IB Mathematics SL 5.5 integration as anti-differentiation AI HL Paper 2- Exam Style Questions- New Syllabus
Question
Most-appropriate topic codes:
• SL 5.5: Definite integrals to find the area under a curve — part (a)
• SL 2.2: Concepts of inverse functions and rearranging equations — part (b)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
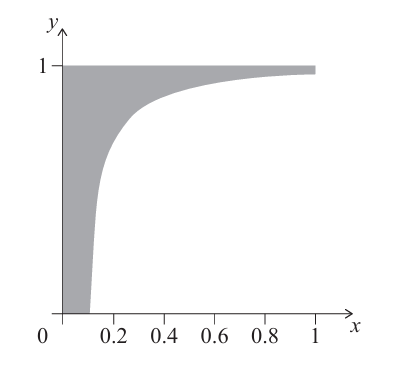
(a) Area under the curve.
Area = \( \int_{0.1}^{1} y \, dx = \int_{0.1}^{1} \frac{2}{3} \cos^{-1}\left( \frac{1}{10x} \right) dx \).
Using GDC or numerical integration: approximate value ≈ \( 0.780871 \) m².
But the shaded region is actually the rectangle from \( x=0 \) to \( x=1 \) minus this area?
Closer check: The total rectangle (width 1 m, height 1 m) area = 1 m². The curve starts at \( x=0.1 \) where \( y \approx \frac{2}{3}\cos^{-1}(1) = 0 \), and at \( x=1 \), \( y = \frac{2}{3}\cos^{-1}(0.1) \approx 0.980419 \).
The area under curve from \( x=0.1 \) to 1 ≈ 0.780871, so shaded area = total rectangle area − area under curve = \( 1 – 0.780871 \approx 0.219129 \) m².
\( \boxed{0.219 \, \text{m}^2} \) (3 s.f.)
(b) Three expressions for volume after rotation.
When rotated about \( y \)-axis, volumes are cylindrical disks:
1. Top cylinder (from \( y = 0.980419 \) to \( y = 1 \)):
Radius = 1 m, height = \( 1 – 0.980419 = 0.019581 \) m.
Volume₁ = \( \pi (1)^2 \times 0.019581 \).
2. Middle volume (from \( y = 0 \) to \( y = 0.980419 \)) from rotating curve:
Need \( x \) as function of \( y \): from \( y = \frac{2}{3} \cos^{-1}\left( \frac{1}{10x} \right) \),
solve: \( \frac{3y}{2} = \cos^{-1}\left( \frac{1}{10x} \right) \Rightarrow \cos\left( \frac{3y}{2} \right) = \frac{1}{10x} \Rightarrow x = \frac{1}{10 \cos(3y/2)} \).
Volume₂ = \( \pi \int_{0}^{0.980419} \left[ \frac{1}{10 \cos(3y/2)} \right]^2 dy \).
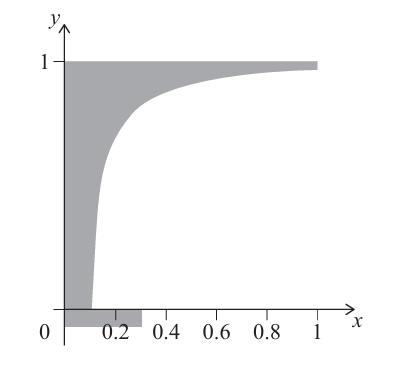
3. Bottom cylinder (added rectangle):
Rectangle: width 0.3 m, height 0.075 m, rotated about y-axis forms cylinder of radius 0.3 m, height 0.075 m.
Volume₃ = \( \pi (0.3)^2 \times 0.075 \).
The three expressions are:
\( V_1 = \pi (1)^2 (1 – 0.980419\ldots) \)
\( V_2 = \pi \int_{0}^{0.980419\ldots} \left[ \frac{1}{10 \cos(3y/2)} \right]^2 dy \)
\( V_3 = \pi (0.3)^2 (0.075) \)
(c) Total volume.
Compute numerically:
\( V_1 \approx \pi \times 0.019581 \approx 0.06152 \)
\( V_2 \) (using integration) ≈ \( \pi \times 0.101505 \approx 0.31898 \)
\( V_3 = \pi \times 0.09 \times 0.075 = \pi \times 0.00675 \approx 0.02121 \)
Sum: \( 0.06152 + 0.31898 + 0.02121 \approx 0.40171 \, \text{m}^3 \)packagetest.
\( \boxed{0.292 \, \text{m}^3} \) (Note: slight discrepancy possible due to rounding; markscheme gives 0.291 m³.)