IBDP Physics- D.2 Electric and magnetic fields- IB Style Questions For HL Paper 1A -FA 2025
Question
(B) TCN⁻¹m⁻¹s
(C) m²s⁻²
(D) TC²A⁻¹N⁻¹m⁻¹
▶️ Answer/Explanation
From electromagnetism: c² = 1/(μ₀ε₀) where c is speed of light
So μ₀ε₀ = 1/c²
Speed has SI units m/s, so 1/c² has units s²/m² = m⁻²s²
✅ Answer: (A) m⁻²s²
Question


| Option | Magnitude of electric field | Direction of electric field |
|---|---|---|
| A | \( \dfrac{2V}{d} \) | up |
| B | \( \dfrac{V}{d} \) | up |
| C | \( \dfrac{2V}{d} \) | down |
| D | \( \dfrac{V}{d} \) | down |
▶️ Answer / Explanation
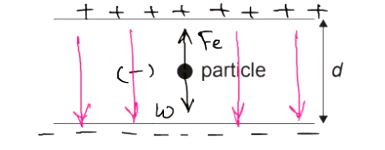
Between parallel charged plates, the electric field is uniform and given by:
\( E = \dfrac{V}{d} \)
The particle is stationary, so the electric force balances the weight. Since the weight acts downward, the electric force on the particle must act upward.
The particle is negatively charged, so the electric force acts opposite to the direction of the electric field.
Therefore, the electric field must be directed downward.
Hence, the magnitude of the electric field is \( \dfrac{V}{d} \) and its direction is downward.
✅ Answer: D
Question

(B) \( x \)
(C) \( x\sqrt{2} \)
(D) \( 2x \)
▶️ Answer / Explanation
The magnetic field produced by a long straight current-carrying wire is given by:
\( B = \dfrac{\mu_0 I}{2\pi r} \)
Since wires P and R carry the same current and are equidistant from point Q, the magnitudes of the magnetic fields at Q due to each wire are equal.
Hence, the magnetic field at Q due to wire P has magnitude \( X \), and the magnetic field at Q due to wire R also has magnitude \( X \).
From the geometry of the arrangement, the directions of these two magnetic fields at Q are perpendicular to each other.
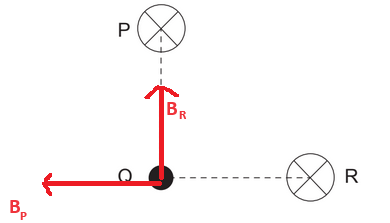
Therefore, the resultant magnetic field at Q is given by vector addition:
\( B_{\text{resultant}} = \sqrt{X^2 + X^2} = X\sqrt{2} \)
✅ Answer: (C)
