IB PHYSICS SL (Standard level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 5.4 – Magnetic effect of electric currents
Topic 5 Weightage : 8 %
All Questions for Topic 5.4 – Magnetic fields , Magnetic force
Question
A long straight vertical conductor carries a current I upwards. An electron moves with horizontal speed v to the right.
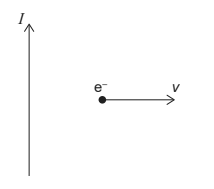
What is the direction of the magnetic force on the electron?
A Downwards
B Upwards
C Into the page
D Out of the page
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
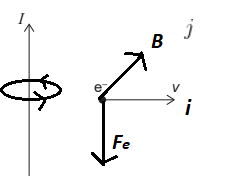
\(\vec F_m=q(\vec v \times \vec B)\)
Now \(q = -e\)
\(\vec v = v \; i , \vec B = B \; j\)
\(\vec F_m=-evB(\vec i \times \vec j) =evB (-\vec k)\)
Question
An electron enters the region between two charged parallel plates initially moving parallel to the plates.
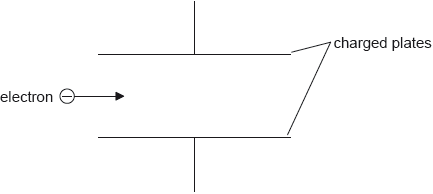
The electromagnetic force acting on the electron
A. causes the electron to decrease its horizontal speed.
B. causes the electron to increase its horizontal speed.
C. is parallel to the field lines and in the opposite direction to them.
D. is perpendicular to the field direction.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
\(\vec F_q=q\vec E\)
\(q= -e\)
\(\vec F_e =-e \vec E\)
opposite to Electric field
Question
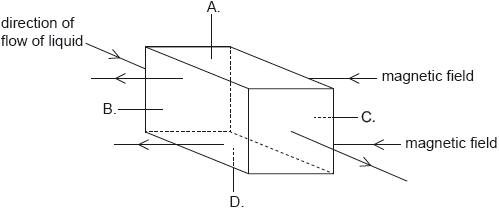
A liquid that contains negative charge carriers is flowing through a square pipe with sides A, B, C and D. A magnetic field acts in the direction shown across the pipe.
On which side of the pipe does negative charge accumulate?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
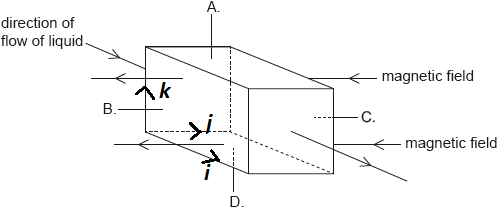
\(\vec B=-B\;j\)
charge \(= -q\)
\(\vec v = v\; i\)
\(\vec F_m = q(\vec V \times \vec B)\)
\(=-q (v\; i \times -B\;j) =qvB(i \times j) =qvB \; k\)
A is in \(k\) direction
Question
The diagram shows two current-carrying wires, P and Q, that both lie in the plane of the paper. The arrows show the conventional current direction in the wires.

The electromagnetic force on Q is in the same plane as that of the wires. What is the direction of the electromagnetic force acting on Q?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
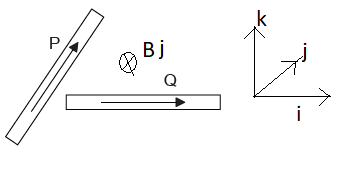
Due to current-carrying wires, P magnetic field developed at Q is in direction of inside the plan i.e. \(j\)
Current in current-carrying wires, Q is in \(i\) direction
Now force on current-carrying wires, Q due to P is given as
\(\vec F_m = I (\vec l \times \vec B) = IlB (i \times j) =IlB \; k\)
