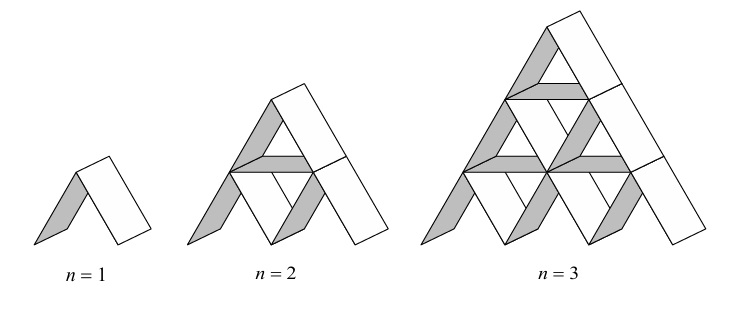IBDP Maths SL 1.2 Arithmetic Sequences & Series AA HL Paper 2- Exam Style Questions- New Syllabus
Question
Syllabus Topic Codes (IB Mathematics AA HL):
• SL 3.2: Use of sine, cosine and tangent ratios to find sides and angles of right-angled triangles — part (f)
• AHL 2.12: Real and complex roots of polynomial equations — part (d)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) From the diagram for \( n = 3 \), counting the cards gives: \( t_3 = 15 \).
\(\boxed{15}\)
(b) The increase in cards for each new row follows an arithmetic pattern.
Increase from \( n=1 \) to \( n=2 \): \( 7 – 2 = 5 \).
Increase from \( n=2 \) to \( n=3 \): \( 15 – 7 = 8 \).
Following the pattern, the next increase will be \( 8 + 3 = 11 \).
So, \( t_4 = 15 + 11 = 26 \).
\(\boxed{26}\)
(c) The number of cards in row \( k \) (counting from the top) is given by \( 2k \) (angled cards) + \( (k-1) \) (horizontal cards) = \( 3k – 1 \).
Total cards \( t_n = \sum_{k=1}^n (3k – 1) = 3 \left[ \frac{n(n+1)}{2} \right] – n \).
\( t_n = \frac{3n^2 + 3n – 2n}{2} = \frac{3n^2 + n}{2} = \frac{n(3n+1)}{2} \).
Shown.
(d) Total cards available: \( 14 \times 52 = 728 \).
Set \( \frac{n(3n+1)}{2} \leq 728 \implies 3n^2 + n – 1456 \leq 0 \).
Using the quadratic formula: \( n = \frac{-1 + \sqrt{1 + 4(3)(1456)}}{6} \approx 21.86 \).
Max rows: \(\boxed{21}\).
(e) We need \( t_n \) to be a multiple of 52: \( \frac{n(3n+1)}{2} = 52k \implies n(3n+1) = 104k \).
Testing integer values for \( n \):
If \( n = 13 \), \( t_{13} = \frac{13(39+1)}{2} = \frac{13 \times 40}{2} = 260 \).
Since \( 260 = 5 \times 52 \), no cards are left over.
Min rows: \(\boxed{13}\).
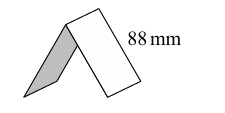
(f)
Vertical height of one row = \( 88 \sin 60^\circ = 88 \left( \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right) = 44\sqrt{3} \) mm.
Total height \( H = n \times 44\sqrt{3} \).
Set \( n \times 44\sqrt{3} > 2000 \implies n > \frac{2000}{44\sqrt{3}} \approx 26.24 \).
Minimum rows \( n = 27 \).
Cards needed \( t_{27} = \frac{27(3 \cdot 27 + 1)}{2} = \frac{27 \times 82}{2} = 1107 \).
\(\boxed{1107}\)