IB PHYSICS SL (Standard level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 4.4 – Wave behavior
Topic 4 Weightage : 10 %
All Questions for Topic 4.4 – Reflection and refraction , Snell’s law, critical angle and total internal reflection , Diffraction through a single-slit and around objects , Interference patterns , Double-slit interference , Path difference
Question
Three quantities used to describe a light wave are
frequency
wavelength
speed.
Which quantities increase when the light wave passes from water to air?
A I and II only
B I and III only
C II and III only
D I, II and III
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
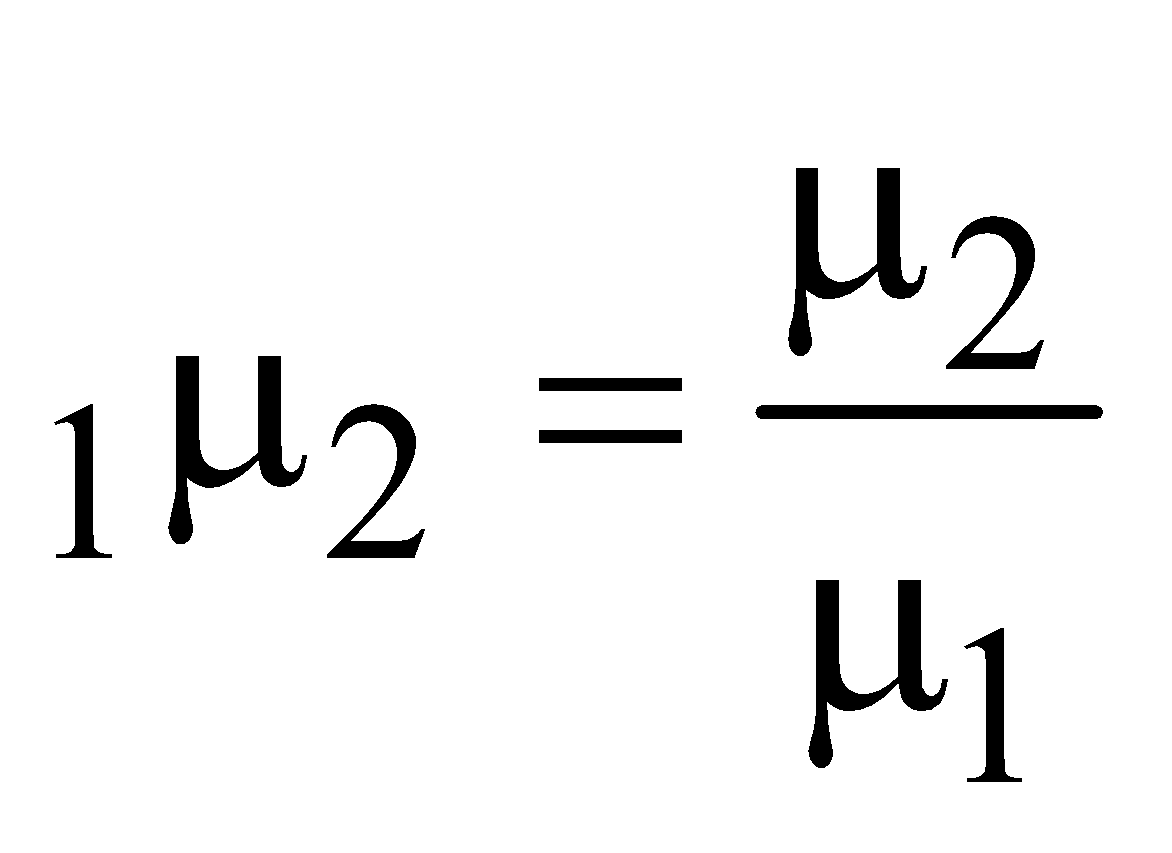
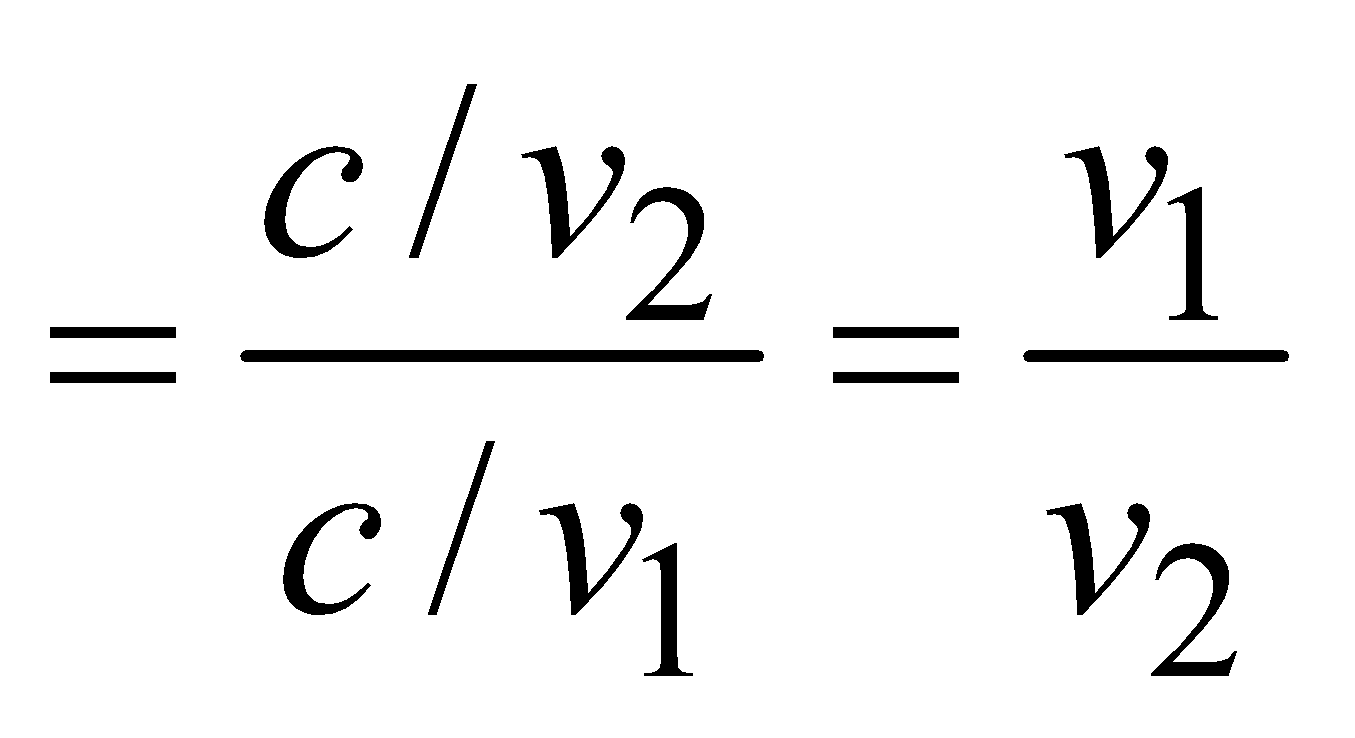
Question
What are the changes in the speed and in the wavelength of monochromatic light when the light passes from water to air?
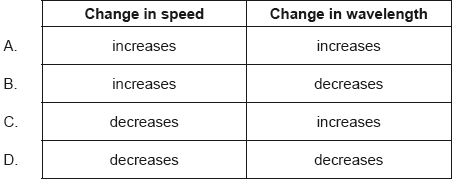
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
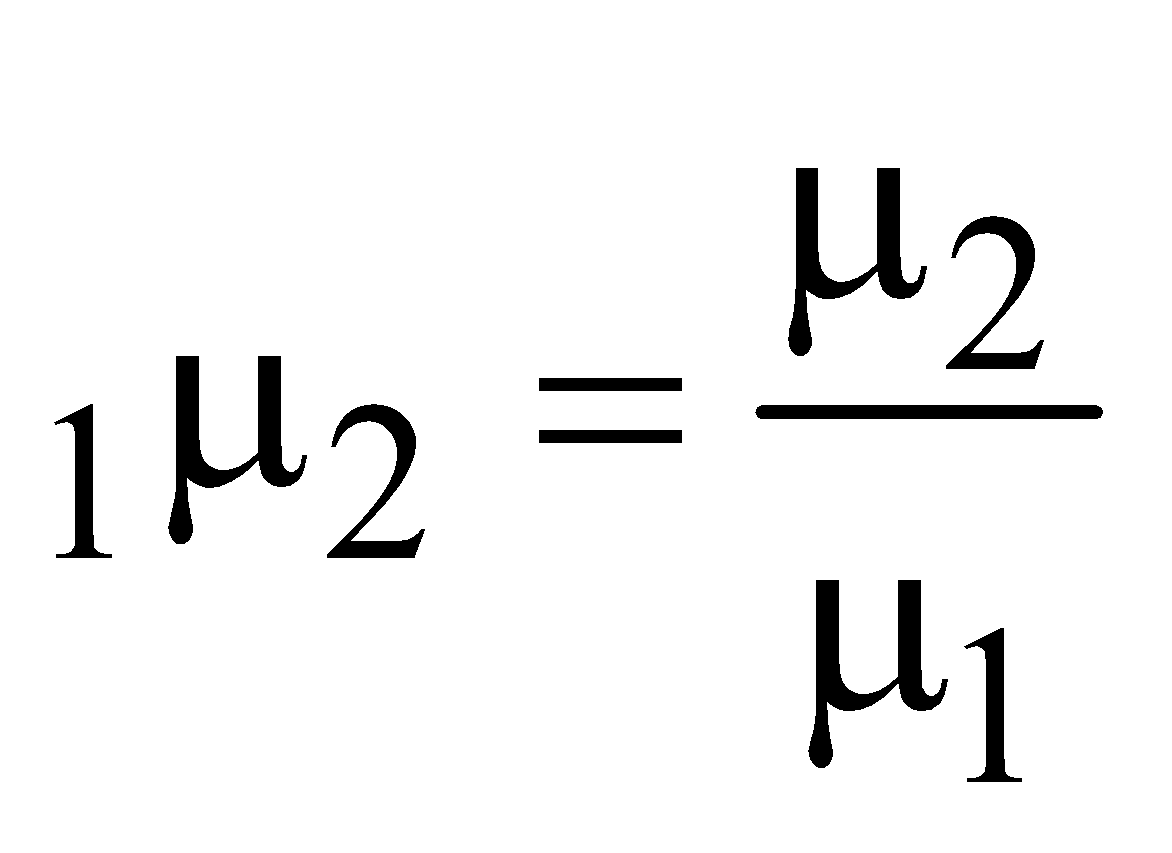
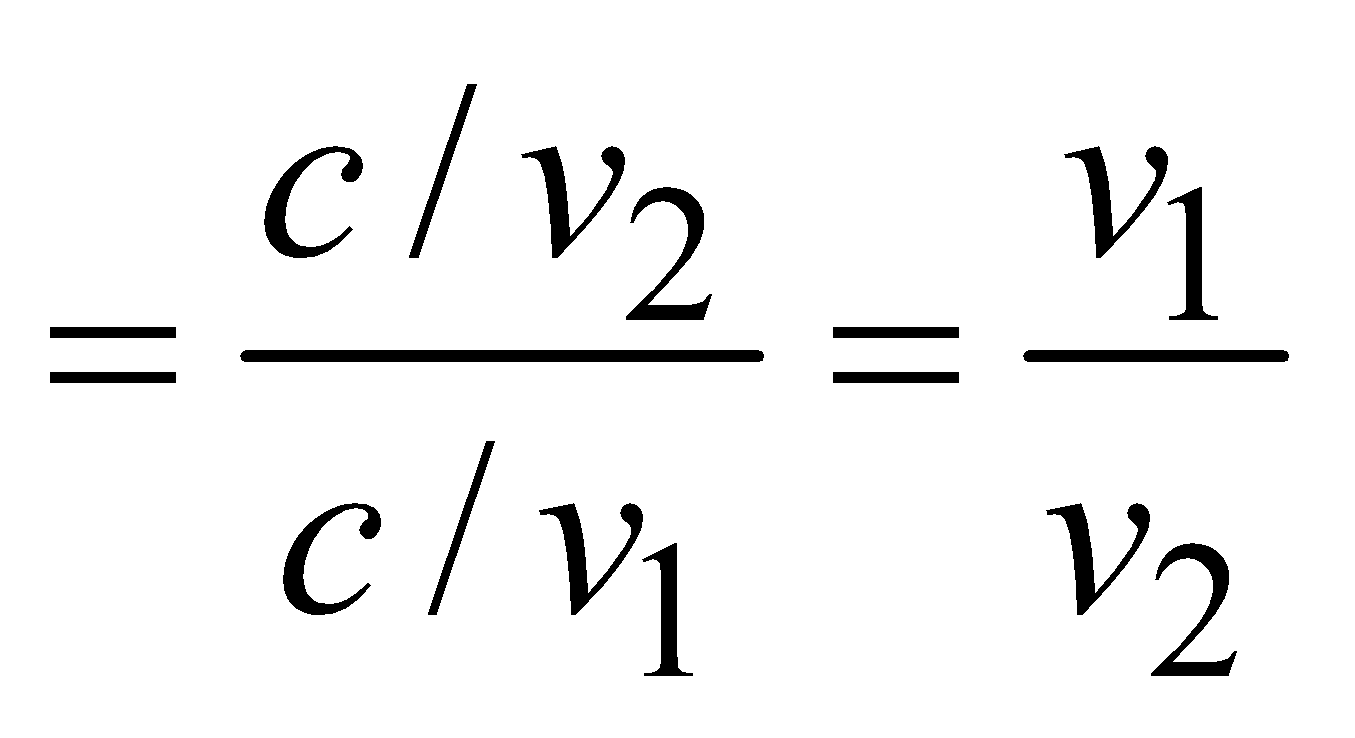
Question
A pair of slits in a double slit experiment are illuminated with monochromatic light of wavelength 480 nm. The slits are separated by 1.0 mm. What is the separation of the fringes when observed at a distance of 2.0 m from the slits?
A. 2.4 × 10–4 mm
B. 9.6 × 10–4 mm
C. 2.4 × 10–1 mm
D. 9.6 × 10–1 mm
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
\(\beta =\frac{\lambda D}{d}\)
\(=\frac{480\times 10^{-9} \times 2}{10^{-3}}\)
\(=9.6\times 10^{-4}=9.6\times 10^{-1} mm\)
Question
The diagram shows an interference pattern produced by two sources that oscillate on the surface of a liquid.

Which of the distances shown in the diagram corresponds to one fringe width of the interference pattern?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
Fringe width is the distance between two consecutive bright spots (maximas, where constructive interference take place) or two consecutive dark spots (minimas, where destructive interference take place).
Question
The refractive index for light travelling from medium X to medium Y is \(\frac{4}{3}\). The refractive index for light travelling from medium Y to medium Z is \(\frac{3}{5}\). What is the refractive index for light travelling from medium X to medium Z?
A. \(\frac{4}{5}\)
B. \(\frac{15}{12}\)
C. \(\frac{5}{4}\)
D. \(\frac{29}{15}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
\(^X\mu _Y =\frac{\mu_Y}{\mu_X}=\frac{4}{3}\)
\(^Y\mu _Z =\frac{\mu_Z}{\mu_Y}=\frac{3}{5}\)
\(^X\mu _Z =\frac{\mu_Z}{\mu_X}=\frac{\mu_Y}{\mu_X} \times \frac{\mu_Z}{\mu_Y} =\frac{4}{3} \times \frac{3}{5} =\frac{4}{5}\)
Question
When a sound wave travels from a region of hot air to a region of cold air, it refracts as shown.
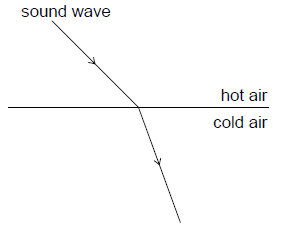
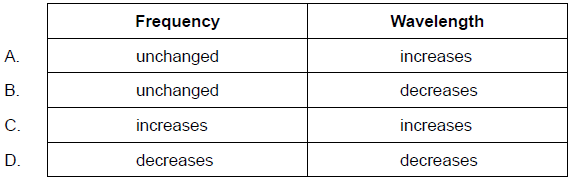
What changes occur in the frequency and wavelength of the sound as it passes from the hot air to the cold air?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
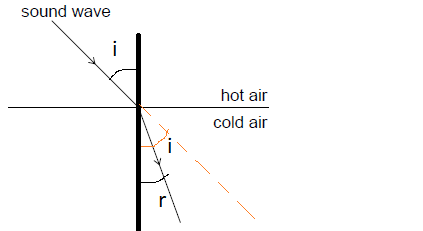
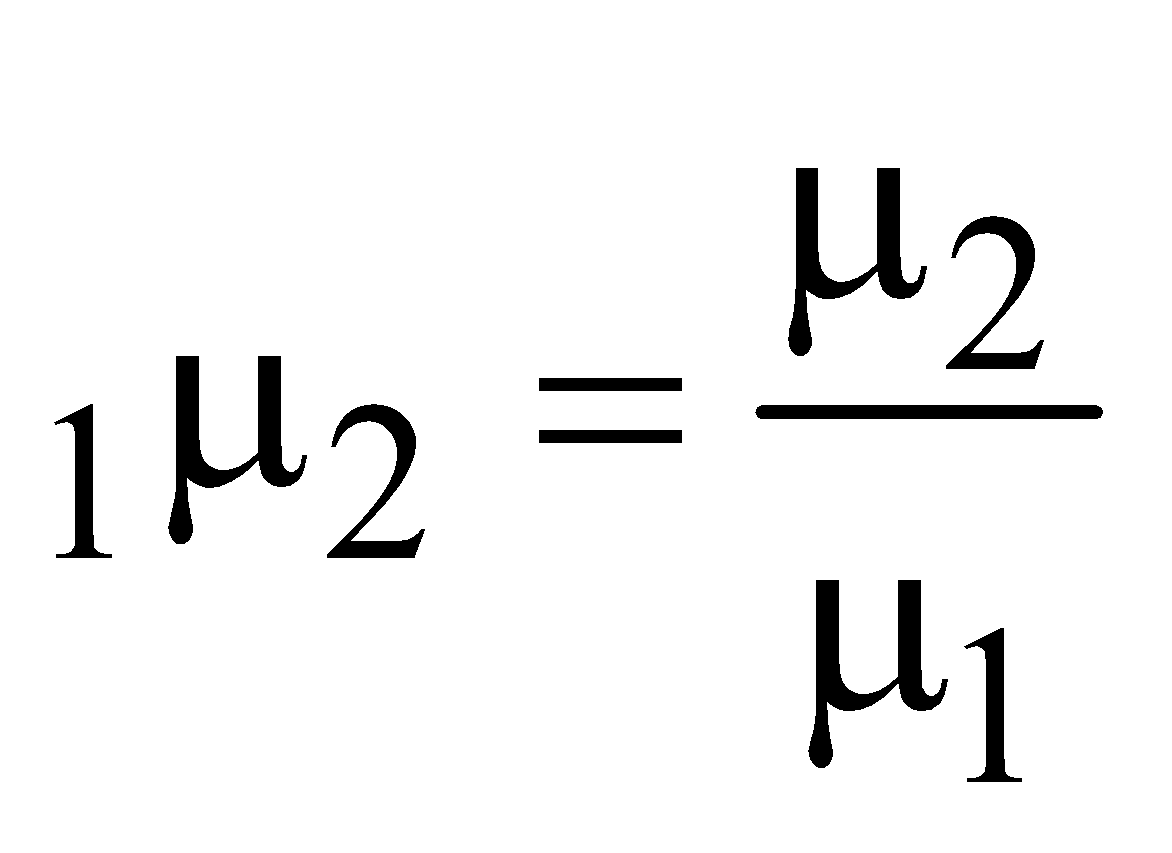
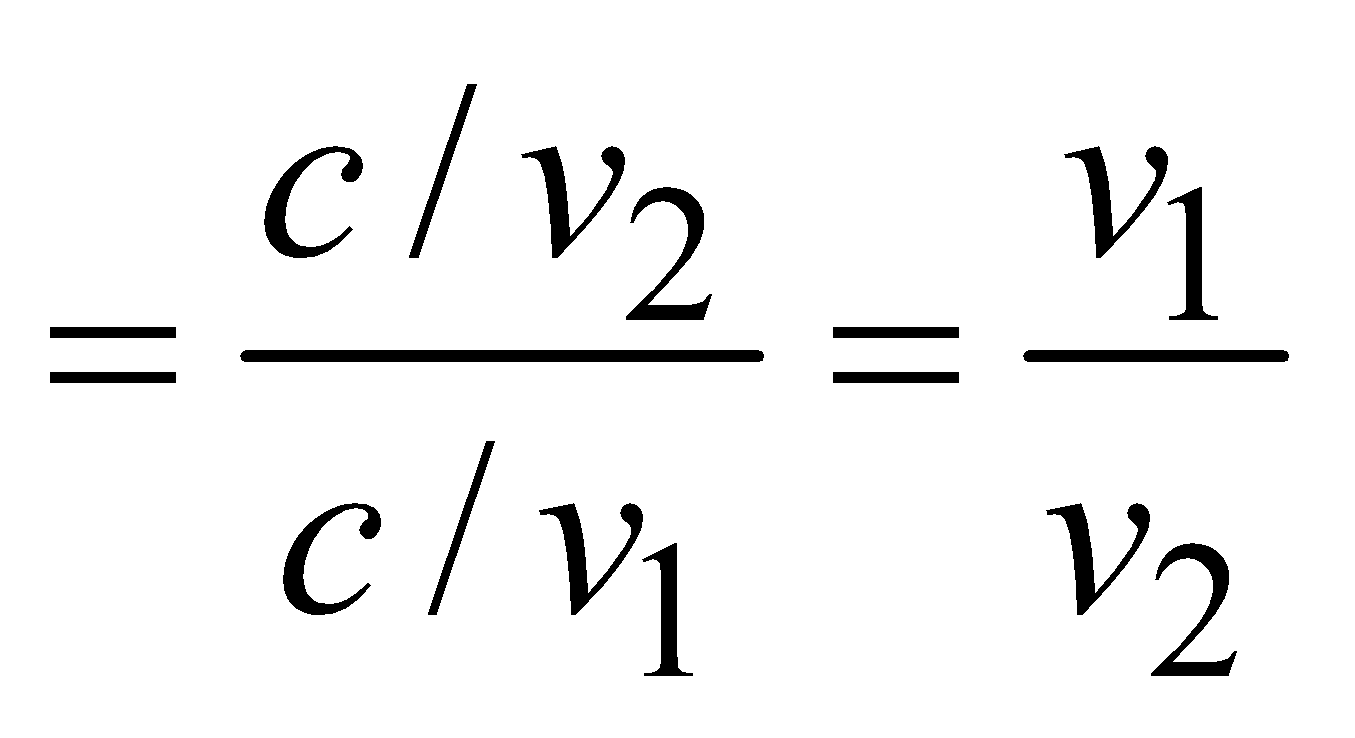
now \( i> r\) hence \(\mu_{cold}>\mu_{hot}\)
hence
\(v_{cold} <v_{hot}\) or \(\lambda_{cold}<\lambda_{hot}\) as \(v=f\lambda\)
Velocity decreases
Frequency does not depend on medium
