IBDP Maths SL 3.2 Use of sine, cosine and tangent ratios AA HL Paper 1- Exam Style Questions- New Syllabus
Question
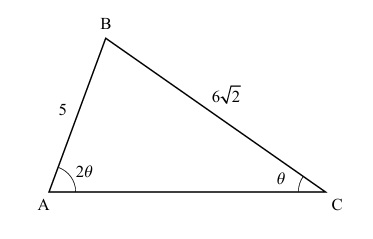 Let \( AB = 5,\; BC = 6\sqrt{2},\; \angle ACB = \theta,\; \angle BAC = 2\theta,\; \) and \( 0 < \theta < \frac{\pi}{2}. \)
Let \( AB = 5,\; BC = 6\sqrt{2},\; \angle ACB = \theta,\; \angle BAC = 2\theta,\; \) and \( 0 < \theta < \frac{\pi}{2}. \)Relevant Syllabus Topic Codes (IB Mathematics AA HL):
• SL 3.5: Definition of \( \cos \theta, \sin \theta \) in terms of the unit circle — part (a)
• SL 3.6: Pythagorean identity and Double angle identities — parts (a), (b)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)
According to the sine rule in \( \triangle ABC \): \( \dfrac{BC}{\sin(2\theta)} = \dfrac{AB}{\sin\theta} \). [cite: 3374]
Substituting the given lengths: \( \dfrac{6\sqrt{2}}{\sin 2\theta} = \dfrac{5}{\sin \theta} \).
Using the double angle identity \( \sin 2\theta = 2\sin \theta \cos \theta \): [cite: 3417]
\( \dfrac{6\sqrt{2}}{2\sin \theta \cos \theta} = \dfrac{5}{\sin \theta} \).
Since \( 0 < \theta < \frac{\pi}{2} \), \( \sin \theta \neq 0 \), so we can cancel it:
\( \dfrac{3\sqrt{2}}{\cos \theta} = 5 \implies \cos \theta = \dfrac{3\sqrt{2}}{5}. \)
\( \boxed{\cos \theta = \dfrac{3\sqrt{2}}{5}} \)
(b)
Using the Pythagorean identity \( \sin^2 \theta + \cos^2 \theta = 1 \): [cite: 3417]
\( \sin^2 \theta = 1 – \left( \dfrac{3\sqrt{2}}{5} \right)^2 = 1 – \dfrac{18}{25} = \dfrac{7}{25}. \)
Because \( \theta \) is in the first quadrant, \( \sin \theta \) is positive:
\( \sin \theta = \sqrt{\dfrac{7}{25}} = \dfrac{\sqrt{7}}{5}. \)
\( \boxed{\sin \theta = \dfrac{\sqrt{7}}{5}} \)
(c)
The area of \( \triangle BCD \) is given by \( \frac{1}{2} \cdot BC \cdot DC \cdot \sin(\angle BCD) \). [cite: 3374]
Since \( \angle BCD \) is the same as \( \angle ACB = \theta \):
\( 2\sqrt{14} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 6\sqrt{2} \times DC \times \dfrac{\sqrt{7}}{5} \).
\( 2\sqrt{14} = \dfrac{3\sqrt{14}}{5} \times DC \).
\( DC = 2\sqrt{14} \times \dfrac{5}{3\sqrt{14}} = \dfrac{10}{3}. \)
\( \boxed{DC = \dfrac{10}{3}} \)
