IBDP Maths SL 3.3 Applications of trigonometry AA HL Paper 2- Exam Style Questions- New Syllabus
Question
Most-appropriate topic codes (IB Mathematics: Analysis and Approaches HL 2025):
• SL 3.3: Applications of right and non-right angled trigonometry — context of problem
▶️ Answer/Explanation
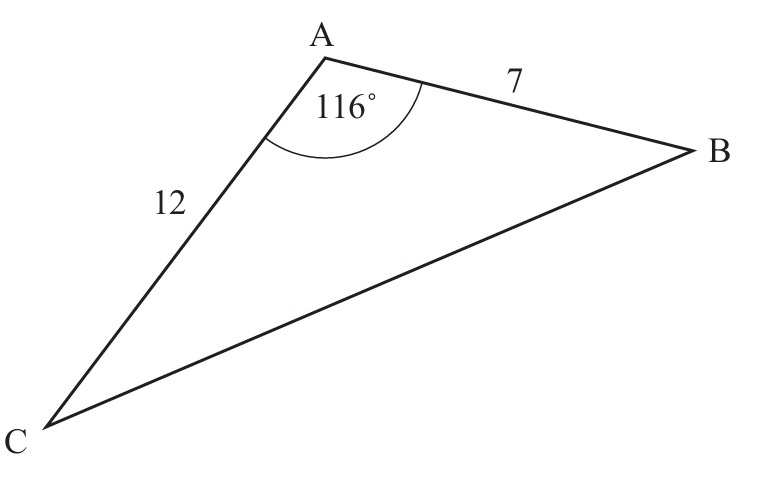
(a)
We use the cosine rule in triangle \( ABC \):
\( BC^2 = AB^2 + AC^2 – 2(AB)(AC)\cos(\angle BAC) \)
Substituting the given values:
\( BC^2 = 7^2 + 12^2 – 2 \times 7 \times 12 \times \cos(116^\circ) \)
\( BC^2 = 49 + 144 – 168\cos(116^\circ) \)
\( BC^2 = 193 – 168\cos(116^\circ) \)
Using \( \cos(116^\circ) \approx -0.438371 \):
\( BC^2 \approx 193 – 168 \times (-0.438371) = 193 + 73.646328 \approx 266.646328 \)
\( BC \approx \sqrt{266.646328} \approx 16.3293 \)
To three significant figures:
\( \boxed{BC \approx 16.3} \)
(b)
We can apply the sine rule in triangle \( ABC \):
\( \frac{\sin(\angle ACB)}{AB} = \frac{\sin(\angle BAC)}{BC} \)
\( \frac{\sin(\angle ACB)}{7} = \frac{\sin(116^\circ)}{16.3293} \)
\( \sin(\angle ACB) = \frac{7 \times \sin(116^\circ)}{16.3293} \)
Using \( \sin(116^\circ) \approx 0.898794 \):
\( \sin(\angle ACB) \approx \frac{7 \times 0.898794}{16.3293} \approx \frac{6.291558}{16.3293} \approx 0.38529 \)
\( \angle ACB \approx \arcsin(0.38529) \approx 22.6618^\circ \)
To three significant figures:
\( \boxed{\angle ACB \approx 22.7^\circ} \) (accept \( 22.8^\circ \) if using 3 sf value of \( BC \) with cosine rule)
Alternative method: Once \( BC \) is known, the angle \( ACB \) can also be found using the cosine rule or by first finding \( \angle ABC \) and using the angle sum of a triangle (\( 180^\circ \)).