This question is about thin-film interference.
A thin film of oil lies on a puddle of water. White light from above shines on the film at normal incidence.
a.Outline the process by which coloured fringes are formed.[3]
Refractive index of oil = 1.4
Refractive index of water = 1.3
Thickness of the oil film = 250 nm
Calculate the maximum wavelength of the incident light for which destructive interference occurs.[2]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a.
light reflects from the top surface of the oil and the top surface of the water;
mention of interference/superposition;
path difference exists between both reflected rays;
different wavelengths interfere constructively for different positions/angles (hence colours appear/shift);
\(\lambda \left( { = t\frac{{2n}}{m}} \right) = 250 \times {10^{ – 9}}\frac{{2 \times 1.4}}{1}\);
\(\lambda = 700\left( {{\rm{nm}}} \right)\);
This question is about thin-film interference.
Monochromatic light with wavelength 572 nm is incident from air on a thin soap film.
The soap solution has a refractive index of 1.3.
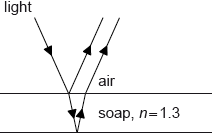
a.Calculate the wavelength of the light within the soap solution.[1]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a.\(\lambda ‘ = \frac{\lambda }{{1.33}} = \frac{{572}}{{1.3}} = 440{\text{ nm}}\);
but the phase change at the first surface means that there is always destructive interference;
