Question
Consider the following right-angled triangle, where A = 90o.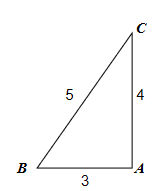
(a) Find the size of angle B in three different ways.
(i) by using the definition of sin B
(ii) by using the definition of cos B
(iii) by using the definition of tan B
(b) Hence find the size of angle C.
(c) Confirm that the sine rule holds.
(d) Confirm that all three versions of the cosine rule hold.
(e) Find the area of the triangle, by using all the three versions below.
\(Area=\frac{1}{2} ab sin C=\frac{1}{2}bcsinA=\frac{1}{2}casinB\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans
(a) (i) \(sin B=\frac{4}{5} \Rightarrow B=53.1\), (ii) \(cos B=\frac{3}{5} \Rightarrow B = 53.1\), (iii) (i) \(tan B = \frac{4}{3} \Rightarrow B = 53.1\)
(b) C = 180 – 90 – 53.1 = 36.9
(c) (d) just confirm
(e) \(A=\frac{1}{2}(3)(4)=6\) \(A=\frac{1}{2}(3)(5)sin53.1≅6\) \(A=\frac{1}{2}(4)(5)sin 36.9 ≅ 6\)
Question
In each of the following triangles one of the angles has size 40o, two of the sides have lengths 5 and 7 respectively.
(a) For the following triangle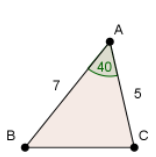
(i) Find the area of the triangle
(ii) Find BC
(iii) Find the size of B and hence the size of C.
(b) For the following triangle.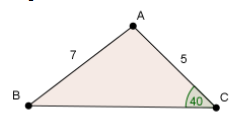
find the size of B and hence the size of A.
(c) For each of the following triangles (ambiguous case)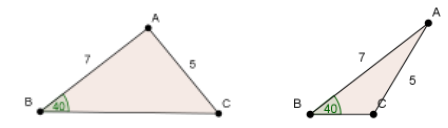
find the size of C and hence the size of A.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans
(a) (i) \(A=\frac{1}{2}(7)(5)sin 40≅11.2\) (ii) \(BC^2=5^2+7^2-2(5)(7)cos 40 \Rightarrow BC = 4.51\)
(iii) \(\frac{sin 40}{4.51}=\frac{sin B}{5} \Rightarrow 45.4\) and so C = 180 -40 – 45.4 = 94.6
(b) B = 27.3 , A = 112.7
(c) C = 64.1, A = 75.9 or C = 115.9, A = 24.1
Question
The following diagram shows triangle ABC.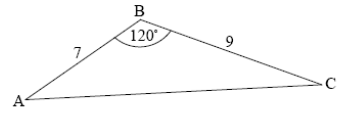
AB = 7 cm, BC = 9 cm and ABC = 120o.
(a) Find AC
(b) Find BAC.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans
(a) \(AC^2=7^2+9^2-2(7)(9)cos 120^o\)
\(AC=13.9(=\sqrt{193})\)
(b) MEHTOD 1
sine rule \(\frac{sin A}{9}=\frac{sin120}{13.9} \Rightarrow A = 34.1o\)
METHOD 2
cosine rule \(cos A=\frac{7^2+13.9^2-9^2}{2(7)(13.9)} \Rightarrow A = 34.1^o\)
Question
A triangle has sides of length 4, 5, 7 units. Find, to the nearest tenth of a degree, the size of the largest angle.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans
Note: largest angle opposite largest side
\(c0s \alpha =\frac{4^2+5^2-7^2}{2 \times 4 \times 5}=-\frac{1}{5} \Rightarrow \alpha = 101.5^o\)
Question
The following diagram shows a triangle with sides 5 cm, 7 cm, 8 cm.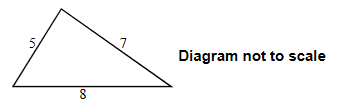
(a) Find the size of the smallest angle, n degrees;
(b) Find the area of the triangle.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans
(a) The smallest angle is opposite the smallest side.
\(cos \theta =\frac{8^2+7^2-5^2}{2 \times 8 \times 7}=\frac{88}{112}=\frac{11}{14}=0.7857\)
Therefore, \(\theta = 38.2^o\)
(b) Area \(=\frac{1}{2} \times 8 \times 7 \times sin 38.2^o=17.3cm^2\)
