IB PHYSICS HL(Higher level) – 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 12.1 The interaction of matter wih radiation
Topic 12 Weightage : 7 %
All Questions for Topic 12.1 – Photons , The photoelectric effect , Matter waves , Pair production and pair annihilation , Quantization of angular momentum in the Bohr model for hydrogen , The wave function , The uncertainty principle for energy and time and position and momentum , Tunnelling, potential barrier and factors affecting tunnelling probability
Question
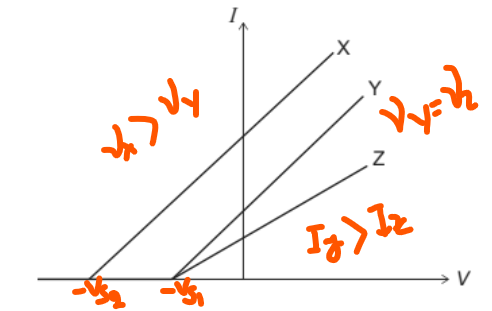
In a photoelectric effect experiment, a beam of light is incident on a metallic surface W in a vacuum.
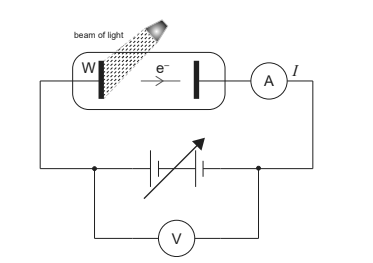
The graph shows how the current I varies with the potential difference V when three different beams X, Y, and Z are incident on W at different times.
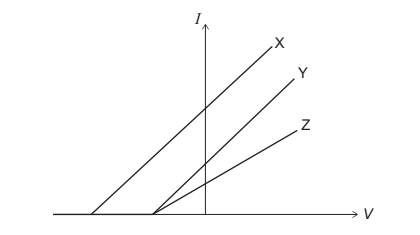
(i) X and Y have the same frequency.
(ii) Y and Z have different intensity.
(iii) Y and Z have the same frequency.
Which statements are correct?
A I and II only
B I and III only
C II and III only
D I, II and III
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
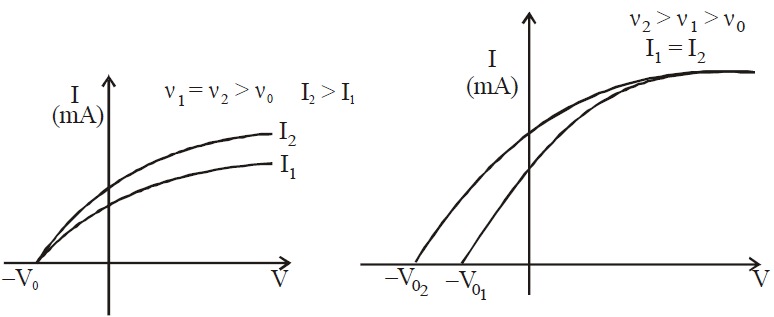
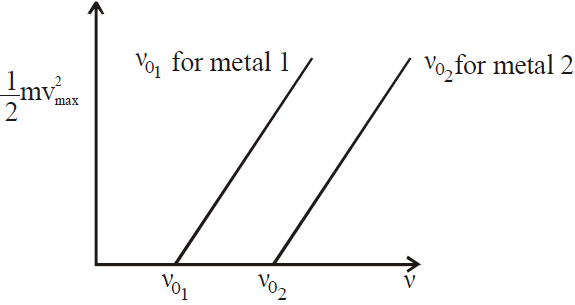
VARIOUS GRAPHS RELATED TO PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT
Question
What is a consequence of the uncertainty principle?
A The absorption spectrum of hydrogen atoms is discrete.
B Electrons in low energy states have short lifetimes.
C Electrons cannot exist within nuclei.
D Photons do not have momentum.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
We know that electron has around 13.6 eV in ground state of hydrogen atom.
\(E_k=\frac{p^2}{2m}\approx\frac{(\Delta p)^2}{2m} =\frac{h^2}{8\pi^2 mL^2}\)
Hence for \( E_k \approx 13.6 eV \) we get \(L \approx 10^{-10}\) , But size of nucleus is around \(10^{-15}\) . Hence electron can not be confined in nucleus as deduced from uncertainty principle
Question
Which of the following is evidence for the wave nature of the electron?
A. Continuous energy spectrum in β– decay
B. Electron diffraction from crystals
C. Existence of atomic energy levels
D. Existence of nuclear energy levels
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
Wave Nature of Electron was experimentally verified by Davisson and Germer by observing diffraction effects with an electron beam
Question
A photoelectric cell is connected in series with a battery of emf 2 V. Photons of energy 6 eV are incident on the cathode of the photoelectric cell. The work function of the surface of the cathode is 3 eV.
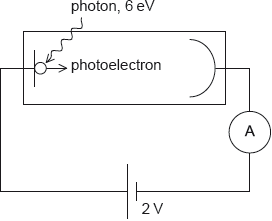
What is the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons that reach the anode?
A. 1 eV
B. 3 eV
C. 5 eV
D. 8 eV
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons is given by
Energy of electron when it leave cathode = \(h\nu-\phi= 6 -3 = 3 eV\)
Electron is de-accelerated by a potential difference of 2 V as anode is connected to negative terminal .
Hence Kinetic energy of electron in reaching to Anode \(= 3-2 = 1eV\)
Question
Which of the following experiments provides evidence for the existence of matter waves?
A. Scattering of alpha particles
B. Electron diffraction
C. Gamma decay
D. Photoelectric effect
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
Matter (or “de Broglie”) Waves
As suggested by de Broglie, to any particle of momentum p, there corresponds a wave of wavelength given by the formula λ = h/p, something known as the duality of matter.
- **Electron diffraction: **Electrons shot through or to a thin slice of crystal have a low probability of reaching a place where the path difference is not an integer number of wavelengths (constructive and destructive interference).
- Electrons accelerated through a pd, they gain kinetic energy. Hence, we have eV = 1/2 mv = p²/2m.
- \(\lambda =hl\sqrt{2meV}\)
Question
A photoelectric cell is connected in series with a battery of emf 2 V. Photons of energy 6 eV are incident on the cathode of the photoelectric cell. The work function of the surface of the cathode is 3 eV.

What is the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons that reach the anode?
A. 1 eV
B. 3 eV
C. 5 eV
D. 8 eV
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons is given by
Energy of electron when it leave cathode = \(h\nu-\phi= 6 -3 = 3 eV\)
Electron is de-accelerated by a potential difference of 2 V as anode is connected to negative terminal .
Hence Kinetic energy of electron in reaching to Anode \(= 3-2 = 1eV\)
Question
According to the Bohr model for hydrogen, visible light is emitted when electrons make transitions from excited states down to the state with n = 2. The dotted line in the following diagram represents the transition from n = 3 to n = 2 in the spectrum of hydrogen.
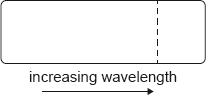
Which of the following diagrams could represent the visible light emission spectrum of hydrogen?
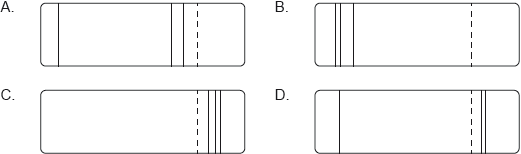
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
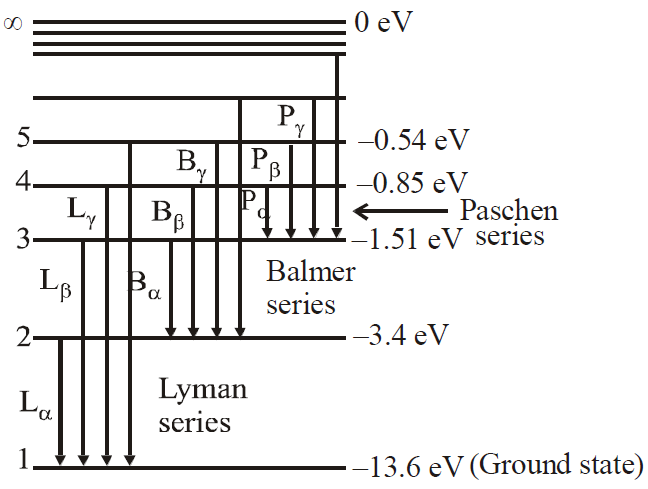
B
Visible light is in Balmer series (lies in visible region)
Question
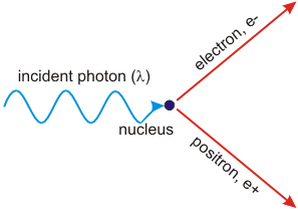
A photon interacts with a nearby nucleus to produce an electron. What is the name of this process?
A. Pair annihilation
B. Pair production
C. Electron diffraction
D. Quantum tunnelling
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
Pair production and annihilation
- Pair production: close to an atomic nucleus, where the electric field is very strong, a photon with minimum energy given by
E = 2mc² can produce a particle and its anti-particle (e.g. e− and e+), where m is the rest mass.- The atomic nucleus helps conserving energy and momentum.
- Any excess energy (above 2mc²) will be converted into kinetic energy of the particles