs of scores that give a sum of 6.
The probability distribution for the sum of the scores on the two dice is shown below.
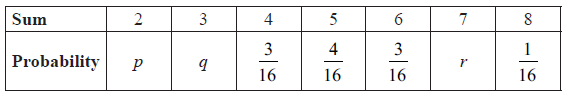
Find the value of p , of q , and of r .
Fred plays a game. He throws two fair 4-sided dice four times. He wins a prize if the sum is 5 on three or more throws.
Find the probability that Fred wins a prize.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
three correct pairs A1A1A1 N3
e.g. (2, 4), (3, 3), (4, 2) , R2G4, R3G3, R4G2
[3 marks]
\(p = \frac{1}{{16}}\) , \(q = \frac{2}{{16}}\) , \(r = \frac{2}{{16}}\) A1A1A1 N3
[3 marks]
let X be the number of times the sum of the dice is 5
evidence of valid approach (M1)
e.g. \(X \sim {\rm{B}}(n{\text{, }}p)\) , tree diagram, 5 sets of outcomes produce a win
one correct parameter (A1)
e.g. \(n = 4\) , \(p = 0.25\) , \(q = 0.75\)
Fred wins prize is \({\rm{P}}(X \ge 3)\) (A1)
appropriate approach to find probability M1
e.g. complement, summing probabilities, using a CDF function
correct substitution (A1)
e.g. \(1 – 0.949 \ldots \) , \(1 – \frac{{243}}{{256}}\) , \(0.046875 + 0.00390625\) , \(\frac{{12}}{{256}} + \frac{1}{{256}}\)
\({\text{probability of winning}} = 0.0508\) \(\left( {\frac{{13}}{{256}}} \right)\) A1 N3
[6 marks]
Question
A biased four-sided die is rolled. The following table gives the probability of each score.
Find the value of k.
Calculate the expected value of the score.
The die is rolled 80 times. On how many rolls would you expect to obtain a three?
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
evidence of summing to 1 (M1)
eg 0.28 + k + 1.5 + 0.3 = 1, 0.73 + k = 1
k = 0.27 A1 N2
[2 marks]
correct substitution into formula for E (X) (A1)
eg 1 × 0.28 + 2 × k + 3 × 0.15 + 4 × 0.3
E (X) = 2.47 (exact) A1 N2
[2 marks]
valid approach (M1)
eg np, 80 × 0.15
12 A1 N2
[2 marks]
