Question
The function f has a derivative given by a positive constant. \(f'(x) = \frac{1}{x(k-x)}\) \(x\in \mathbb{R},x\neq 0,x\neq k\) where \(k\) is a positive constant.
The expression for f ′(x) can be written in the form \(\frac{a}{x}+\frac{b}{k-x}\) , where \(a,b\in \mathbb{R}\)
Find a and b in terms of k. [3]
Hence, find an expression for f (x) . [3]
Consider P , the population of a colony of ants, which has an initial value of 1200.
The rate of change of the population can be modelled by the differential equation \(\frac{dP}{dt}=\frac{p(k-p)}{5k}\)
where t is the time measured in days, t ≥ 0, and k is the upper bound for the population.
By solving the differential equation, show that \(P =\frac{1200k}{(k-120)e^{\frac{t}{5}}+1200}\)
At t = 10 the population of the colony has doubled in size from its initial value.
Find the value of k , giving your answer correct to four significant figures. [3]
Find the value of t when the rate of change of the population is at its maximum. [3]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)
\(\frac{1}{x(k-x)}= \frac{a}{x}+ \frac{b}{k-x}\)
a (k-x)+ bx = 1
attempt to compare coefficients OR substitute x = k and x = o and solve
a = \(\frac{1}{k} \) and \( b = \frac{1}{k }\)
\(f ‘(x)= \frac{1}{kx}+ \frac{1}{k(k-x)}\)
(b)
attempt to integrate their \(\frac{a}{x}+ \frac{b}{k-x}\)
\(f(x)=\frac{1}{k}\int (\frac{1}{x}+ \frac{1}{k-x})dx\)
= \(\frac{1}{k}(ln |x| – ln | k-x |)+c\)
\(\frac{1}{k}ln |\frac{x}{k-x}|+c\)
(c) attempt to separate variables and integrate both sides
5k \(\int \frac{1}{p(k-p)}dp = \int 1 dt\)
5 (ln p – ln (k-P))= t+ c
EITHER
attempt to substitute t = o , P = 1200 into an equation involving c
c= 5( ln 1200 – ln (k-1200))
= 5ln \(\frac{1200}{k-1200}\)
5 (ln p- ln (k-p ))= t+5 \((ln 1200-ln (k-1200))\)
\(ln (\frac{p(k-1200)}{1200(k-p)})=\frac{t}{5}\)
\(\frac{p(k-1200)}{1200(k-p)}= e ^{^{\frac{t}{5}}}\)
OR
ln \(\frac{p}{k-p}= \frac{t+ c }{5 }\)
\(\frac{p }{k-p }= Ae ^{\frac{t}{5}}\)
attempt to substitute t = 0, p = 1200
\(\frac{1200}{k-1200}= A\)
\(\frac{p }{k-p }= \frac{1200 e^{\frac{t}{5}}}{k- 1200}\)
THEN
attempt to rearrange and isolate p
\(pk – 1200p = 1200ke ^{\frac{t}{5}}- 1200 pe ^{\frac{t}{5 }}\)
OR \(pke ^{\frac{-t}{5}}-1200pe^{\frac{-t}{5}}= 1200k – 1200p\)
OR
\(\frac{K}{P}-1 = \frac{K-1200}{1200e^{\frac{t}{5}}} \)
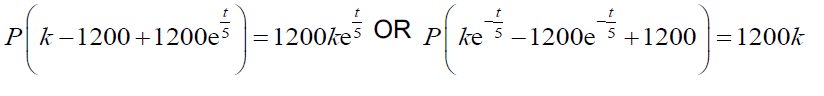
p = \(\frac{1200k}{(k-1200)e ^{\frac{t}{5}}+1200}\)
(d)
attempt to substitute t = 10 p = 2400
2400=\(\frac{1200k}{(k-1200)e^{-2}+ 1200 }\)
k = 2845.34..
k= 2845
(e)
attempt to find the maximum of the first derivative graph OR zero of the second derivative graph OR that p =\(\frac{k}{2}(=1422.67..)\)
t =1.57814…
=1.58 (days)
Question
The graph of a function f passes through the point (ln4, 20).
Given that f ′(x) = 6e2x , find f (x).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
evidence of integration
eg \(\int f'(x)dx, \int 6e^{2x}\)
correct integration (accept missing + c)
eg \(\frac{1}{2}\times 6e^{2x}, 3e^{2x}\) +c
substituting initial condition into their integrated expression (must have +c )
eg \(3e^{2\times ln4}\)+c = 20
correct application of log (\(a^{b})\)= b log a rule (seen anywhere)
eg 2ln4 = ln16, eln16, ln42
correct application of elna= a rule (seen anywhere)
eg \(e^{ln16}= 16, (e^{ln4})^{2}=4^{2}\)
correct working
eg \(3\times 16+c= 20, 3\times (4^{2})+c= 20, c=20 c=-28\)
\(f(x)=3e^{2x}- 28\)
Question
Let \(f(x) = \int {\frac{{12}}{{2x – 5}}} {\rm{d}}x\) , \(x > \frac{5}{2}\) . The graph of \(f\) passes through (\(4\), \(0\)) .
Find \(f(x)\) .
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
attempt to integrate which involves \(\ln \) (M1)
eg \(\ln (2x – 5)\) , \(12\ln 2x – 5\) , \(\ln 2x\)
correct expression (accept absence of \(C\))
eg \(12\ln (2x – 5)\frac{1}{2} + C\) , \(6\ln (2x – 5)\) A2
attempt to substitute (4,0) into their integrated f (M1)
eg \(0 = 6\ln (2 \times 4 – 5)\) , \(0 = 6\ln (8 – 5) + C\)
\(C = – 6\ln 3\) (A1)
\(f(x) = 6\ln (2x – 5) – 6\ln 3\) \(\left( { = 6\ln \left( {\frac{{2x – 5}}{3}} \right)} \right)\) (accept \(6\ln (2x – 5) – \ln {3^6}\) ) A1 N5
Note: Exception to the FT rule. Allow full FT on incorrect integration which must involve \(\ln\).
[6 marks]
Question
A function f (x) has derivative f ′(x) = 3x2 + 18x. The graph of f has an x-intercept at x = −1.
a.Find f (x).[6]
b.The graph of f has a point of inflexion at x = p. Find p.[4]
c.Find the values of x for which the graph of f is concave-down.[3]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
evidence of integration (M1)
eg \(\int {f’\left( x \right)} \)
correct integration (accept absence of C) (A1)(A1)
eg \({x^3} + \frac{{18}}{2}{x^2} + C,\,\,{x^3} + 9{x^2}\)
attempt to substitute x = −1 into their f = 0 (must have C) M1
eg \({\left( { – 1} \right)^3} + 9{\left( { – 1} \right)^2} + C = 0,\,\, – 1 + 9 + C = 0\)
Note: Award M0 if they substitute into original or differentiated function.
correct working (A1)
eg \(8 + C = 0,\,\,\,C = – 8\)
\(f\left( x \right) = {x^3} + 9{x^2} – 8\) A1 N5
[6 marks]
METHOD 1 (using 2nd derivative)
recognizing that f” = 0 (seen anywhere) M1
correct expression for f” (A1)
eg 6x + 18, 6p + 18
correct working (A1)
6p + 18 = 0
p = −3 A1 N3
METHOD 1 (using 1st derivative)
recognizing the vertex of f′ is needed (M2)
eg \( – \frac{b}{{2a}}\) (must be clear this is for f′)
correct substitution (A1)
eg \(\frac{{ – 18}}{{2 \times 3}}\)
p = −3 A1 N3
[4 marks]
valid attempt to use f” (x) to determine concavity (M1)
eg f” (x) < 0, f” (−2), f” (−4), 6x + 18 ≤ 0
correct working (A1)
eg 6x + 18 < 0, f” (−2) = 6, f” (−4) = −6
f concave down for x < −3 (do not accept x ≤ −3) A1 N2
[3 marks]
Question
Let \(f\left( x \right) = 6{x^2} – 3x\). The graph of \(f\) is shown in the following diagram.
a.Find \(\int {\left( {6{x^2} – 3x} \right){\text{d}}x} \).[2]
b.Find the area of the region enclosed by the graph of \(f\), the x-axis and the lines x = 1 and x = 2 .[4]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\(2{x^3} – \frac{{3{x^2}}}{2} + c\,\,\,\left( {{\text{accept}}\,\,\frac{{6{x^3}}}{3} – \frac{{3{x^2}}}{2} + c} \right)\) A1A1 N2
Notes: Award A1A0 for both correct terms if +c is omitted.
Award A1A0 for one correct term eg \(2{x^3} + c\).
Award A1A0 if both terms are correct, but candidate attempts further working to solve for c.
[2 marks]
substitution of limits or function (A1)
eg \(\int_1^2 {f\left( x \right)} \,{\text{d}}x,\,\,\left[ {2{x^3} – \frac{{3{x^2}}}{2}} \right]_1^2\)
substituting limits into their integrated function and subtracting (M1)
eg \(\frac{{6 \times {2^3}}}{3} – \frac{{3 \times {2^2}}}{2} – \left( {\frac{{6 \times {1^3}}}{3} + \frac{{3 \times {1^2}}}{2}} \right)\)
Note: Award M0 if substituted into original function.
correct working (A1)
eg \(\frac{{6 \times 8}}{3} – \frac{{3 \times 4}}{2} – \frac{{6 \times 1}}{3} + \frac{{3 \times 1}}{2},\,\,\left( {16 – 6} \right) – \left( {2 – \frac{3}{2}} \right)\)
\(\frac{{19}}{2}\) A1 N3
[4 marks]
