IB PHYSICS HL(Higher level) – 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 9.4 Resolution
Topic 9 Weightage : 5 %
All Questions for Topic 9.4 – The size of a diffracting aperture , The resolution of simple monochromatic two-source systems
Question
Two points illuminated by monochromatic light are separated by a small distance. The light from the two sources passes through a small circular aperture and is detected on a screen far away.
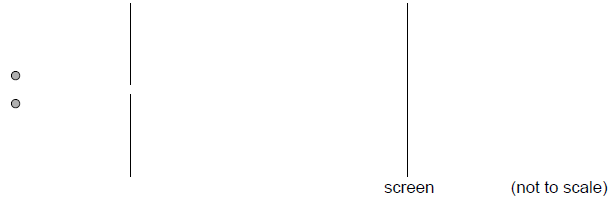
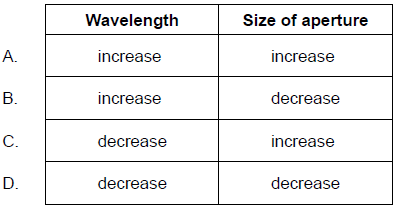
The image of the the two light sources are just resolved . What changes to the wavelength and size of aperture will definitely allow the two images to be well resolved.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
Question
A diffraction grating is used to observe light of wavelength 400 nm. The light illuminates 100 slits of the grating. What is the minimum wavelength difference that can be resolved when the second order of diffraction is viewed?
A. 1 nm
B. 2 nm
C. 4 nm
D. 8 nm
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
For resolution in diffraction grating , we have equation as
\(Nm =\frac{\lambda_{avg}}{\Delta \lambda}\)
Given in question
\(\lambda = 400 \;nm\)
2nd order means \(m = 2\)
\(N= 100\)
Hence from formula , we have
\(Nm =\frac{\lambda_{avg}}{\Delta \lambda}\)
or
\(\Delta \lambda =\frac{\lambda_{avg}}{2N} =\frac{400}{2\times 100}=2\)
Question
Which of the following experiments provides evidence for the existence of matter waves?
A. Scattering of alpha particles
B. Electron diffraction
C. Gamma decay
D. Photoelectric effect
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
Matter (or “de Broglie”) Waves
As suggested by de Broglie, to any particle of momentum p, there corresponds a wave of wavelength given by the formula λ = h/p, something known as the duality of matter.
- **Electron diffraction: **Electrons shot through or to a thin slice of crystal have a low probability of reaching a place where the path difference is not an integer number of wavelengths (constructive and destructive interference).
- Electrons accelerated through a pd, they gain kinetic energy. Hence, we have eV = 1/2 mv = p²/2m.
- \(\lambda =hl\sqrt{2meV}\)
Question
The graph below shows the variation of the intensity of light with angle for the diffraction pattern produced when light is diffracted by a slit.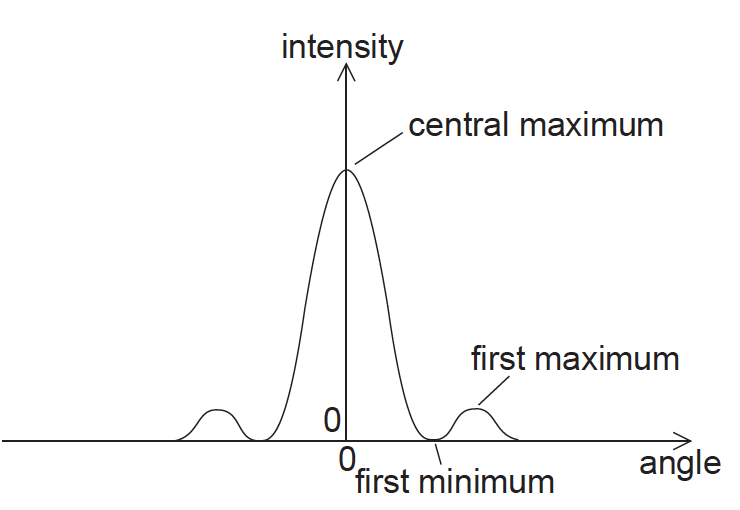
According to the Rayleigh criterion, when the diffraction patterns of two slits are just resolved
A. the first maximum of one diffraction pattern coincides with the central maximum of the other diffraction pattern.
B. the central maximum of one diffraction pattern coincides with the central maximum of the other diffraction pattern.
C. the first minimum of one diffraction pattern coincides with the central maximum of the other diffraction pattern.
D. the first minimum of one diffraction pattern coincides with the first minimum of the other diffraction pattern.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
Green light is emitted by two point sources. The light passes through a narrow slit and is received by an observer. The images of the two sources just fail to be resolved. Which change allows for the images to be resolved?
A. Replacing the narrow slit with a circular aperture of same size.
B. Moving the two sources further from the aperture.
C. Using red light.
D. Using violet light.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
