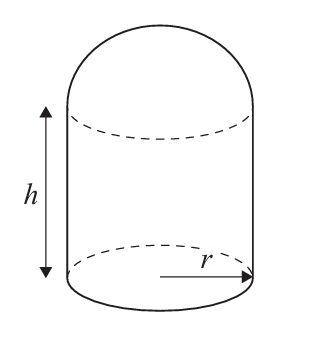
IB Mathematics SL 5.7 Optimization problems in context AI HL Paper 2- Exam Style Questions- New Syllabus
Question
Most-appropriate topic codes:
• SL 5.7: Optimization problems in context (maximizing/minimizing) — parts (d), (f), (g)
• AHL 5.9: Derivatives of power functions \( x^n, n \in \mathbb{Q} \) for optimization — part (e)
• SL 2.6: Modelling skills: creating, fitting and using theoretical models — all parts
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)
Surface area = curved surface area of hemisphere + curved surface area of cylinder (no bottom):
\( A = 2\pi r^2 + 2\pi rh \).
\( \boxed{A = 2\pi r^2 + 2\pi rh} \).
(b)
Volume = hemisphere volume + cylinder volume:
\( V = \frac{2}{3}\pi r^3 + \pi r^2 h \).
Combine over common denominator:
\( V = \frac{2\pi r^3 + 3\pi r^2 h}{3} \).
Shown.
(c)
Given \( V = 10000 \):
\( \frac{2\pi r^3 + 3\pi r^2 h}{3} = 10000 \).
Multiply by 3: \( 2\pi r^3 + 3\pi r^2 h = 30000 \).
Rearrange: \( 3\pi r^2 h = 30000 – 2\pi r^3 \).
\( h = \frac{30000 – 2\pi r^3}{3\pi r^2} \).
Shown.
(d)
Substitute \( h \) into \( A = 2\pi r^2 + 2\pi rh \):
\( A = 2\pi r^2 + 2\pi r \left( \frac{30000 – 2\pi r^3}{3\pi r^2} \right) \).
Simplify: \( A = 2\pi r^2 + \frac{2(30000 – 2\pi r^3)}{3r} \).
\( A = 2\pi r^2 + \frac{60000}{3r} – \frac{4\pi r^3}{3r} \).
\( A = 2\pi r^2 + \frac{20000}{r} – \frac{4\pi r^2}{3} \packagetest.
Combine \( r^2 \) terms: \( 2\pi r^2 – \frac{4\pi r^2}{3} = \frac{2\pi r^2}{3} \).
\( A = \frac{2\pi r^2}{3} + \frac{20000}{r} \packagetest.
Shown.
(e)
Differentiate \( A \) with respect to \( r \):
\( \frac{dA}{dr} = \frac{4\pi r}{3} – \frac{20000}{r^2} \).
\( \boxed{\frac{dA}{dr} = \frac{4\pi r}{3} – \frac{20000}{r^2}} \).
(f)
Set \( \frac{dA}{dr} = 0 \):
\( \frac{4\pi r}{3} = \frac{20000}{r^2} \).
Multiply by \( r^2 \): \( \frac{4\pi r^3}{3} = 20000 \).
\( r^3 = \frac{15000}{\pi} \).
\( r = \sqrt[3]{\frac{15000}{\pi}} \approx 16.8 \ \text{cm} \).
Substitute into \( h \):
\( h = \frac{30000 – 2\pi (16.8)^3}{3\pi (16.8)^2} \approx 0 \ \text{cm} \).
\( \boxed{r \approx 16.8 \ \text{cm}, \ h \approx 0 \ \text{cm}} \).
(g)
Since \( h \approx 0 \), the optimal shape is essentially a hemisphere.
\( \boxed{\text{Hemisphere}} \).