IB myp 4-5 Chemistry – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic :Types of chemical reaction-Reactivity Series
Topic :Types of chemical reaction-Weightage : 21 %
All Questions for Topic :acids and bases,neutral solutions,acid/base reactions,$\mathrm{pH}$ and indicators,formation of salts,uses of salts,redox reactions,reactivity series,extraction of metals and corrosion,electrochemical cells
Question (28 marks)
The position of a metal in the reactivity series is related to that metal’s ability to displace a different metal from its compound. This can be summarized by the equation:
Metal A + Metal B Compound → Metal A compound + Metal B.

Question a (1 mark)
Copper sulfate is toxic. Select the hazard symbol that is used for copper sulfate.

▶️Answer/Explanation
Topic: Types of chemical reaction – Acids and bases
Answer: C
Explanation: Copper sulfate is classified as harmful/irritant (exclamation mark symbol) rather than toxic (skull) or other hazards. The exclamation mark indicates it can cause skin/eye irritation and may be harmful if swallowed.
Question b (1 mark)
Select one piece of equipment needed to collect appropriate data in this experiment.
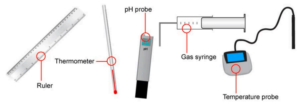
▶️Answer/Explanation
Topic: Bonding – Energy changes in reactions
Answer: Thermometer
Explanation: Since the experiment measures temperature changes during metal displacement reactions, a thermometer (or temperature probe) is essential to collect the temperature data.
Question c (15 marks)
Design a method which would allow you to collect sufficient data to place these metals in order of reactivity. The metals you will use are zinc, iron, magnesium, lead and aluminium. In your answer should include:
- a list of equipment you will use
- the method you will follow
- details of the measurements you will make to collect sufficient, valid data
- how you will make sure your method is safe
▶️Answer/Explanation
Topic: Types of chemical reaction – Reactivity series
Answer:
Equipment: Test tubes, thermometer, measuring cylinder, copper sulfate solution, metal powders (Zn, Fe, Mg, Pb, Al), stopwatch, safety goggles
Method:
1. Measure 20ml copper sulfate solution into test tube
2. Record initial temperature
3. Add measured amount of metal powder
4. Record maximum temperature reached
5. Repeat for all metals
Measurements: Temperature change for each metal, time taken for reaction, observations of reactivity
Safety: Wear goggles, handle metals carefully, clean spills immediately
Explanation: The method measures exothermic reaction temperatures to compare reactivity. More reactive metals will cause greater temperature increases when displacing copper from its sulfate solution.
Question d (1 mark)
Here are some results from a similar investigation. In this investigation only one set of results was collected.
| Metal added | Temperature change (°C) |
|---|---|
| Aluminium | 39 |
| Iron | 16 |
| Lead | 12 |
| Magnesium | 46 |
| Zinc | 32 |
Using the data in the table, determine the order of reactivity of these five metals.
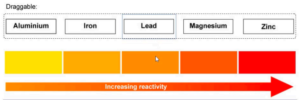
▶️Answer/Explanation
Topic: Types of chemical reaction – Reactivity series
Answer: Magnesium → Aluminium → Zinc → Iron → Lead
Explanation: The greater the temperature increase, the more reactive the metal is in displacing copper. Magnesium caused the largest temperature change (46°C) making it most reactive, while lead caused the smallest (12°C) making it least reactive.
Question e (2 marks)
Justify your answer using scientific reasoning.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Topic: Bonding – Energy changes in reactions
Answer: The order of reactivity is based on the temperature rise – the larger the temperature change/rise the more reactive the metal is.
Explanation: More reactive metals release more energy when they displace copper from its compound, resulting in greater temperature increases. This follows the reactivity series where metals higher in the series are more reactive and undergo more vigorous displacement reactions.
Question f (1 mark)
Select the most appropriate graph to present the temperature change data.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Topic: Pure and impure substance – Separation techniques
Answer: Bar chart
Explanation: A bar chart is best for comparing discrete categories (different metals) against a measured value (temperature change). Line graphs are for continuous data, while pie charts show proportions of a whole.
Question g (5 marks)
Present the data in the graph. You need to give your graph an appropriate title, label the x axis and add the correct unit to the y axis.
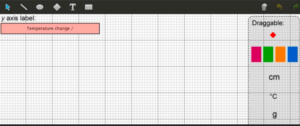
▶️Answer/Explanation
Topic: Pure and impure substance – Separation techniques
Answer:
Title: Temperature change during metal displacement reactions
X-axis: Metal (Aluminium, Iron, Lead, Magnesium, Zinc)
Y-axis: Temperature change / °C
Explanation: The graph should show metal names on the x-axis and temperature changes on the y-axis with proper scaling (0-50°C). Bars should be correctly sized according to the data table values.
Question h (2 marks)
Comment on the validity of the results in the table and suggest an improvement to this investigation.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Topic: Bonding – Chemical reactions
Answer: Limited validity as results were produced once only and may contain errors. Improvement: Carry out more than one trial to produce an average.
Explanation: Single trials are unreliable due to potential experimental errors. Repeating the investigation and averaging results would improve reliability. Other improvements could include controlling variables more precisely (e.g., metal particle size, solution concentration).
Question:
For each of the following word equations, use the reactivity series to decide if the reaction will proceed spontaneously, as written.
a) magnesium + hydrochloric acid ➝ magnesium chloride + hydrogen
b) aluminium + iron(III) oxide ➝ iron + aluminium oxide
c) magnesium oxide + copper ➝ copper(II) oxide + magnesium
d) potassium nitrate + zinc ➝ zinc nitrate + potassium
e) sodium + water ➝ sodium hydroxide + hydrogen
f) iron(III) oxide + carbon ➝ iron + carbon dioxide
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: a) Spontaneous
b) Spontaneous
c) Non–spontaneous
d) Non–spontaneous
e) Spontaneous
f) Spontaneous
