IB PHYSICS SL (Standard level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 5.1 – Electric Fields
Topic 5 Weightage : 8 %
All Questions for Topic 5.1 – Charge , Electric field , Coulomb’s law , Electric current , Direct current (dc) , Potential difference
Question
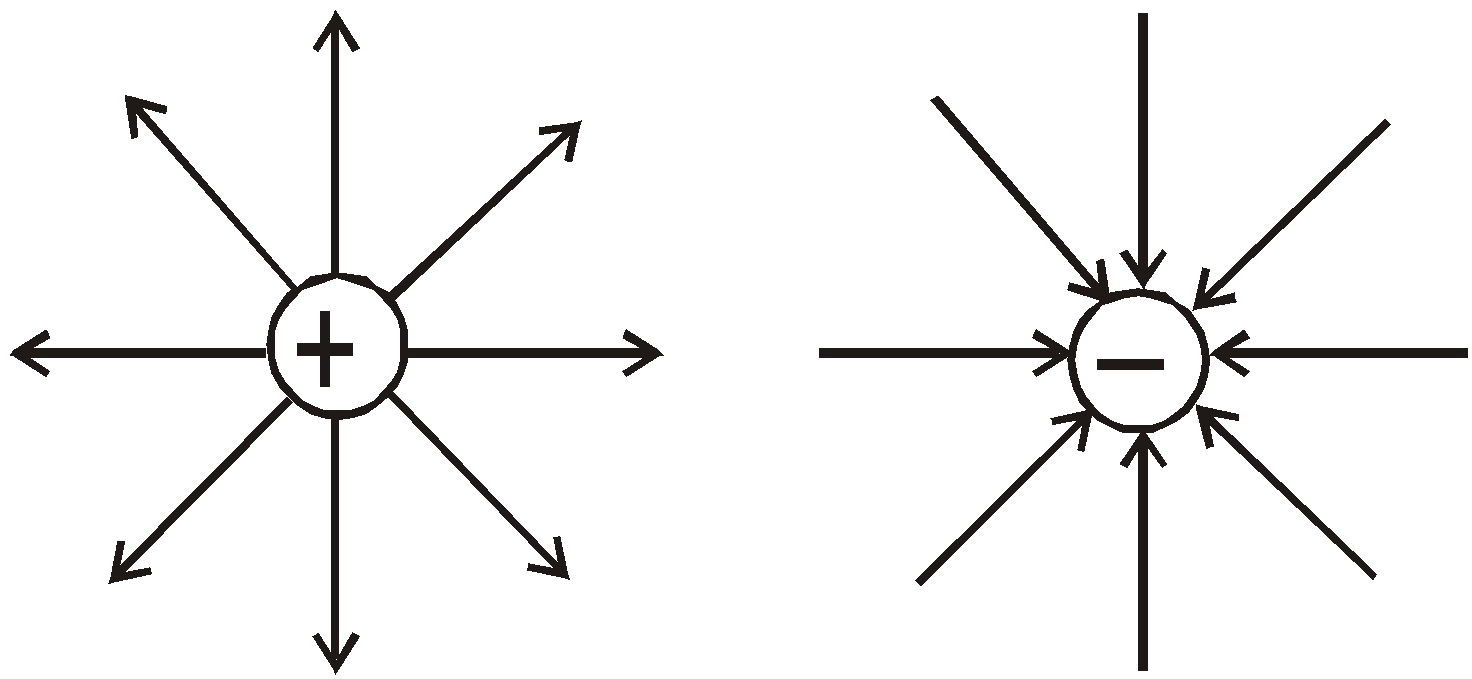
Two charges 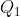 and
and 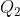 , each equal to 2 nC, are separated by a distance 3 m in a vacuum.
, each equal to 2 nC, are separated by a distance 3 m in a vacuum.
What is the electric force on 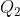 and the electric field due to
and the electric field due to 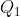 at the position of
at the position of 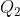 ?
?
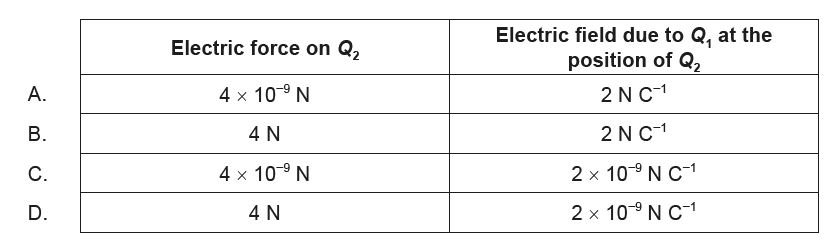
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
\(F_{Q_2}=k\frac{Q_1Q_2}{r^2}\)
\(=\frac{9\times 10^9 \times 2\times 10^{-9}\times 2\times 10^{-9}}{3^2}=4\times 10^{-9}\)
\(E_{Q_{21}}=\frac{F}{Q_1}=\frac{4\times 10^{-9}}{2\times 10^{-9}}=2\; NC^{-1}\)
Question
A metal wire has n free charge carriers per unit volume. The charge on the carrier is q. What additional quantity is needed to determine the current per unit area in the wire?
A Cross-sectional area of the wire
B Drift speed of charge carriers
C Potential difference across the wire
D Resistivity of the metal
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
A = area of cross-section, vd = drift velocity
Question
An electron is accelerated through a potential difference of 2.5 MV. What is the change in kinetic energy of the electron?
A. 0.4μJ
B. 0.4 nJ
C. 0.4 pJ
D. 0.4 fJ
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
work done = change in kinetic energy
\(=qV = e V= 1.6\times 10^{-19}\times 2.5 \times 10^6 = 4 \times 10^{-13} =0.4 \times 10^{-12} =0.4 \; pJ\)
Which of the following diagrams illustrates the electric field pattern of a negatively charged sphere?
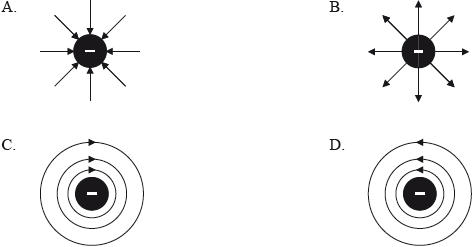
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A