IB MYP 4-5 Chemistry -Acid rain and air pollution- Study Notes - New Syllabus
IB MYP 4-5 Chemistry -Acid rain and air pollution- Study Notes
Key Concepts
- Acid Rain and Air Pollution
Acid Rain and Air Pollution
Acid Rain and Air Pollution
Acid rain is any form of precipitation (rain, snow, fog, or dust) that has a pH less than 5.6. It forms when pollutants such as sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and nitrogen oxides (NOₓ) react with water vapour in the atmosphere to produce acidic compounds like sulfuric acid and nitric acid.
Air pollution refers to the presence of harmful substances in the air that can damage the environment and human health.
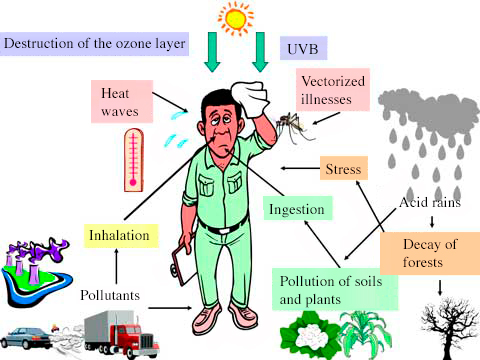
Major Air Pollutants
Air pollutants can be classified as primary (directly emitted) or secondary (formed by reactions in the atmosphere).
| Type | Examples | Source | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Pollutants | SO₂, CO, NO, particulate matter | Combustion of fuels, vehicles, industries | Respiratory issues, acid rain |
| Secondary Pollutants | O₃, HNO₃, H₂SO₄, smog | Formed from primary pollutants reacting in the atmosphere | Smog formation, acid rain, climate effects |
Formation of Acid Rain
Main Pollutants Involved: Sulfur dioxide (\( \mathrm{SO_2} \)) and nitrogen oxides (\( \mathrm{NO_x} \)) are the primary gases that form acid rain.
![]()
Step 1: Formation of Acidic Compounds
- Sulfur Dioxide: Produced by burning sulfur-containing fuels (coal, oil).
- Nitrogen Oxides: Produced in vehicle engines and power plants at high temperatures.
Step 2: Chemical Reactions in the Atmosphere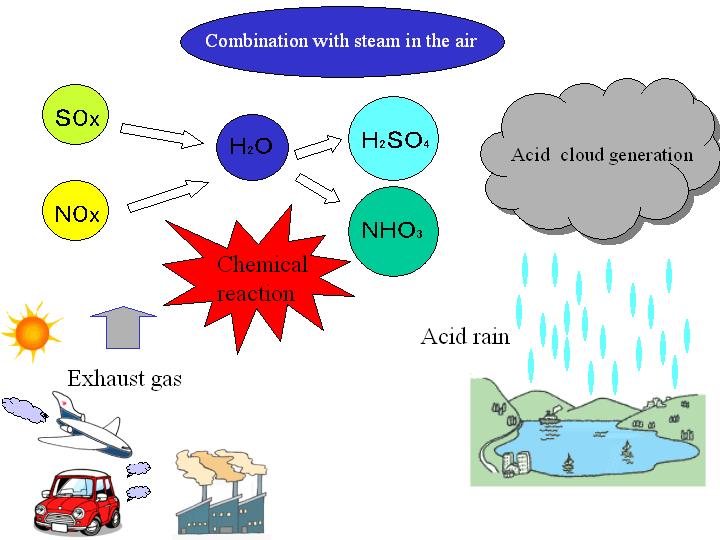
Sulfur-based Reactions:
\( \mathrm{S + O_2 \rightarrow SO_2} \)
\( \mathrm{2SO_2 + O_2 \rightarrow 2SO_3} \)
\( \mathrm{SO_3 + H_2O \rightarrow H_2SO_4} \)
Nitrogen-based Reactions:
\( \mathrm{N_2 + O_2 \rightarrow 2NO} \)
\( \mathrm{2NO + O_2 \rightarrow 2NO_2} \)
\( \mathrm{4NO_2 + 2H_2O + O_2 \rightarrow 4HNO_3} \)
Result: These acids dissolve in rainwater and fall to Earth as acid rain.
Effects of Acid Rain
On the Environment: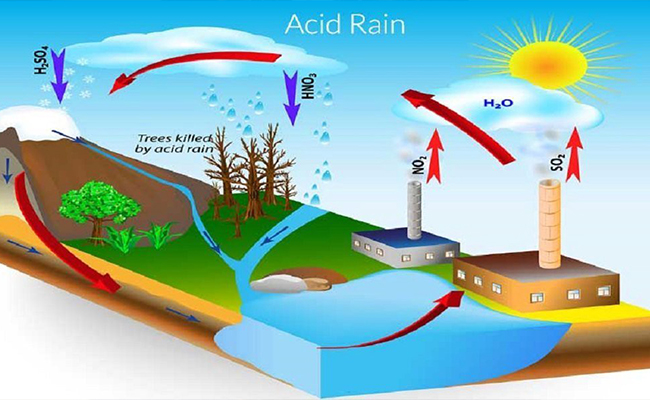
- Soil and Plants: Reduces soil pH → loss of nutrients → damage to vegetation.
- Water Bodies: Makes lakes and rivers acidic → harms aquatic life.
- Buildings and Monuments: Reacts with calcium carbonate in marble and limestone → erosion.
- Equation: \( \mathrm{CaCO_3 + H_2SO_4 \rightarrow CaSO_4 + H_2O + CO_2} \)
On Human Health:
- Causes respiratory problems like asthma and bronchitis.
- Contaminates drinking water sources.
- Indirectly affects food chains through soil and water acidity.
Air Pollution and Related Problems
- Smog (Smoke + Fog): Formed when pollutants mix with fog and sunlight — especially in urban areas.
- Particulate Matter (PM₂.₅, PM₁₀): Tiny particles that damage lungs and heart.
- Ozone (O₃): At ground level, it’s a pollutant causing breathing problems.
Control and Prevention of Acid Rain and Air Pollution
- Use of low-sulfur fuels or desulfurized fuels.
- Installation of scrubbers and electrostatic precipitators in factories to remove SO₂ and dust.
- Use of catalytic converters in vehicles to reduce NOₓ emissions.
- Switch to renewable energy sources (wind, solar, hydroelectric).
- Promote reforestation to absorb CO₂ and balance air composition.
Example
Which gases are mainly responsible for acid rain and how are they produced?
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: Sulfur dioxide (SO₂) is produced by burning coal and oil containing sulfur.
Step 2: Nitrogen oxides (NOₓ) are formed in vehicle engines at high temperatures.
Final Answer: SO₂ and NOₓ are the main acid rain gases — produced from fuel combustion and vehicles.
Example
Explain why marble buildings and statues are damaged by acid rain.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: Marble is made of calcium carbonate (CaCO₃).
Step 2: Acid rain contains sulfuric and nitric acids.
Step 3: \( \mathrm{CaCO_3 + H_2SO_4 \rightarrow CaSO_4 + H_2O + CO_2} \)
Final Answer: The acid reacts with marble, forming calcium sulfate, which washes away — eroding the surface.
Example
Suggest and explain three measures that governments can take to reduce acid rain formation.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: Enforce laws limiting sulfur emissions from industries.
Step 2: Encourage the use of renewable energy (solar, wind) instead of coal.
Step 3: Install scrubbers and catalytic converters to reduce SO₂ and NOₓ emissions.
Final Answer: Legislation, clean energy adoption, and emission control technologies reduce acid rain effectively.
