IBDP Maths AHL 3.9 Reciprocal trigonometric ratios AA HL Paper 2- Exam Style Questions- New Syllabus
Question
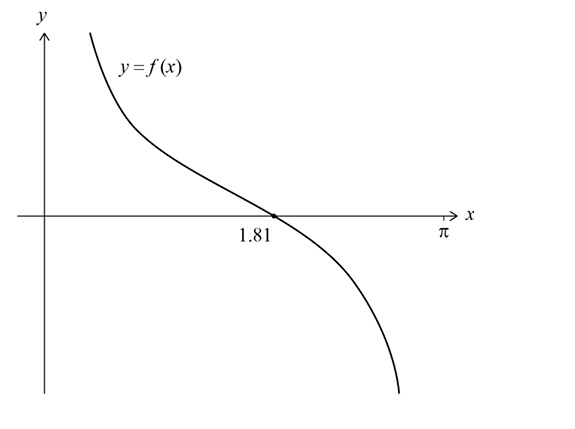
(ii) Sketch the graph of \( y = f(x) \), clearly indicating the coordinates of the \( x \)-intercept.
Syllabus Topic Codes (IB Mathematics AA HL):
• SL 3.5: Definition of \( \tan \theta \) as \( \frac{\sin \theta}{\cos \theta} \) — part (a)(i)
• SL 3.8: Solving trigonometric equations analytically in a finite interval — parts (a)(ii), (b)
• AHL 3.9: Definition of reciprocal trigonometric ratios \( \sec \theta \), \( \csc \theta \) and \( \cot \theta \) — parts (a)(i), (c)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)(i)
Since \( \cot x = \frac{\cos x}{\sin x} \),
\( f(x) = 4 \cdot \frac{\cos x}{\sin x} + \sin x = \frac{4\cos x}{\sin x} + \sin x \)
\( \boxed{f(x) = \frac{4\cos x}{\sin x} + \sin x} \)
(a)(ii)
The domain is \( 0 < x < \pi \). The function has vertical asymptotes at \( x = 0 \) and \( x = \pi \) because \( \sin x = 0 \) there.
Find \( x \)-intercept: set \( f(x) = 0 \):
\( \frac{4\cos x}{\sin x} + \sin x = 0 \)
Multiply by \( \sin x \): \( 4\cos x + \sin^2 x = 0 \)
Use \( \sin^2 x = 1 – \cos^2 x \): \( 4\cos x + 1 – \cos^2 x = 0 \)
\( \cos^2 x – 4\cos x – 1 = 0 \)
Let \( u = \cos x \): \( u^2 – 4u – 1 = 0 \)
\( u = \frac{4 \pm \sqrt{16+4}}{2} = \frac{4 \pm \sqrt{20}}{2} = 2 \pm \sqrt{5} \)
Only \( 2 – \sqrt{5} \approx -0.23607 \) is in \([-1,1]\).
So \( \cos x \approx -0.23607 \implies x \approx \arccos(-0.23607) \approx 1.8091 \) rad.
\( x \)-intercept: \( \boxed{x \approx 1.81} \)
(b)
\( f^{-1}(2) \) is the \( x \) such that \( f(x) = 2 \).
Solve \( \frac{4\cos x}{\sin x} + \sin x = 2 \) numerically.
Using calculator: \( x \approx 1.31837 \) rad.
Rounded to three significant figures: \( \boxed{1.32} \)
(c)
Given \( \sec \alpha = 1.5 \implies \cos \alpha = \frac{2}{3} \).
Since \( 0 < \alpha < \pi \) and \( \cos \alpha > 0 \), \( \alpha \) is in the first quadrant.
\( \sin \alpha = \sqrt{1 – \left( \frac{2}{3} \right)^2} = \sqrt{1 – \frac{4}{9}} = \frac{\sqrt{5}}{3} \).
Then \( f(\alpha) = \frac{4\cos \alpha}{\sin \alpha} + \sin \alpha = \frac{4 \cdot \frac{2}{3}}{\frac{\sqrt{5}}{3}} + \frac{\sqrt{5}}{3} = \frac{8}{\sqrt{5}} + \frac{\sqrt{5}}{3} \).
Common denominator 15: \( \frac{24\sqrt{5}}{15} + \frac{5\sqrt{5}}{15} = \frac{29\sqrt{5}}{15} \approx 4.32306 \).
Rounded to three significant figures: \( \boxed{4.32} \)