IB PHYSICS HL(Higher level) – 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 4.2 Travelling waves
Topic 4 Weightage : 5 %
All Questions for Topic 4.2 –Travelling waves , Wavelength, frequency, period and wave speed , Transverse and longitudinal waves , The nature of electromagnetic waves , The nature of sound waves
Question
A travelling wave has a frequency of 500 Hz. The closest distance between two points on the wave that have a phase difference of 60° is 0.050 m. What is the speed of the wave?
A 25 m s–1
B 75 m s–1
C 150 m s–1
D 300 m s–1
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Formula to be used
\(\phi =\frac{2\pi}{\lambda}d\)
\(\frac{\pi}{3}=\frac{2\pi}{\lambda}\times 0.05\)
\(\lambda = 0.3\)
\(v= \vartheta \times \lambda =500 \times 0.3=150\; m/s\)
Question
A sound wave has a frequency of 1.0 kHz and a wavelength of 0.33 m. What is the distance travelled by the wave in 2.0 ms and the nature of the wave?
Distance travelled in 2.0 ms | Nature of the wave |
0.17 m | longitudinal |
0.17 m | transverse |
0.66 m | longitudinal |
0.66 m | transverse |
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
The speed of the sound, distance travelled and the time taken relationship is given as follows.
distance travelled = \(Speed \times time\)
Now for sound wave ,
\(v=n\lambda \) , \(\lambda \)= 0.33 m and \(n\) = 1k Hz
\(\therefore v= 10^3 \times 0.33 = 330 ms^{-1}\)
\(Distance \; travelled = 330 \times 2 \times 10^{-3} =0.66m\)
And Sound wave is longitudinal Wave.
Question
The graph shows the variation with position s of the displacement x of a wave undergoing simple harmonic motion (SHM).
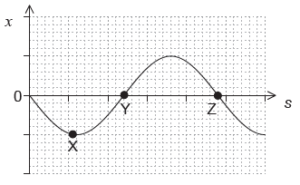
What is the magnitude of the velocity at the displacements X, Y and Z?
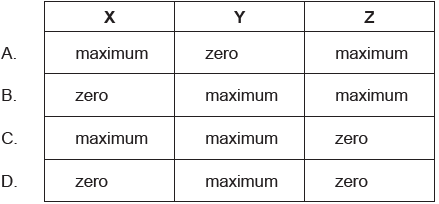
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
Graphical Representation of Simple Harmonic Motion
The graphical representation of displacement, velocity and acceleration of the particle vibrating in SHM is given below.
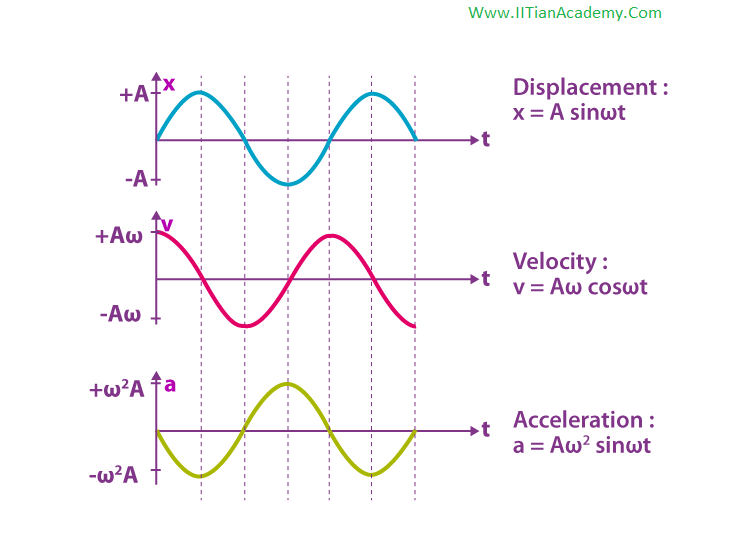
When \(x\) is zero \(v\) is maximum
Question
Which of the following is a correct comparison between standing waves and travelling waves?
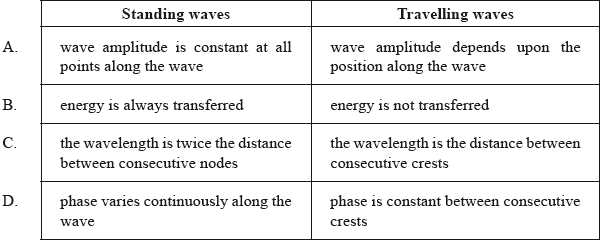
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
Ref: https://www.iitianacademy.com/ib-dp-physics-topic-4-waves-4-5-standing-waves-study-notes/
Standing and travelling waves
The main differences between a standing wave and a travelling wave are summarised below.
- In a travelling wave, the disturbance produced in a region propagates with a definite velocity but in a standing wave, it is confined to the region where it
is produced. - In a travelling wave, the motion of all the particles are similar in nature. In a standing wave, different particles move with different amplitudes.
- In a standing wave, the particles at nodes always remain in rest. In travelling waves, there is no particle which always remains in rest.
- In a standing wave, all the particles cross their mean positions together. In a travelling wave, there is no instant when all the particles are at the mean positions together.
- In a standing wave, all the particles between two successive nodes reach their extreme positions together, thus moving in phase. In a travelling wave, the phases of nearby particles are always different.
- In a travelling wave, energy is transmitted from one region of space to other but in a standing wave, the energy of one region is always confined in that region.
