Question:
Consider the expansion of \(\left ( 8x^{3} -\frac{1}{2x} \right )^{n}\) where n ∈ R+. Determine all possible values of n for which the expansion has a non-zero constant term.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
EITHER
attempt to obtain the general term of the expansion
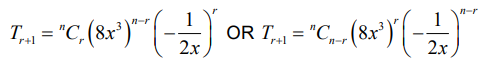
OR
recognize power of x starts at 3n and goes down by 4 each time
THEN
recognizing the constant term when the power of x is zero (or equivalent)
\(r = \frac{3n}{4} or n = \frac{4}{3}r or 3n – 4r = 0 OR 3r – (n-r) = 0 (or equivalent)\)
r is a multiple of 3 (r = 3,6,9,…) or one correct value of n (seen anywhere)
n = 4k, k ∈ Z+
Note: Accept n is a (positive) multiple of 4 or n = 4,8,12,…
Do not accept n = 4,8,12
Note: Award full marks for a correct answer using trial and error approach showing n = 4,8,12,… and for recognizing that this pattern continues.
Question:
Consider the binomial expansion (x + 1)7 = x7 + ax6 + bx5 + 35x4 + … + 1 where x ≠ 0 and a, b ∈ Z+.
(a) Show that b = 21 .
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: EITHER
recognises the required term (or coefficient) in the expansion
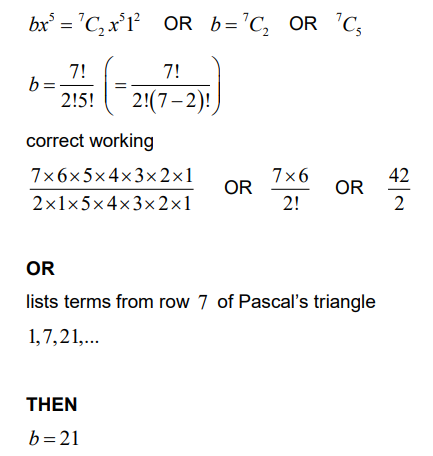
The third term in the expansion is the mean of the second term and the fourth term in the expansion.
(b) Find the possible values of x .
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: 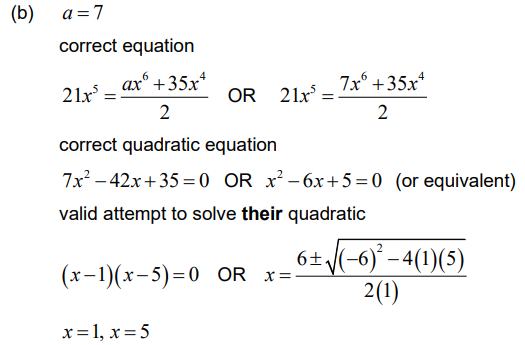
Note: Award final A0 for obtaining x = 0, x = 1, x = 5.
Question:
Consider the expansion of \(\left ( 8x^{3} -\frac{1}{2x} \right )^{n}\) where n ∈ R+. Determine all possible values of n for which the expansion has a non-zero constant term.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
EITHER
attempt to obtain the general term of the expansion
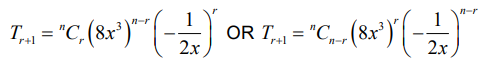
OR
recognize power of x starts at 3n and goes down by 4 each time
THEN
recognizing the constant term when the power of x is zero (or equivalent)
\(r = \frac{3n}{4} or n = \frac{4}{3}r or 3n – 4r = 0 OR 3r – (n-r) = 0 (or equivalent)\)
r is a multiple of 3 (r = 3,6,9,…) or one correct value of n (seen anywhere)
n = 4k, k ∈ Z+
Note: Accept n is a (positive) multiple of 4 or n = 4,8,12,…
Do not accept n = 4,8,12
Note: Award full marks for a correct answer using trial and error approach showing n = 4,8,12,… and for recognizing that this pattern continues.
Question:
In the expansion of (x + k)7, where k ∈ \(\mathbb{R}\) , the coefficient of the term in x5 is 63 .
Find the possible values of k .[Maximum mark: 5]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
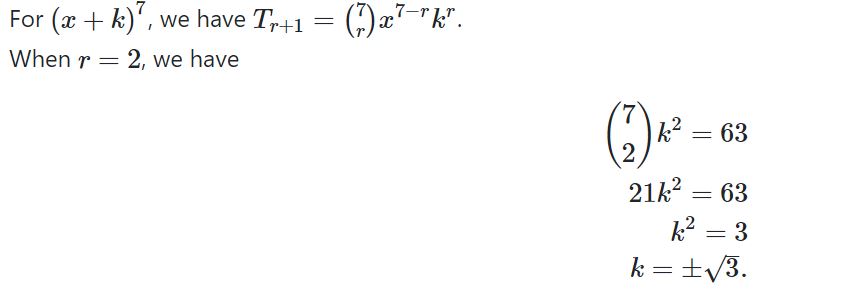
Question:
a. Expand and simplify \({\left( {x – \frac{2}{x}} \right)^4}\).[3]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:\({\left( {x – \frac{2}{x}} \right)^4} = {x^4} + 4{x^3}\left( { – \frac{2}{x}} \right) + 6{x^2}{\left( { – \frac{2}{x}} \right)^2} + 4x{\left( { – \frac{2}{x}} \right)^3} + {\left( { – \frac{2}{x}} \right)^4}\) (A2)
Note: Award (A1) for 3 or 4 correct terms.
Note: Accept combinatorial expressions, e.g. \(\left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
4 \\
2
\end{array}} \right)\) for 6.
\( = {x^4} – 8{x^2} + 24 – \frac{{32}}{{{x^2}}} + \frac{{16}}{{{x^4}}}\) A1
[3 marks]
b. Hence determine the constant term in the expansion \((2{x^2} + 1){\left( {x – \frac{2}{x}} \right)^4}\).[2]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:constant term from expansion of \((2{x^2} + 1){\left( {x – \frac{2}{x}} \right)^4} = -64 + 24 = -40\) A2
Note: Award A1 for –64 or 24 seen.
[2 marks]
Question
Expand and simplify \({\left( {\frac{x}{y} – \frac{y}{x}} \right)^4}\).
▶️Answer/Explanation
\({\left( {\frac{x}{y} – \frac{y}{x}} \right)^4} = {\left( {\frac{x}{y}} \right)^4} + 4{\left( {\frac{x}{y}} \right)^3}\left( { – \frac{y}{x}} \right) + 6{\left( {\frac{x}{y}} \right)^2}{\left( { – \frac{y}{x}} \right)^2} + 4\left( {\frac{x}{y}} \right){\left( { – \frac{y}{x}} \right)^3} + {\left( { – \frac{y}{x}} \right)^4}\) (M1)(A1)
Note: Award M1 for attempt to expand and A1 for correct unsimplified expansion.
\( = \frac{{{x^4}}}{{{y^4}}} – 4\frac{{{x^2}}}{{{y^2}}} + 6 – 4\frac{{{y^2}}}{{{x^2}}} + \frac{{{y^4}}}{{{x^4}}}\,\,\,\,\,\left( { = \frac{{{x^8} – 4{x^6}{y^2} + 6{x^4}{y^4} – 4{x^2}{y^6} + {y^8}}}{{{x^4}{y^4}}}} \right)\) A1A1
Note: Award A1 for powers, A1 for coefficients and signs.
Note: Final two A marks are independent of first A mark.
[4 marks]
Question
Expand and simplify \({\left( {{x^2} – \frac{2}{x}} \right)^4}\).
▶️Answer/Explanation
\({\left( {{x^2} – \frac{2}{x}} \right)^4} = {({x^2})^4} + 4{({x^2})^3}\left( { – \frac{2}{x}} \right) + 6{({x^2})^2}{\left( { – \frac{2}{x}} \right)^2} + 4({x^2}){\left( { – \frac{2}{x}} \right)^3} + {\left( { – \frac{2}{x}} \right)^4}\) (M1)
\( = {x^8} – 8{x^5} + 24{x^2} – \frac{{32}}{x} + \frac{{16}}{{{x^4}}}\) A3
Note: Deduct one A mark for each incorrect or omitted term. [4 marks]
Question
Expand \({(2 – 3x)^5}\) in ascending powers of x, simplifying coefficients.
▶️Answer/Explanation
clear attempt at binomial expansion for exponent 5 M1
\({2^5} + 5 \times {2^4} \times ( – 3x) + \frac{{5 \times 4}}{2} \times {2^3} \times {( – 3x)^2} + \frac{{5 \times 4 \times 3}}{6} \times {2^2} \times {( – 3x)^3}\)
\( + \frac{{5 \times 4 \times 3 \times 2}}{{24}} \times 2 \times {( – 3x)^4} + {( – 3x)^5}\) (A1)
Note: Only award M1 if binomial coefficients are seen.
\( = 32 – 240x + 720{x^2} – 1080{x^3} + 810{x^4} – 243{x^5}\) A2
Note: Award A1 for correct moduli of coefficients and powers. A1 for correct signs.
Total [4 marks]
