IB MYP 4-5 Biology-Tissues ,Organs and Systems- Study Notes - New Syllabus
IB MYP 4-5 Biology-Tissues ,Organs and Systems- Study Notes – New syllabus
IB MYP 4-5 Biology-Tissues ,Organs and Systems- Study Notes – IB MYP 4-5 Biology – per latest IB MYP Biology Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- Tissues: Types (muscle, epithelial, nervous, connective) and functions.
- Organs: Structure linked to function (e.g., heart, lungs, leaf, root).
- Systems: Digestive, circulatory, respiratory (interdependence).
- Plant Systems: Xylem/phloem, transpiration.
🔬 Tissues: Types & Functions
🔍 What Are Tissues?
A tissue is a group of similar cells working together to perform a specific function.
🧫 Studying tissues is called Histology.
📌 Found in multicellular organisms.
🦠 In unicellular organisms like Paramecium, one cell does everything. But in humans and other multicellular organisms, cells specialize → form tissues → build organs → work in systems.
🧠 The 4 Basic Types of Animal Tissues:
| Tissue Type | Function 🛠️ | Example 🧍♂️ |
|---|---|---|
| Epithelial | Covers body surfaces, protects, absorbs | Skin, lining of stomach, lungs |
| Connective | Supports, binds, stores, transports | Bone, blood, fat, cartilage |
| Muscle | Contracts to allow movement | Biceps, heart muscle, intestines |
| Nervous | Sends electrical signals | Brain, spinal cord, nerves |
🧱 1. Epithelial Tissue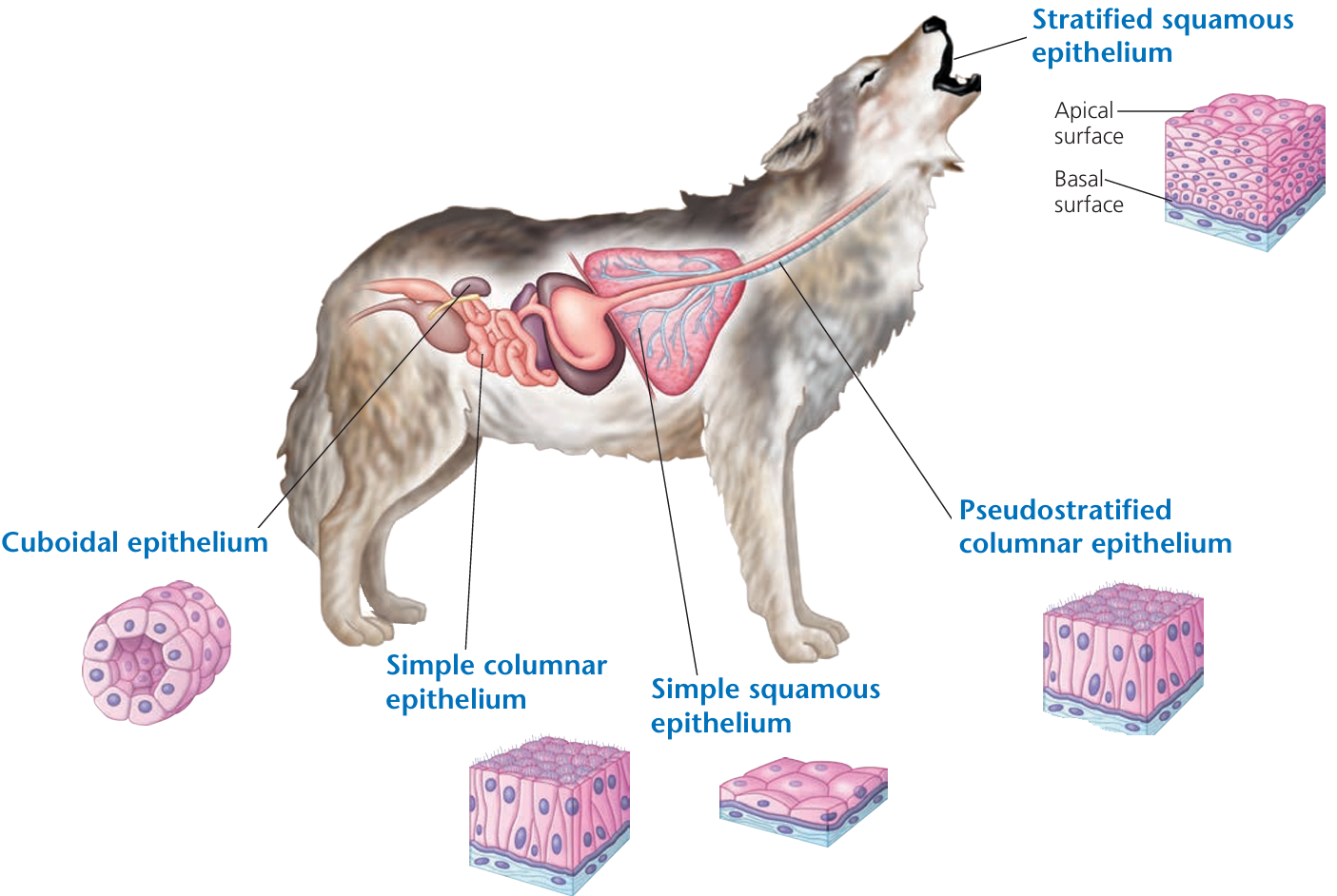
- Covers the outside and inside of the body (skin, inner linings)
- Lines blood vessels and organs
- Some absorb (e.g. intestines), some secrete (e.g. glands)
- Acts like a protective barrier
Examples:
- Skin epithelium protects from germs
- Lung epithelium helps in gas exchange
🧲 2. Connective Tissue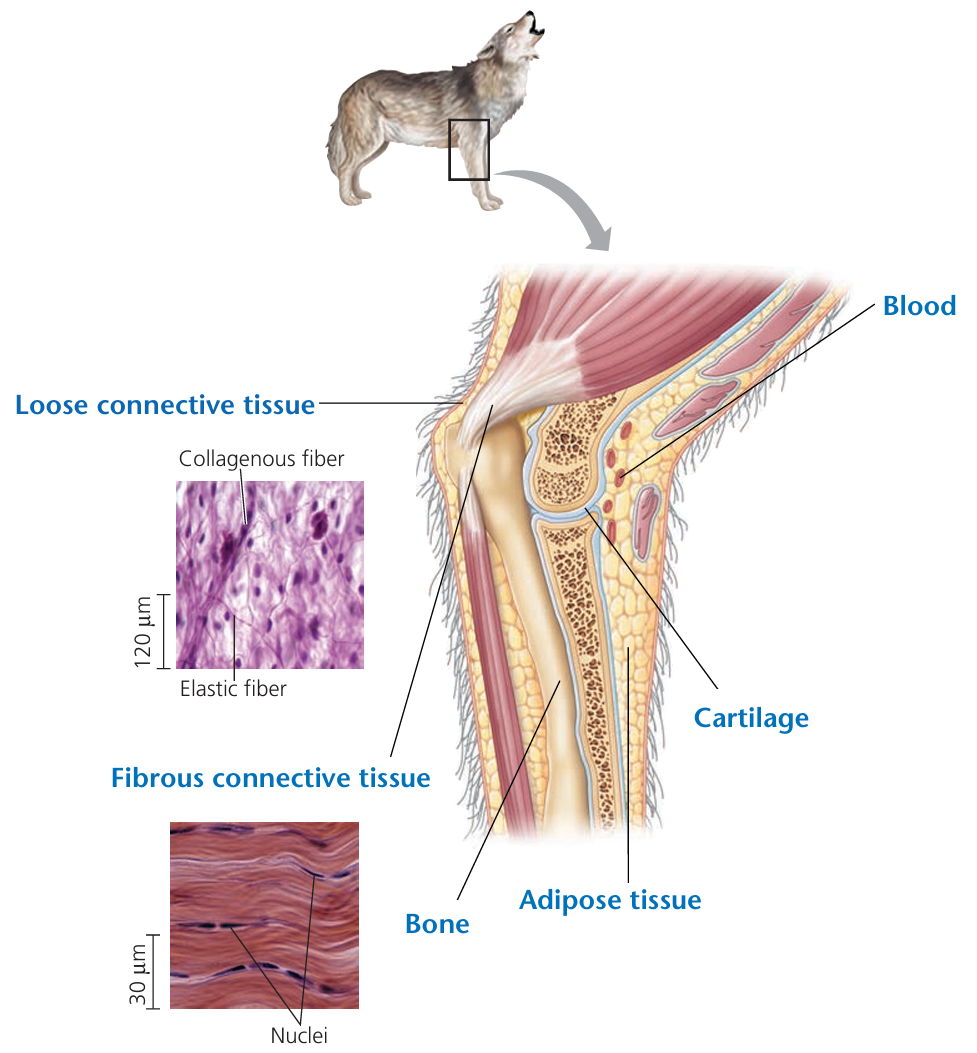
- Supports, connects, stores & transports
- Made of cells + matrix (fibers and ground substance)
- Can be soft (fat), flexible (cartilage), or hard (bone)
Examples:
- Bone – support & structure
- Blood – transports oxygen, nutrients
- Fat (adipose) – stores energy & insulates
- Tendons & ligaments – attach muscles to bones
💡 Did you know? Blood is a connective tissue because it connects all parts of the body by transporting materials!
💪 3. Muscle Tissue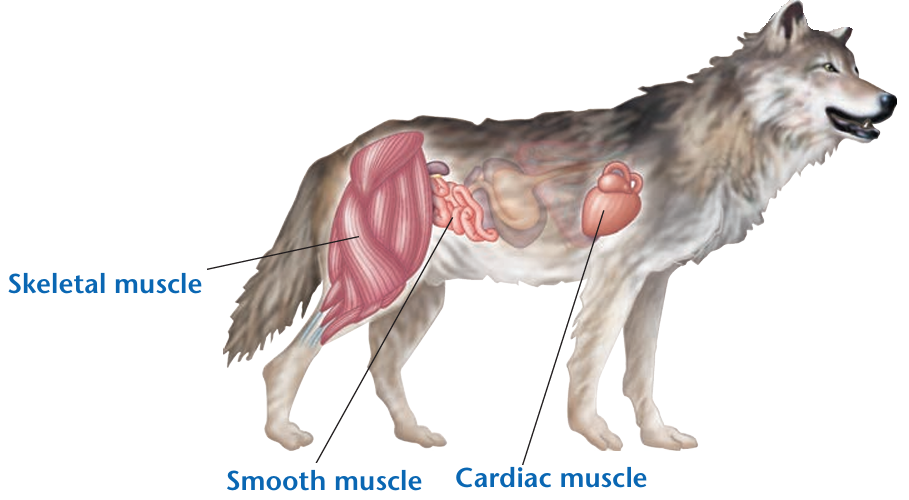
🚴♂️ Allows movement by contraction
Needs energy (ATP) to work
| Muscle Type | Features | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Skeletal | Voluntary, striated | Arms, legs, face |
| Cardiac | Involuntary, striated, rhythmic | Heart ❤️ |
| Smooth | Involuntary, not striated | Stomach, intestines, bladder |
🧠 Skeletal muscles work in antagonistic pairs (one contracts, the other relaxes).
⚡ 4. Nervous Tissue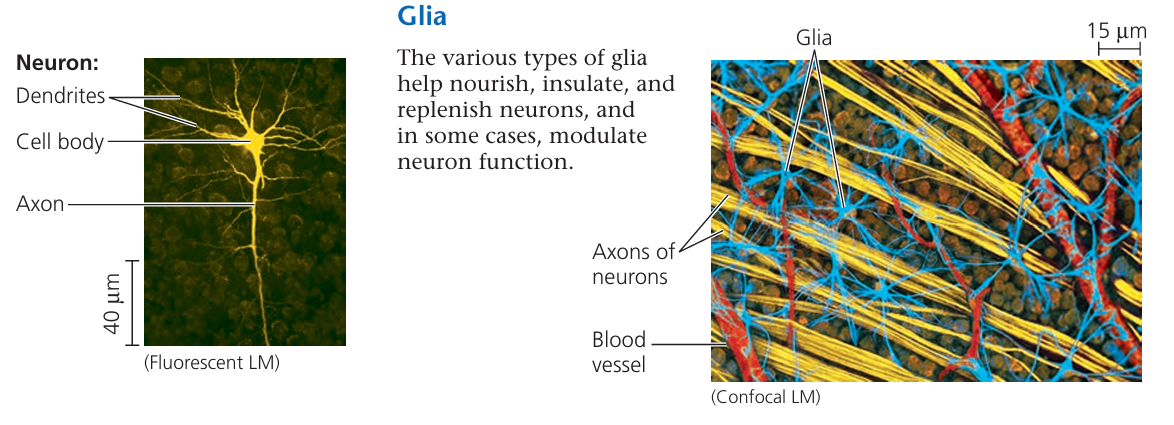
- Sends fast electrical signals (nerve impulses)
- Made up of neurons and supporting cells
- Controls and coordinates body activities
Found in:
- Brain
- Spinal cord
- Peripheral nerves
🌱 Plant Tissues
| Tissue Type | Function | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Epidermal | Protects plant surfaces | Leaf surface, roots |
| Mesophyll | Photosynthesis | Inside leaves |
| Xylem | Transports water and minerals | Roots to leaves |
| Phloem | Transports sugars (food) | Throughout plant |
| Meristematic | Growth (can divide) | Tips of roots and shoots |
🧩 Summary: Cells → Tissues → Organs → Systems → Organism
- Tissues are building blocks of organs
- Different tissues perform different roles
- Multiple tissues form an organ
- Multiple organs form a system
Muscle – movement
Epithelial – external & internal covering
Nervous – nerve impulses
Connective – connects & supports
Organs: Structure Linked to Function
🔄 What is an Organ?
An organ is a group of different tissues working together to perform a specific function. Its structure is perfectly suited to its role.
🧱 Structure → How it’s built
🛠️ Function → What it does
👀 Structure supports function efficiently!
HUMAN AND PLANT ORGANS: Structure + Function
1. 🫀 Heart
- Function: Pumps blood around the body
- Structure:
- Thick muscular walls → pump with force
- Left side thicker → to body (more pressure)
- 4 chambers → separates oxygenated & deoxygenated blood
- Valves → prevent backflow
- Coronary arteries → supply the heart muscle
- Made of: Muscle, epithelial, connective tissues
💡 Did you know? Your heart beats ~100,000 times/day! ❤️
2. 🫁 Lungs
- Function: Gas exchange – oxygen in, CO₂ out
- Structure:
- Millions of alveoli → huge surface area
- Thin walls (1 cell thick)
- Moist lining for diffusion
- Rich capillary network
- Elastic tissue → helps expansion & recoil
- Made of: Epithelial, connective, capillary tissues
💡 Did you know? Spread out, your alveoli cover a tennis court! 🎾
3. 🍃 Leaf
- Function: Photosynthesis
- Structure:
- Broad & flat → capture sunlight
- Stomata → gas exchange
- Thin → easy gas diffusion
- Chloroplasts in palisade cells
- Veins (xylem + phloem)
- Made of: Epidermis, mesophyll, vascular tissues
💡 Did you know? Stomata act like tiny plant mouths! 🌱
4. 🌱 Root
- Function: Absorbs water/minerals, anchors plant
- Structure:
- Root hairs → increase absorption
- Thin walls for osmosis
- Xylem → transports water
- No chloroplasts
- Strong structure → support
- Made of: Epidermis, cortex, xylem, phloem
💡 Did you know? Just 1 mm² of root = 200+ root hairs! 🌱
5. 🧠 Brain
- Function: Controls body, memory, senses
- Structure:
- Cerebrum, cerebellum, medulla
- Capillary-rich → oxygen & glucose
- Protected by skull + fluid
- Made of: Nervous, connective tissues
💡 Did you know? Your brain uses 20% of your body’s energy! 🔋
6. 🍔 Stomach
- Function: Digests food
- Structure:
- Muscles churn food
- Glandular tissue → acid + enzymes
- Mucus lining → protection
- Stretchable walls
- Made of: Muscle, epithelial, glandular tissues
💡 Did you know? Stomach acid can dissolve metal! 😮
7. 🩸 Liver
- Function: Detox, bile, vitamin storage
- Structure:
- Lobules → liver units
- Bile ducts → transport bile
- Rich blood supply
- Stores glucose, iron
- Made of: Hepatic cells, blood, connective tissue
💡 Did you know? Liver is the only organ that regenerates! 🧬
8. 🩺 Kidney
- Function: Filters blood, makes urine
- Structure:
- Nephrons filter waste
- Loop of Henle → reabsorbs water
- Collecting ducts → drain urine
- Renal artery + vein
- Made of: Epithelial, connective tissues
💡 Did you know? Each kidney filters 50 gallons/day! 🧃
9. 🍽️ Small Intestine
- Function: Absorbs nutrients
- Structure:
- Villi + microvilli → high surface area
- Thin walls → fast absorption
- Capillary network → glucose, amino acids
- Lacteals → absorb fats
- Made of: Epithelial, muscle, blood tissues
💡 Did you know? It’s over 6 meters long! 🍝
10. 🌼 Flower
- Function: Reproduction
- Structure:
- Petals → attract pollinators
- Stamens → make pollen
- Carpel → makes seeds
- Nectaries → attract insects
- Made of: Epidermal, reproductive tissues
💡 Did you know? Some flowers self-pollinate! 🌼
11. 🌿 Stem
- Function: Support + transport
- Structure:
- Xylem → water up
- Phloem → sugar down
- Nodes/internodes → hold leaves/flowers
- Lignin → strength
- Made of: Vascular, ground, epidermal tissues
💡 Did you know? Water can travel 100 meters in tall trees! 🌲
🧠 Summary Table
| Organ | Function | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Heart | Pump blood | 4 chambers, valves, muscle walls |
| Lungs | Gas exchange | Alveoli, thin moist walls, capillaries |
| Leaf | Photosynthesis | Chloroplasts, stomata, veins |
| Root | Absorb water/minerals | Root hairs, no chloroplasts, xylem |
| Brain | Process & control | Cerebrum, cerebellum, skull |
| Stomach | Digest food | Muscles, acid, mucus lining |
| Liver | Detox + bile | Lobules, bile ducts, blood supply |
| Kidney | Filter blood → urine | Nephrons, collecting ducts, artery |
| Intestine | Absorb nutrients | Villi, capillaries, lacteals |
| Flower | Reproduction | Petals, anthers, ovary |
| Stem | Support + transport | Xylem, phloem, lignin |
Organ Systems: Digestive, Circulatory & Respiratory – Interdependence
🧠 Why Learn This?
These three systems are like best friends 🧑🤝🧑 they work closely to keep every single cell alive by providing oxygen, nutrients, and removing waste like carbon dioxide and urea. Without even one of them, your body would crash!
🥙 1. Digestive System – Break It Down to Build You Up!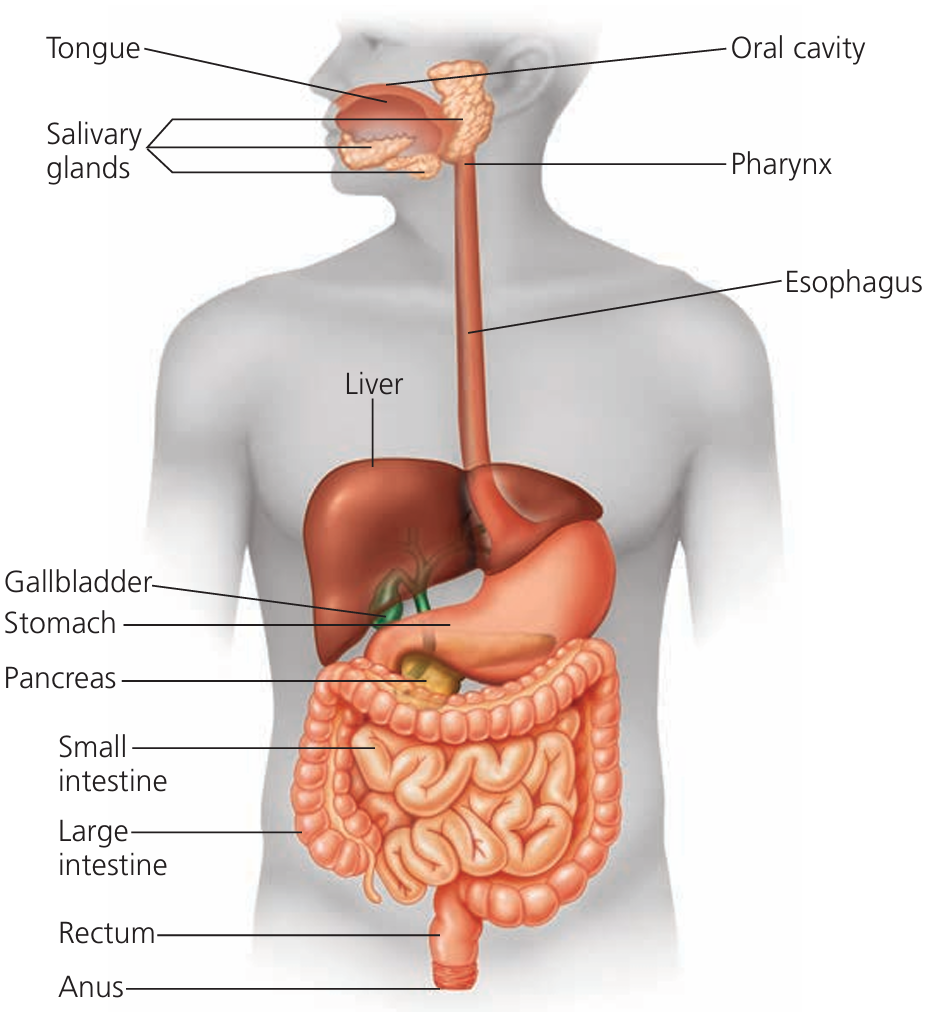
🔍 Function: Breaks down food into simpler nutrients (like glucose, amino acids, fatty acids) that are small enough to be absorbed into the blood and used by cells.
| Organ | Function |
|---|---|
| Mouth | Mechanical breakdown (teeth) + chemical digestion of starch by amylase |
| Stomach | Hydrochloric acid + pepsin enzyme → protein digestion; muscular churning |
| Small Intestine | Enzymes complete digestion, villi absorb nutrients into blood capillaries |
| Large Intestine | Absorbs water, forms semi-solid faeces |
| Liver | Produces bile → emulsifies fats for digestion |
| Pancreas | Releases digestive enzymes and bicarbonate to neutralize acid |
➡️ Nutrients → enter bloodstream via villi → go to all cells via circulatory system.
💓 2. Circulatory System – Body’s Delivery Network
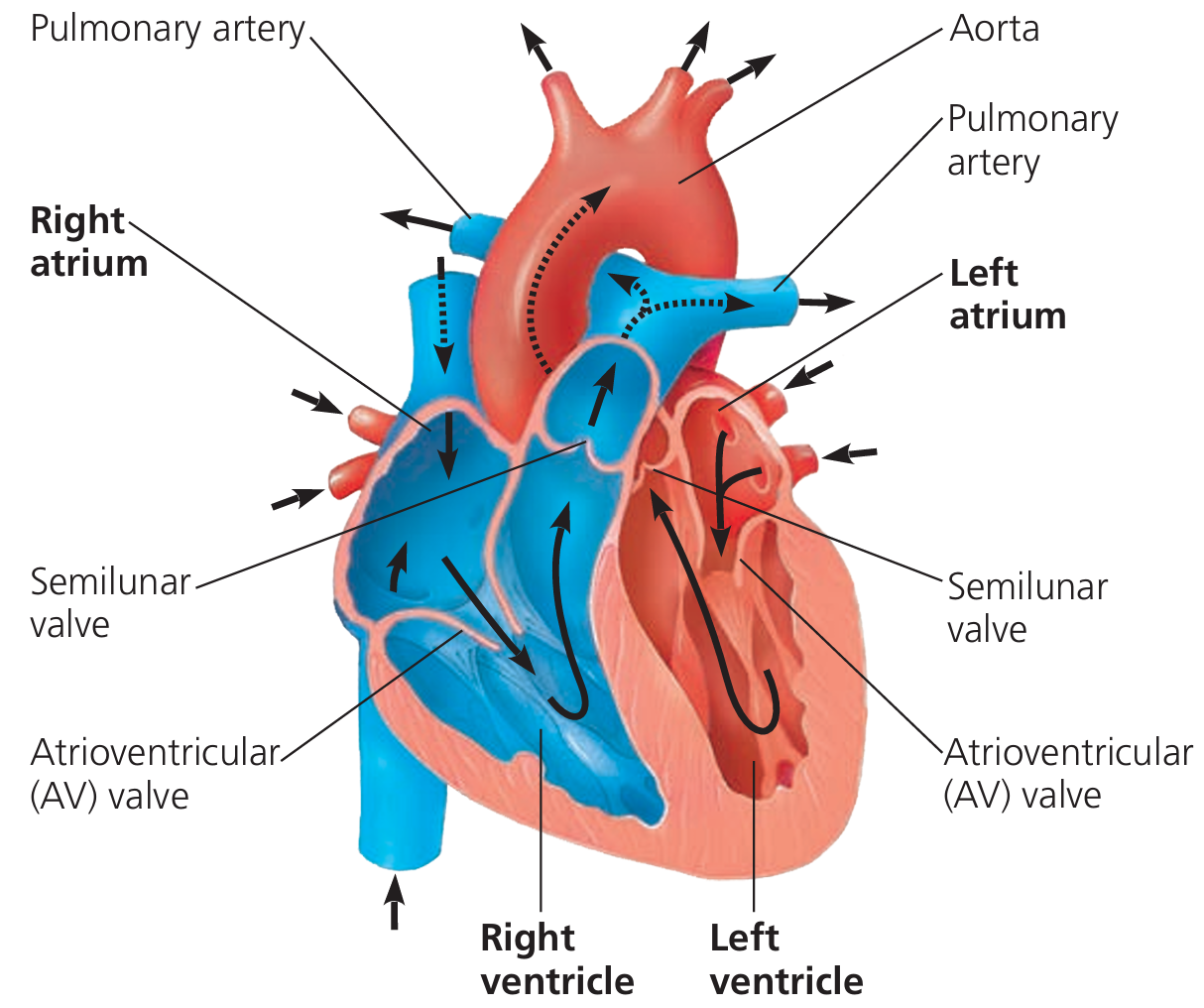
🔍 Function: Transports oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and removes waste (like CO₂ and urea) to maintain homeostasis.
| Organ | Function |
|---|---|
| Heart | Pumps oxygen-rich blood to the body and receives deoxygenated blood |
| Arteries | Carry blood away from heart (usually oxygenated) |
| Veins | Carry blood back to the heart (usually deoxygenated) |
| Capillaries | Microscopic exchange of gases/nutrients at cells |
| Blood | Contains RBCs (O₂), WBCs (immunity), plasma (nutrients, hormones), platelets (clotting) |
🧬 Nutrients from gut + oxygen from lungs = delivered to body cells for cellular respiration!
🌍 Did You Know? The heart pumps ~7,500 litres of blood every day!
🌬️ 3. Respiratory System – Your Oxygen Engine
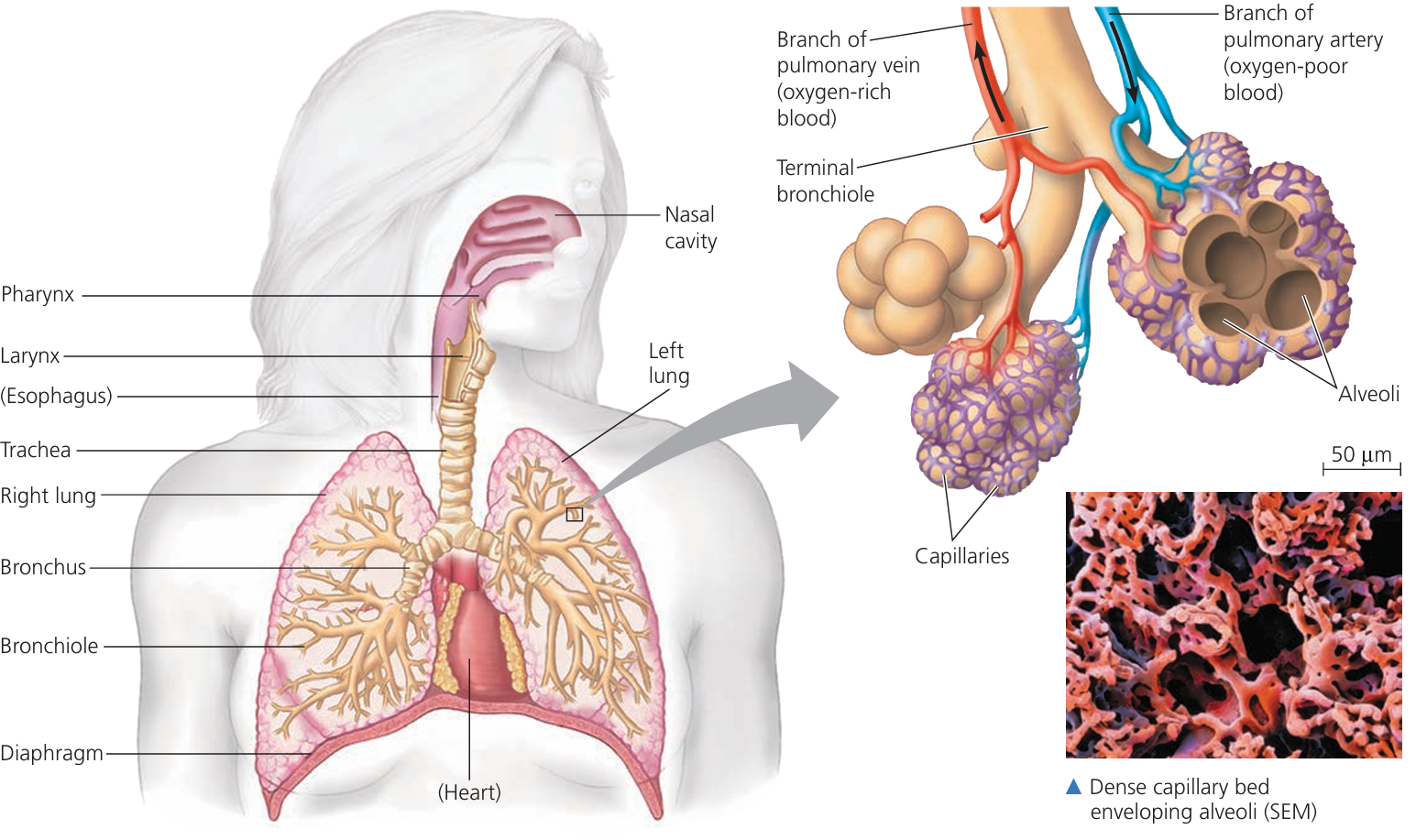
🔍 Function: Brings in oxygen from the air and removes carbon dioxide from the blood.
| Organ | Function |
|---|---|
| Nose & Mouth | Air enters, filtered and warmed |
| Trachea | Windpipe, air passes to bronchi |
| Bronchi/Bronchioles | Carry air into lungs |
| Alveoli | Gas exchange, O₂ in, CO₂ out |
| Diaphragm | Contracts/relaxes to draw air in and out |
🫁 O₂ → into blood from alveoli | CO₂ → into alveoli from blood → exhaled out
🔄 Interdependence: How They Work Together
- Digestive: Breaks down food into glucose + amino acids
- Respiratory: Brings in oxygen needed for respiration
- Circulatory: Transports both glucose + oxygen to all cells
- Cells: Perform aerobic respiration → ATP (energy) + CO₂
- CO₂: Taken back to lungs and exhaled
⚠️ If One Fails:
❌ Lungs stop → no oxygen
❌ Digestive issues → no nutrients
❌ Heart stops → no delivery → no energy → organs shut down
💡 Memory Trick: “DRC – Digestive, Respiratory, Circulatory → Deliver Respiration Constantly!”
📝 Summary Table
| System | Main Role | Depends On |
|---|---|---|
| Digestive | Supplies glucose & nutrients | Circulatory for delivery |
| Respiratory | Provides oxygen, removes CO₂ | Circulatory for gas transport |
| Circulatory | Delivers O₂ & nutrients, removes wastes | Digestive & Respiratory for supply |
📌 Final Thought: These systems don’t work alone – they rely on each other like gears in a machine! Miss one, and the body breaks down.
Plant Transport Systems: Xylem, Phloem & Transpiration
🌿 1. Why Do Plants Need Transport Systems?
- Water 💧 (for photosynthesis and structure)
- Minerals 🧂 (for growth and enzymes)
- Sugars 🍬 (for energy)
🚫 No heart or blood – but smart transport tissues!
🚛 2. The Two Main Transport Systems in Plants
| Tissue | What It Carries | Direction | Living/Dead? | Special Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xylem | Water + Minerals 💧🧂 | UP (roots → leaves) | Dead cells | Thick walls, lignin, hollow tubes |
| Phloem | Sugars (food) 🍬 | UP & DOWN (leaves ↔ all parts) | Living cells | Companion cells help with energy |
🌊 Xylem = “Water Highway”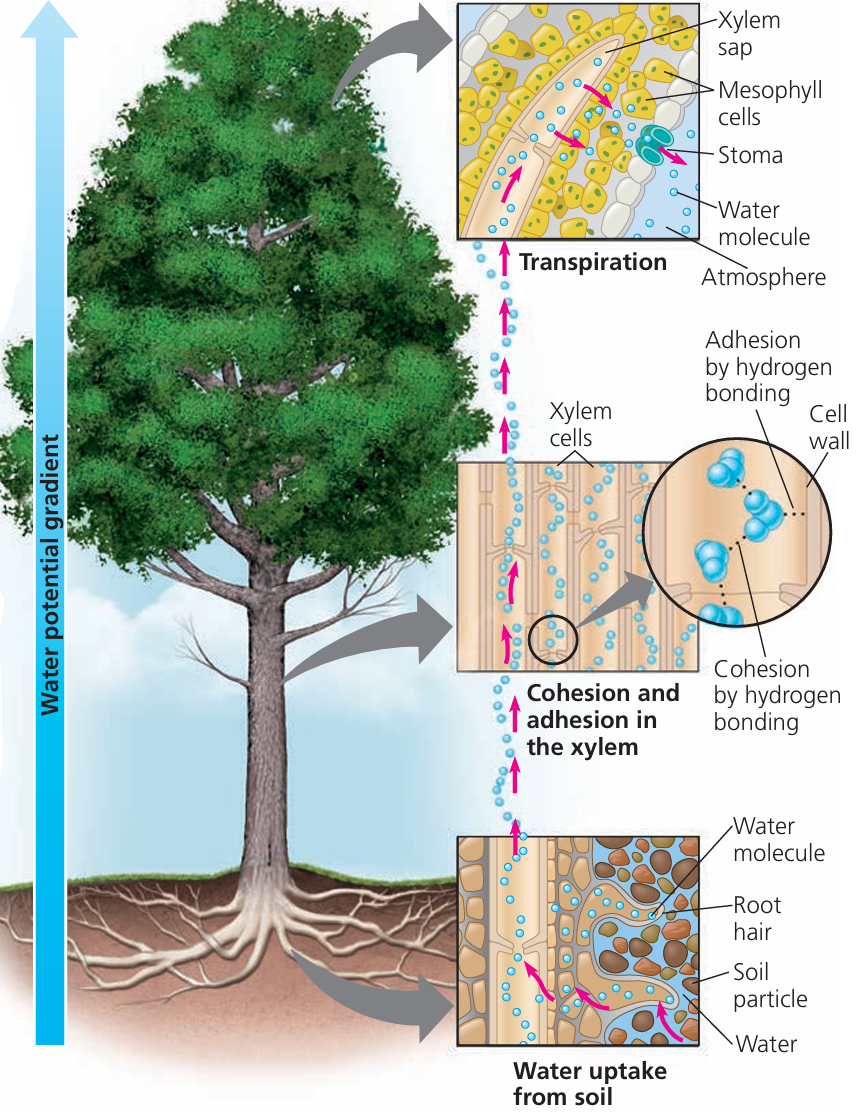
- One-way only – UP!
- Made of dead, hollow cells
- Strengthened by lignin
- Water enters roots by osmosis and moves up by:
- Root pressure
- Capillary action
- Transpiration pull 🌬️
🍭 Phloem = “Food Delivery”
- Glucose from photosynthesis 🍃
- Moves UP & DOWN (called translocation)
- Made of living cells with sieve plates
- Companion cells provide energy (ATP)
💡 Can deliver sugars to growing fruit or storage (like potatoes!)
💨 3. Transpiration – Plants ‘Sweating’
Transpiration = loss of water vapor from the stomata of leaves. It creates suction to pull water up the xylem.
🚀 Why Transpiration is Important:
- Pulls water up (xylem flow)
- Cools the plant 🌬️
- Delivers minerals to leaves
- Keeps leaves firm (turgid)
🧪 Factors That Affect Transpiration
| Factor | Effect |
|---|---|
| ☀️ Light | More light → more transpiration (stomata open) |
| 🌡️ Temperature | Higher temp → faster evaporation |
| 💨 Wind | Removes water vapor → faster transpiration |
| 💧 Humidity | High humidity → slower transpiration |
📉 Too Much Transpiration?
• Plants wilt! 😓
• Stomata close in dry heat 🌵
• Waxy cuticle slows water loss
• Desert plants may have thick leaves or fewer stomata
🪴 4. Root Hair Cells – Water Absorption Heroes
- Located near root tips
- Long extensions = more surface area
- Absorb water by osmosis
- Take in minerals by active transport
📝 Summary Table
| Concept | Key Info |
|---|---|
| Xylem | Moves water UP from roots, dead cells |
| Phloem | Moves sugars UP & DOWN, living cells |
| Transpiration | Water loss from leaves, drives water movement |
| Root hairs | Absorb water/minerals from soil |
🌳 A single tree can lose hundreds of liters of water per day through transpiration!
