IB MYP 4-5 Maths- Calculating network pathways- Study Notes - New Syllabus
IB MYP 4-5 Maths- Calculating network pathways – Study Notes
Extended
- Calculating network pathways
IB MYP 4-5 Maths- Calculating network pathways – Study Notes – All topics
Calculating Network Pathways
Calculating Network Pathways
Network Pathways
A pathway in a network is a sequence of edges connecting nodes. Counting the number of possible pathways between two nodes helps in planning routes, communication systems, and transportation networks.
Key Concepts
- Path: A sequence of edges connecting distinct nodes.
- Trail: A path where edges are not repeated.
- Walk: A sequence of nodes where repetition of nodes and edges is allowed.
- Cycle: A closed path starting and ending at the same node without repeating an edge.
- Network Pathways: The total number of possible paths between two nodes in a network.
How to Calculate Pathways
There are two main methods:
- Listing Method: List all possible paths manually (works for small networks).
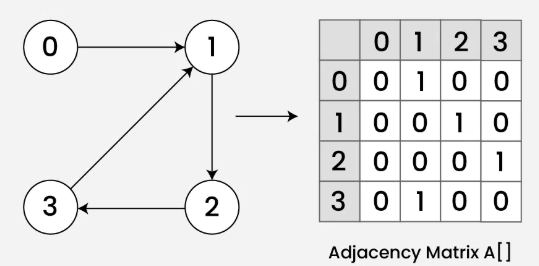
- Adjacency Matrix Method:
- Create a matrix showing direct connections between nodes (1 for connection, 0 for none).
- Raise the matrix to a power \( n \) to find the number of paths of length \( n \).

Example:
A network has nodes A, B, and C. Connections: A-B, B-C, and A-C. How many different paths exist from A to C?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Solution:
Connections: A → B → C, and A → C directly.
Total paths: 2 (A → C and A → B → C).
Example:
A network has 3 nodes (1, 2, 3) with edges: 1-2, 2-3, 1-3. Find the number of paths of length 2 from node 1 to node 3 using an adjacency matrix.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Solution:
Adjacency Matrix \( A \):
\( A = \begin{bmatrix} 0 & 1 & 1 \\ 1 & 0 & 1 \\ 1 & 1 & 0 \end{bmatrix} \)
Compute \( A^2 \):
\( A^2 = \begin{bmatrix} 2 & 1 & 1 \\ 1 & 2 & 1 \\ 1 & 1 & 2 \end{bmatrix} \)
The entry (1, 3) in \( A^2 \) = 1 → There is 1 path of length 2 from node 1 to node 3.