IBDP Physics-B.3 Gas laws- IB Style Questions For SL Paper 2 -FA 2025
Question
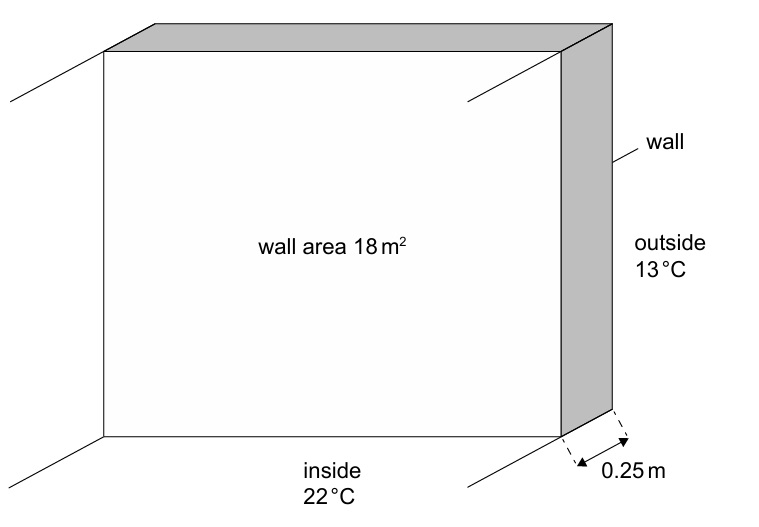
• Thickness of wall = 0.25 m
• Area of wall = 18 m²
• Thermal conductivity of wall = 1.3 W m⁻¹ K⁻¹
• Constant room temperature = 22 °C
• Constant outside temperature = 13 °C
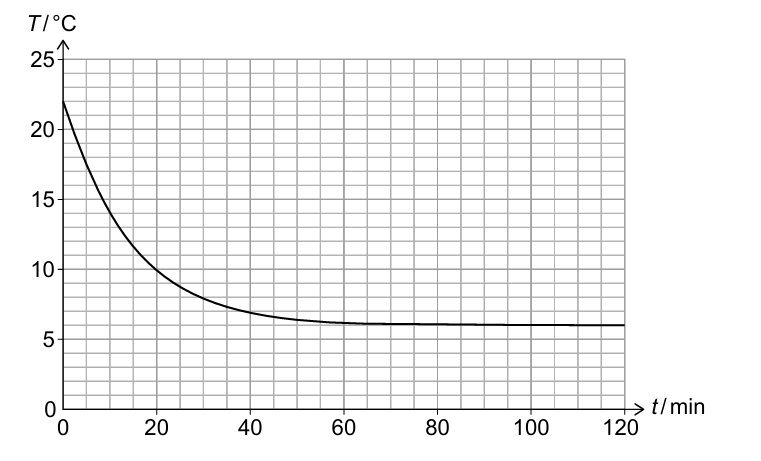
(ii) The pressure and volume of the air in the room remain constant, but the number of air molecules increases. Calculate the percentage increase in the number of air molecules in the room between t = 0 and t = 120 min.
Most-appropriate topic codes (IB Physics 2025):
• B.3: Gas laws — part (c)(ii)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)
ALT 1 (in solids):
Reference to particle/atomic vibrations OR kinetic energy transferred ✓
via collisions OR between adjacent particles/atoms ✓
ALT 2 (in metallic conductors):
Reference to motion of electrons ✓
that collide with atoms/ions ✓
(b)
Using the thermal conduction formula:
\( \frac{\Delta Q}{\Delta t} = kA\frac{\Delta T}{\Delta x} = \frac{1.3 \times 18 \times (22-13)}{0.25} \)
\( = \frac{1.3 \times 18 \times 9}{0.25} = \frac{210.6}{0.25} = 842.4 \ \text{W} \)
\( \approx 8.4 \times 10^2 \ \text{W} \quad \checkmark \)
Unit is W / J s⁻¹ / kg m² s⁻³ ✓
(c)(i)
The magnitude of the gradient (dT/dt) represents the rate of cooling.
As the temperature difference between the room and outside decreases, the rate of thermal energy transfer decreases, so the cooling rate slows down. ✓
(c)(ii)
ALT 1:
From ideal gas law PV = NkT, with P and V constant: N ∝ 1/T
\( \frac{N_2}{N_1} = \frac{T_1}{T_2} \)
From graph: T₁ = 22°C = 295 K at t = 0, T₂ = 13°C = 286 K at t = 120 min ✓
\( \frac{N_2}{N_1} = \frac{295}{286} \approx 1.0315 \)
\( \text{Percentage increase} = \left(\frac{295}{286} – 1\right) \times 100\% \approx 3.15\% \quad \checkmark \)
ALT 2:
Using nT = constant (since PV = nRT, P and V constant)
\( \frac{n_2}{n_1} = \frac{T_1}{T_2} = \frac{295}{286} \quad \checkmark \)
Percentage increase = \(\left(\frac{295}{286} – 1\right) \times 100\% \approx 3.15\%\) ✓