IB MYP 4-5 Biology-Factors Affecting Human Health- Study Notes - New Syllabus
IB MYP 4-5 Biology-Factors Affecting Human Health- Study Notes – New syllabus
IB MYP 4-5 Biology-Factors Affecting Human Health- Study Notes – IB MYP 4-5 Biology – per latest IB MYP Biology Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- Lifestyle: Diet (malnutrition, obesity), exercise, smoking, alcohol.
- Environmental: Air/water pollution, carcinogens.
- Genetic: Cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia.
- Pathogens: Bacteria (TB), viruses (HIV), parasites (malaria).
Factors Affecting Human Health
✅ What Is Health? (WHO Definition)
According to the World Health Organization, health is:
“A complete state of physical, mental, and social well-being, not merely the absence of disease.”
📌 This means:
- Being healthy is not just about not being sick
- It includes how you feel, how you think, and how you interact with others
🔄 Interaction Between Physical, Mental, and Social Health
These three areas are interconnected:
- If your body is unwell, it may affect your mood or relationships
- Stress or anxiety (mental) can lead to physical illness
- Poor social support can lower motivation for healthy habits
➡️ A change in one can cause imbalance, leading to disease
🧠 What Influences Human Health?
Health is influenced by a mix of genetic factors, environmental conditions, and lifestyle choices.
🍎 1. Diet
Food choices = fuel + health outcomes
✅ A balanced diet includes:
- Carbohydrates – energy
- Proteins – growth + repair
- Fats – energy storage
- Vitamins & Minerals – immune and organ function
- Water – essential for all reactions
❌ Poor Diets Can Cause:
| Condition | Cause | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Malnutrition | Lack of essential nutrients | Weak immunity, poor growth, fatigue, organ problems |
| Obesity | Excess calorie intake (esp. fat/sugar) | Heart disease, type 2 diabetes, joint pain |
| Deficiency diseases | Lack of specific vitamins/minerals | Iron deficiency → anemia, Vitamin D deficiency → rickets |
🏃♂️ 2. Exercise
Movement = medicine
✅ Benefits of Regular Exercise:
- Strengthens heart and lungs
- Builds muscle & bone
- Maintains healthy weight
- Reduces stress, anxiety, and depression
- Improves insulin sensitivity
⚠️ Lack of exercise can lead to:
- Obesity
- Weak cardiovascular system
- Poor mental health
- Reduced immunity
🚬 3. Smoking
A major preventable health risk
🚭 Smoking introduces harmful substances:
- Nicotine – addictive stimulant
- Tar – damages lungs
- Carbon monoxide – reduces oxygen-carrying capacity
❗ Health Effects:
- Lung diseases (bronchitis, emphysema, lung cancer)
- Heart disease and high blood pressure
- Reduced fertility in both sexes
- Weakened immune system
🍷 4. Alcohol Consumption
Depends on dose: occasional vs. chronic
🔥 Short-Term Effects:
- Slowed brain function
- Poor judgment
- Dehydration
- Hangovers
🧠 Long-Term Effects:
| Organ | Effect |
|---|---|
| Liver | Cirrhosis, fatty liver, liver failure |
| Brain | Memory loss, poor coordination |
| Heart | Increased blood pressure, heart disease |
| Reproductive system | Lower fertility, birth defects (if pregnant) |
📊 Summary Table:
| Factor | Positive Impact | Negative Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Diet | Energy, growth, immunity | Obesity, malnutrition |
| Exercise | Fitness, mood, heart health | Lack = weak organs, obesity |
| Smoking | — | Lung disease, cancer, heart disease |
| Alcohol | Social use (if minimal) | Organ damage, addiction, mental health issues |
Environmental Factors Affecting Human Health
🌬️ 1. Air Pollution and Health
Air pollution happens when harmful substances mix into the air – often from human activities like burning fossil fuels, factories, and vehicles.
⚠️ Key Pollutants:
- Particulate matter (PM2.5, PM10) – tiny particles that lodge in lungs
- Carbon monoxide (CO) – binds to hemoglobin, reduces oxygen transport
- Sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and nitrogen oxides (NOₓ) – cause lung irritation
- Ozone (O₃) – a pollutant at ground level, irritates eyes and lungs
- Lead and heavy metals – neurotoxic (damaging to brain/nerves)
🚨 Health Effects:
- Breathing issues: asthma, bronchitis, emphysema
- Increased risk of lung cancer
- Reduced oxygen in the blood → fatigue, confusion
- Harmful for children, elderly, and people with heart/lung conditions
💧 2. Water Pollution and Health
Water pollution occurs when harmful chemicals, waste, or microorganisms contaminate natural water bodies (rivers, lakes, groundwater, etc.)
🧪 Common Pollutants:
- Industrial waste (e.g., mercury, arsenic, lead)
- Pesticides & fertilizers (from farms)
- Sewage & pathogens (E. coli, cholera bacteria)
- Plastic waste and microplastics
🤒 Diseases Spread by Polluted Water:
| Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Bacterial | Cholera, typhoid, dysentery |
| Viral | Hepatitis A, polio |
| Parasitic | Schistosomiasis, giardiasis |
☠️ 3. Carcinogens: Environmental Cancer-Causing Agents
📌 Carcinogens = substances that can cause cancer by damaging DNA or disrupting cell division
🧪 Types of Carcinogens:
| Type | Examples | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical | Benzene, formaldehyde, asbestos | Factories, building materials, cigarette smoke |
| Physical | UV radiation, X-rays | Sunlight, medical imaging |
| Biological | HPV (virus), Helicobacter pylori (bacteria) | Infections that can trigger cancer |
⚠️ How They Harm:
- Mutate DNA → uncontrolled cell division
- Interfere with tumor suppressor genes
- Cause formation of tumors
✏️ Summary Table:
| Factor | Main Source | Health Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Air pollution | Vehicles, industry | Lung disease, heart problems |
| Water pollution | Sewage, chemicals | Diarrhea, hepatitis, heavy metal poisoning |
| Carcinogens | Toxins, radiation, infections | DNA mutations → cancer |
Genetic Factors Affecting Human Health
🧠 What Are Genetic Disorders?
📌 A genetic disorder is a health condition caused by changes (mutations) in a person’s DNA. These mutations can be:
- Inherited from parents
- Or occur spontaneously during DNA replication
➡️ These disorders are usually present from birth and can affect proteins, enzymes, or entire body systems.
🫁 1. Cystic Fibrosis (CF)
Affects lungs, pancreas, and digestive system
🔬 Cause:
- Mutation in the CFTR gene (on chromosome 7)
- Leads to a faulty chloride ion channel protein
- Inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern → both parents must carry the faulty gene
🧪 Biological Effect:
- Faulty CFTR protein = chloride ions can’t move properly
- Thick, sticky mucus builds up in lungs and digestive tract
🩺 Symptoms:
- Chronic lung infections
- Difficulty breathing
- Poor digestion and nutrient absorption
- Frequent coughing, wheezing
- Delayed growth in children
💡 Did You Know? CF used to be fatal in childhood, but with modern treatment, many patients now live into adulthood.
🩸 2. Sickle Cell Anemia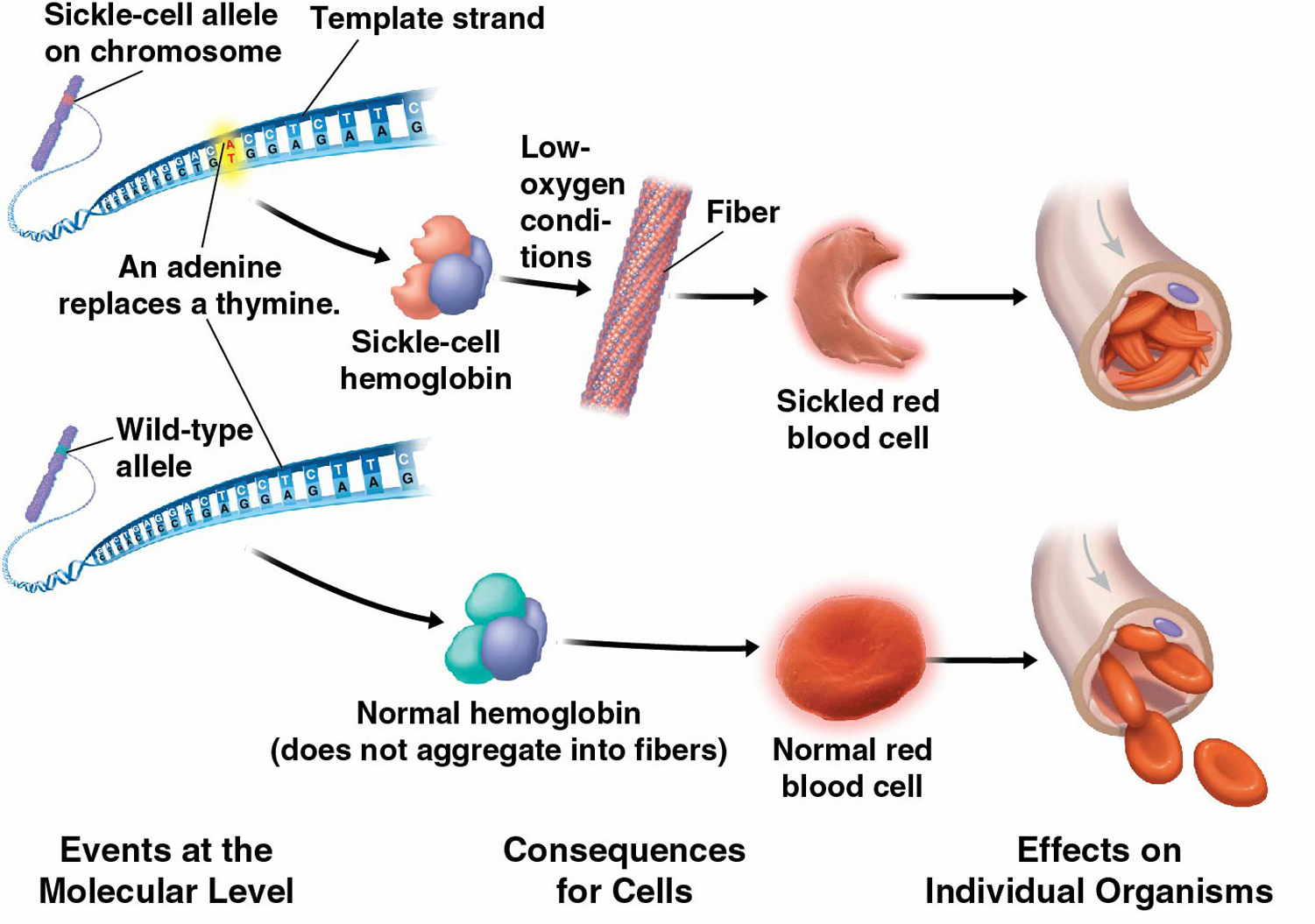
Affects red blood cells & oxygen transport
🔬 Cause:
- Mutation in the HBB gene on chromosome 11
- Alters the structure of hemoglobin (called HbS)
- Inherited in an autosomal recessive manner
🧪 Biological Effect:
- Abnormal hemoglobin causes RBCs to become sickle-shaped (crescent-shaped)
- These cells clog capillaries, break down faster, and carry less oxygen
🩺 Symptoms:
- Chronic fatigue
- Joint pain and swelling (due to blocked blood flow)
- Frequent infections
- Delayed growth in children
- Risk of stroke or organ damage
🧬 Summary Table: Genetic Disorders
| Disorder | Gene Affected | Pattern of Inheritance | Main Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cystic Fibrosis | CFTR (Chr. 7) | Autosomal recessive | Thick mucus, lung infections, digestion problems |
| Sickle Cell Anemia | HBB (Chr. 11) | Autosomal recessive | Fatigue, pain, sickle-shaped RBCs, anemia |
Pathogens and Disease
🦠 What Are Pathogens?
📌 Pathogens are microorganisms that cause disease in humans. These include:
- Bacteria
- Viruses
- Parasites
(Also, fungi and prions, but we’re focusing on the big three here)
They enter the body, multiply, and disrupt normal function often damaging cells or producing toxins.
🧬 1. Bacterial Pathogen: Tuberculosis (TB)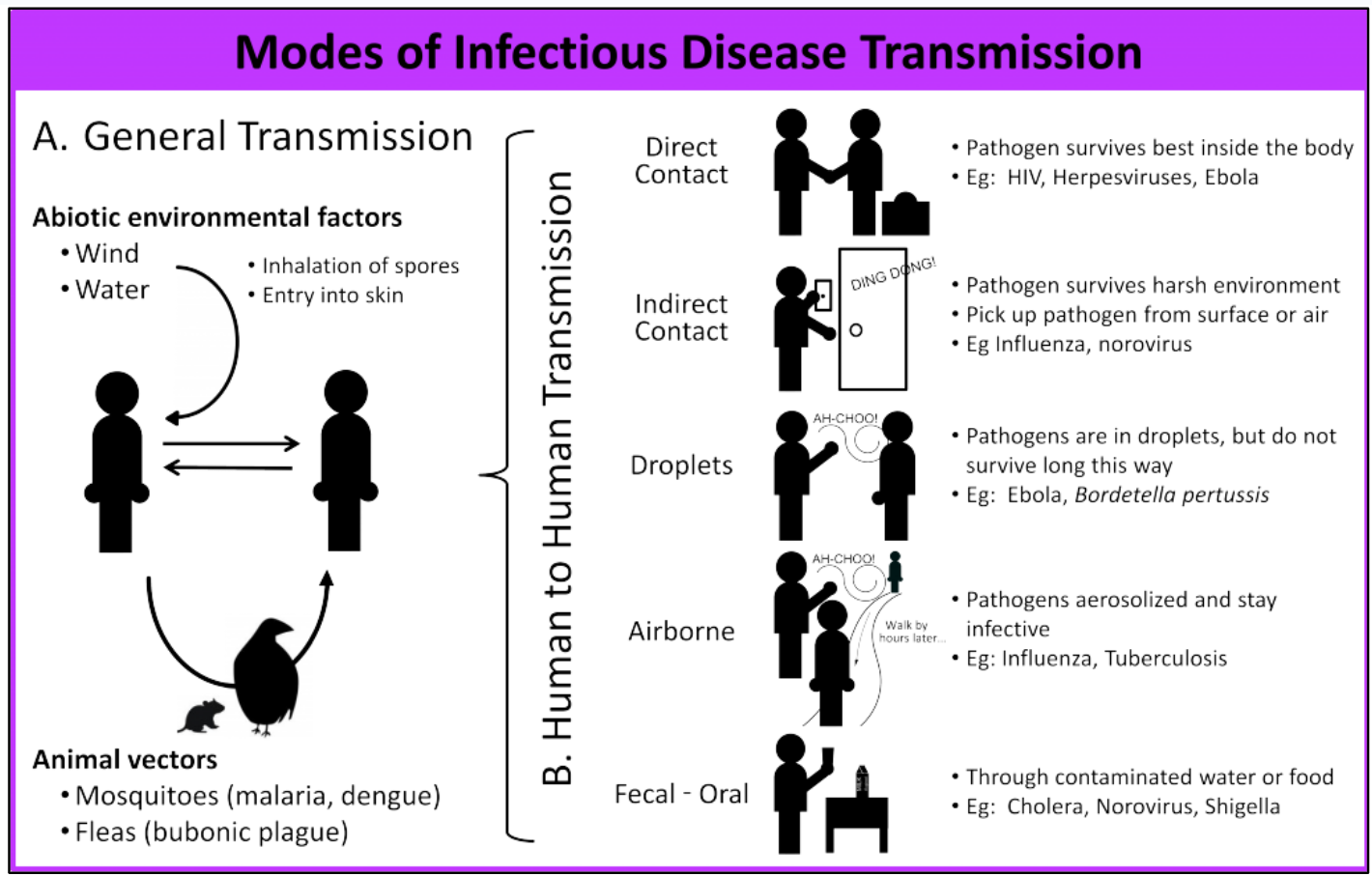
🔬 Caused by:
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (a rod-shaped bacterium)
📍 How It Spreads:
- Through air via droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes
- Highly contagious in crowded or poorly ventilated areas
🩺 What It Does:
- Infects lungs (can spread to brain, spine, kidneys)
- Bacteria reproduce slowly and damage lung tissue
🚨 Symptoms:
- Persistent cough (often with blood)
- Fever, night sweats
- Chest pain
- Weight loss and fatigue
💊 Treatment: Antibiotics (e.g. isoniazid, rifampin) taken for 6+ months. Drug-resistant TB is a growing concern.
🦠 2. Viral Pathogen: HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus)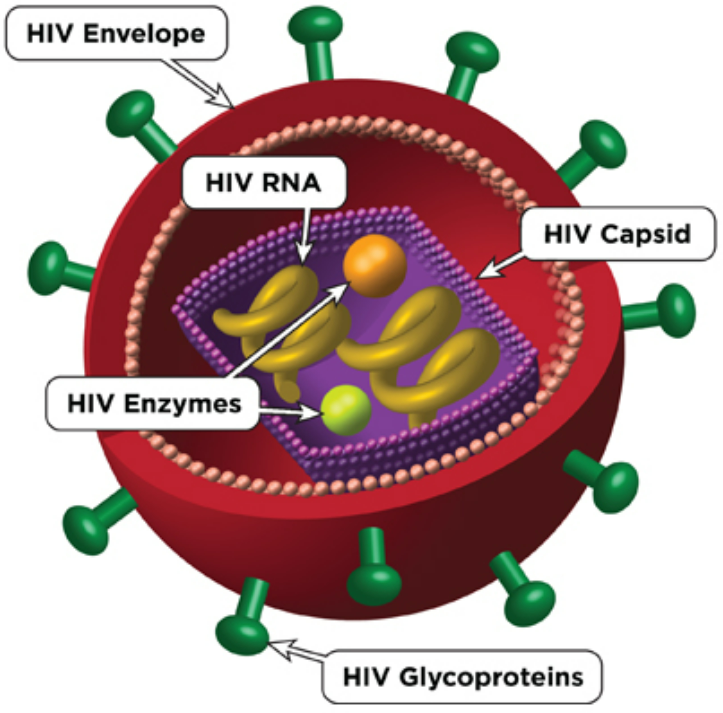
🔬 How It Spreads:
- Through blood, semen, vaginal fluids, or breast milk
- Unprotected sex, sharing needles, mother-to-child during birth
📉 What It Does:
- Targets and destroys helper T cells (immune system)
- Weakens body’s ability to fight infections
- Progresses to AIDS when immune damage is severe
🩺 Symptoms:
- Early: Fever, rash, sore throat
- Latent: Often no symptoms for years
- Late stage (AIDS): Weight loss, infections, cancers (e.g. Kaposi’s sarcoma)
💊 Treatment: No cure yet, but ART (antiretroviral therapy) helps people live long, healthy lives.
🦟 3. Parasitic Pathogen: Malaria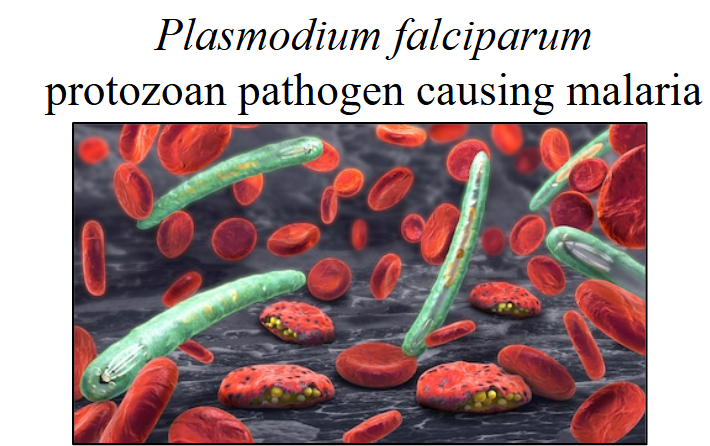
🦠 Caused by: A protozoan parasite called Plasmodium (esp. P. falciparum)
🦟 Spread by: Female Anopheles mosquito bite → injects parasite into blood
🧬 What It Does:
- Parasite travels to liver → multiplies → attacks red blood cells
- Causes cyclic fevers as RBCs burst
🩺 Symptoms:
- Recurring high fever and chills
- Headache and muscle aches
- Severe cases: anemia, coma, or death
💊 Treatment: Antimalarial drugs (e.g. chloroquine, artemisinin). Prevention = mosquito nets, insect repellents, and vector control.
📊 Summary Table: Pathogens & Their Effects
| Pathogen Type | Disease | Microbe | Spread By | Key Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterium | Tuberculosis (TB) | Mycobacterium tuberculosis | Airborne droplets | Cough, weight loss, fever |
| Virus | HIV/AIDS | HIV | Blood, sex, birth | Immunosuppression, infections |
| Parasite | Malaria | Plasmodium | Mosquito bite | Cyclic fever, chills, anemia |
