Question:
Identify the main dissolved salts contributing to the alkalinity of the lake.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Chloride, carbonate and sulfate salts.
Question:
How does the pH of the lake compare to the pH of typical ocean water?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Ocean water has a pH of approximately 8.1 while the lake has a pH of 10.
Question:
Describe how the salinity level of the lake has changed over the past 100 years. To what extent might the lake have changed naturally over time?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: In 1941, the salinity level in the lake was 48 g l–1. In 1982, at the time when the lake was at its lowest recorded water level, the salinity was 98 g l–1. The natural environment is dynamic, with changes occurring in the salinity levels of the lake as a result of natural phenomena.
Question:
State what types of organisms can be found in the lake.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Primary lake life including of algae, brine shrimp, and alkali flies, nesting birds including California gulls and snowy plovers, and migratory birds including eared grebes, Wilson’s phalaropes ,
red–necked phalaropes, and 79 other species of water birds.
Question:
Comment on how the diversion of water for an increasing population of Los Angeles has affected the salinity of the lake.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: As an increasing amount of water was diverted from the lake to provide for the increasing Los Angeles population, the volume of the lake decreased, increasing the salinity of the lake.
Question:
What impact has human development and intervention had on the ecosystem of the lake?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A decrease in the volume of the lake resulted in an increase in the salinity of the lake. As this change was relatively rapid, the ecosystem was unable to adapt at the same rate. Plant and animal species were unable to cope with this rapid change in their environment and the populations began to collapse.
Question:
Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction between calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid. Can you predict the gas produced from the composition of the reactants?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
The carbonate ion CO32– can be seen to contain the gas carbon dioxide CO2 within the formula.
Question:
Describe what you saw happening to the calcium hydroxide solution.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The colorless calcium hydroxide solution slowly began to turn a milky white colour as the gas carbon dioxide is bubbled through the solution.
Question:
Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction between calcium hydroxide solution and carbon dioxide gas.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Ca(OH)2(aq) + CO2(g) → CaCO3(s) + H2O(l)
Question:
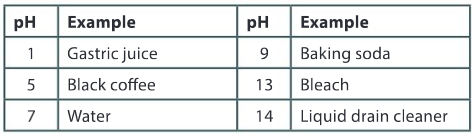
How can you determine which is the more acidic solution, black coffee or gastric juice?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The solution with the lower pH value is more acidic. Gastric juice is more acidic than black coffee.
Question:
Can you deduce how many times greater the concentration of hydrogen ions is in the more acidic of the two solutions?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: For each change in 1 pH unit there is a 10–fold change in the concentration of hydrogen ions. For a difference of 4 pH units, gastric juice has 104 or 10000 times more hydrogen ions than black coffee.
Question:
Black coffee and baking soda are both 2 pH units away from water. Black coffee is acidic and baking soda is alkaline. How do their hydrogen ion concentrations compare?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Black coffee has 100 times more hydrogen ions than water and baking soda has 100 times less hydrogen ions than water.
Question:
Gastric juice is a corrosive liquid and bleach is a caustic liquid. Explain what these terms mean and how the hydrogen ion concentrations compare.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A corrosive liquid has a low pH value and a caustic liquid has a high pH. There is an inverse relationship between the pH value and the concentration of hydrogen ions. As the concentration of hydrogen ions decreases, the pH value increases. A caustic liquid has a much smaller hydrogen ion concentration than a corrosive liquid.
Question:
Hydrochloric acid + lithium hydroxide ➝
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: hydrochloric acid + lithium hydroxide
↓
lithium chloride + water
Question:
Nitric acid + potassium hydroxide ➝
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: nitric acid + potassium hydroxide
↓
potassium nitrate + water
Question:
Sulfuric acid + calcium hydroxide ➝
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: sulfuric acid + calcium hydroxide
↓
calcium sulfate + water
Question:
____________ + sodium hydroxide ➝ sodium sulfate + ___________
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: sulfuric acid + sodium hydroxide
↓
sodium sulfate + water
Question:
Energy is conserved in all chemical reactions. Name one form of energy that you experience in this reaction.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Sound energy
Question:
Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(l) + energy
Summative assessment
Measuring acid rain
Question:
Normal rain has a pH of about 5.6; it is slightly acidic because carbon dioxide (CO2) dissolves into it forming carbonic acid, a weak acid. Acid rain usually has a pH between 4.2 and 4.4. Acid deposition occurs when sulfur dioxide, SO2, and nitrogen oxides, NOx, are emitted into the atmosphere and react with water, oxygen and other chemicals present in the atmosphere.
a) Write balanced chemical equations for the reactions of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen(IV) oxide with water.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: SO2(g) + H2O(l) → H2SO3(aq)
2NO2(g) + H2O(l) → HNO3(aq) + HNO2(aq)
b) Name the acids produced.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Sulfurous acid; nitric acid and nitrous acid.
Question:
Outline the major differences between wet and dry acid deposition.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Wet deposition is commonly referred to as acid rain. Sulfuric acid and nitric acid, when formed in the atmosphere, fall back to Earth mixed with rain, snow or hail. Acidic matter and gases can also be deposited throughout the environment in the absence of moisture. This is known as dry deposition. These substances will remain in this form until rainfall, at which time acidic solutions will form.
Question:
Describe the differences between strong and weak acids
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A strong acid will completely dissociate into its ions in an aqueous solution; while a weak acid will only partially dissociate.
Question:
Deduce the chemical reaction for the formation of carbonic acid. Classify this as either a strong or weak acid
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: CO2(g) + H2O(l) → H2CO3(aq); weak acid [In the equation, 1 mark for the correct reactants and 1 mark for the correct product]
Question:
Acid rain has a pH of 4.2 to 4.4. This is approximately 1 pH unit lower than normal rain water. Given your knowledge of the pH scale, explain how the concentration of hydrogen ions differs between these two solutions.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The pH of a solution is expressed using a log scale to base–10; change in pH of 1 unit is the equivalent to a ten–time change in the hydrogen ion concentration [H+].
Investigating acid rain
Sulfur dioxide, SO2, is emitted into the atmosphere both naturally (volcanoes) and as a consequence of human activities (combustion of fossil fuels). The mixing of this toxic gas with water is the cause of acid deposition.
Question:
Design a way of simulating acid rain formation by sulfur pollutants and investigate the effects of this pollutant on the pH of water. You could use the following points for guidance.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Design should include clear statement of:
- independent and dependent variables,
- rationale for the method and practical details, including
- correct names of apparatus and volume
- amounts and/or concentration of chemicals being used
- consideration of safety, ethical and environmental issues
- description of the step–by–step methodology for the investigation, including the making of sulfur dioxide gas, the formation of the acidic solution and how the variables are controlled
- description of how qualitative observations will be recorded
- identification of any quantitative data that will be recorded and the design of data tables to present this information
Marks awarded on a scale from zero marks for a completely inadequate design to ten marks for an exemplary design.
Question:
Propose a research question for your investigation
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Focused research question; that includes the dependent and independent variables.
Question:
Formulate a testable hypothesis and explain it using scientific reasoning.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Suitable hypothesis is suggested; hypothesis is testable; hypothesis is based on scientific reasoning (2 marks).
Question:
Having formulated an experiment to replicate the formation of acid rain in the first part of the question, design an experiment to demonstrate how increased soil acidity resulting from acid rain can be diminished or reversed. Your design should include:
● how you will neutralize the effect of the acid rain
● how you will demonstrate that the pH has been changed
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The same marking criteria as used in the answer to Question 6 above can be used to grade the investigation designed by the student.
Question:
a) What is the best way to present qualitative observations and quantitative of the type that you would have collected had you performed the investigation you designed in question 6?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Qualitative observations should be presented in two parts, namely, observations made prior to the reaction occurring and observations made after the reaction has occurred. Sometimes it is appropriate to include qualitative observations as the reaction progresses. Depending on the number of observations, these can be recorded in short paragraphs, or as tabulated information. Quantitative data collected during the acid rain investigation will include the pH of solution before and after sulfur dioxide gas has been dissolved into the solution.
b) Work within a small group to evaluate the two experimental methods devised by you and your peers. Identify modifications that could improve the two experiments.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Modifications suggested could include:
- A more focused research question;
- A more complete list of variables;
- Greater detail in the procedure including correct terminology;
- Improve safety considerations;
- Greater attention to the precision with which data is collected.
c) Describe relevant improvements and propose any further experiments that could be performed to investigate the effects of acid rain.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Improvements could include more precise manipulative skills; number of trials performed; identifying possible sources of errors and consequent modification of the methodology to overcome these issues; additional experiments suggested should be realistic; and result in an improved learning outcome (rather than a simple variation on the initial experiments).