IB Mathematics SL 2.2 Function and their domain range graph AA SL Paper 2- Exam Style Questions- New Syllabus
Consider the function \( f(x) = \frac{3}{2} e^{x-2} \), \( 0 \leq x \leq 4 \). The graphs of \( f \) and its inverse \( f^{-1} \) intersect at two points, \( P \) and \( Q \), as shown in the diagram below.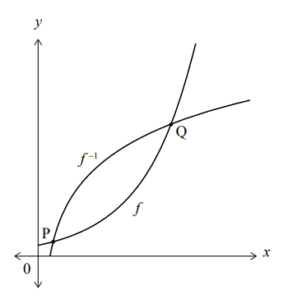
[Image Description: The diagram shows the graphs of \( f(x) = \frac{3}{2} e^{x-2} \) and its inverse \( f^{-1}(x) \), intersecting at points \( P \) and \( Q \) on the line \( y = x \), within the interval \( x \in [0, 4] \).]
Part (a):
Show that the inverse function is \( f^{-1}(x) = 2 + \ln\left(\frac{2x}{3}\right) \). [2]
Part (b):
Find the distance \( PQ \). [3]
Part (c):
The graph of \( f \) is reflected in the x-axis and then translated 5 units in the positive y-direction to give the graph of a function \( g \).
(i) Write down an expression for \( g(x) \). [1]
(ii) Write down the domain of \( g \). [1]
Part (d):
Solve the equation \( f(x) = g(x) \). Give your answer in the form \( x = a + \ln b \), where \( a, b \in \mathbb{Q} \). [2]
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Part (a)
To find the inverse, set \( y = f(x) = \frac{3}{2} e^{x-2} \).
Multiply both sides by \( \frac{2}{3} \): \( \frac{2y}{3} = e^{x-2} \).
Take the natural logarithm: \( \ln\left(\frac{2y}{3}\right) = x – 2 \).
Solve for \( x \): \( x = 2 + \ln\left(\frac{2y}{3}\right) \).
Replace \( y \) with \( x \): \( f^{-1}(x) = 2 + \ln\left(\frac{2x}{3}\right) \) (M1 for rearranging, A1 for final expression, N2).
Verify: \( f(f^{-1}(x)) = \frac{3}{2} e^{\left(2 + \ln\left(\frac{2x}{3}\right) – 2\right)} = \frac{3}{2} \cdot \frac{2x}{3} = x \).
Domain of \( f^{-1} \): \( x > 0 \), range of \( f \): \( \left[\frac{3}{2e^2}, \frac{3}{2}e^2\right] \).
[2 marks]
Part (b)
Solve \( f(x) = f^{-1}(x) \): \( \frac{3}{2} e^{x-2} = 2 + \ln\left(\frac{2}{3} \cdot \frac{3}{2} e^{x-2}\right) = 2 + \ln(e^{x-2}) = 2 + (x – 2) = x \).
Thus: \( \frac{3}{2} e^{x-2} = x \).
Solve numerically in \( [0, 4] \):
Test \( x \approx 0.264456 \): \( \frac{3}{2} e^{0.264456-2} \approx 0.26475 \approx 0.264456 \).
Test \( x \approx 2.51799 \): \( \frac{3}{2} e^{2.51799-2} \approx 2.517 \approx 2.51799 \).
Points: \( P \approx (0.264456, 0.264456) \), \( Q \approx (2.51799, 2.51799) \) (M1 for equation, A1 for coordinates).
Distance on \( y = x \): \( PQ = \sqrt{2} \cdot |2.51799 – 0.264456| \approx \sqrt{2} \cdot 2.253534 \approx 3.186 \approx 3.18 \) (to two decimal places) (M1 for distance formula, N3).
Answer: \( PQ \approx 3.18 \).
[Image Description: Markscheme steps reference https://www.iitianacademy.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/Capturea-300×116.png and https://www.iitianacademy.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/5-2.png, showing equation setup and distance formula.]
[3 marks]
Part (c)(i)
Reflect \( f(x) = \frac{3}{2} e^{x-2} \) in x-axis: \( -f(x) = -\frac{3}{2} e^{x-2} \).
Translate 5 units up: \( g(x) = -\frac{3}{2} e^{x-2} + 5 \) (A1 N1).
Answer: \( g(x) = -\frac{3}{2} e^{x-2} + 5 \).
[1 mark]
Part (c)(ii)
Domain of \( f \): \( [0, 4] \). Reflection and translation do not affect the domain.
Thus, domain of \( g \): \( [0, 4] \) (A1 N1).
Answer: \( [0, 4] \).
[1 mark]
Part (d)
Solve \( f(x) = g(x) \): \( \frac{3}{2} e^{x-2} = -\frac{3}{2} e^{x-2} + 5 \).
Add \( \frac{3}{2} e^{x-2} \): \( 3 e^{x-2} = 5 \).
Divide by 3: \( e^{x-2} = \frac{5}{3} \).
Take natural logarithm: \( x – 2 = \ln\left(\frac{5}{3}\right) \).
Solve: \( x = 2 + \ln\left(\frac{5}{3}\right) \), where \( a = 2 \), \( b = \frac{5}{3} \in \mathbb{Q} \) (M1 for equation, A1 for form, N2).
Verify: \( x \approx 2 + 0.5108 = 2.5108 \in [0, 4] \), \( f(x) = \frac{3}{2} \cdot \frac{5}{3} = \frac{5}{2} \), \( g(x) = -\frac{3}{2} \cdot \frac{5}{3} + 5 = \frac{5}{2} \).
Answer: \( x = 2 + \ln\left(\frac{5}{3}\right) \).
[2 marks]
Total [9 marks]
