IB MYP 4-5 Chemistry -Atoms, elements, and compounds- Study Notes - New Syllabus
IB MYP 4-5 Chemistry -Atoms, elements, and compounds- Study Notes
Key Concepts
- Atoms, Elements, and Compounds
Atoms, Elements, and Compounds
Atoms, Elements, and Compounds
All matter around us is made of tiny particles called atoms. When these atoms combine in different ways, they form elements and compounds. Understanding these basic units helps explain the composition and behavior of all substances.
Atoms![]()
An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains its chemical properties. Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter and cannot be broken down further by ordinary chemical means.
Structure of an Atom
- Atoms consist of three main subatomic particles — protons, neutrons, and electrons.
| Particle | Symbol | Charge | Relative Mass | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proton | \( \mathrm{p^+} \) | +1 | 1 | Nucleus |
| Neutron | \( \mathrm{n^0} \) | 0 | 1 | Nucleus |
| Electron | \( \mathrm{e^-} \) | −1 | 1/1836 (very small) | Electron shells around nucleus |
Key Points
- The nucleus (center) contains protons and neutrons — it is dense and positively charged.
- Electrons move around the nucleus in energy levels (shells).
- Atoms are electrically neutral because they have equal numbers of protons and electrons.
Atomic Number and Mass Number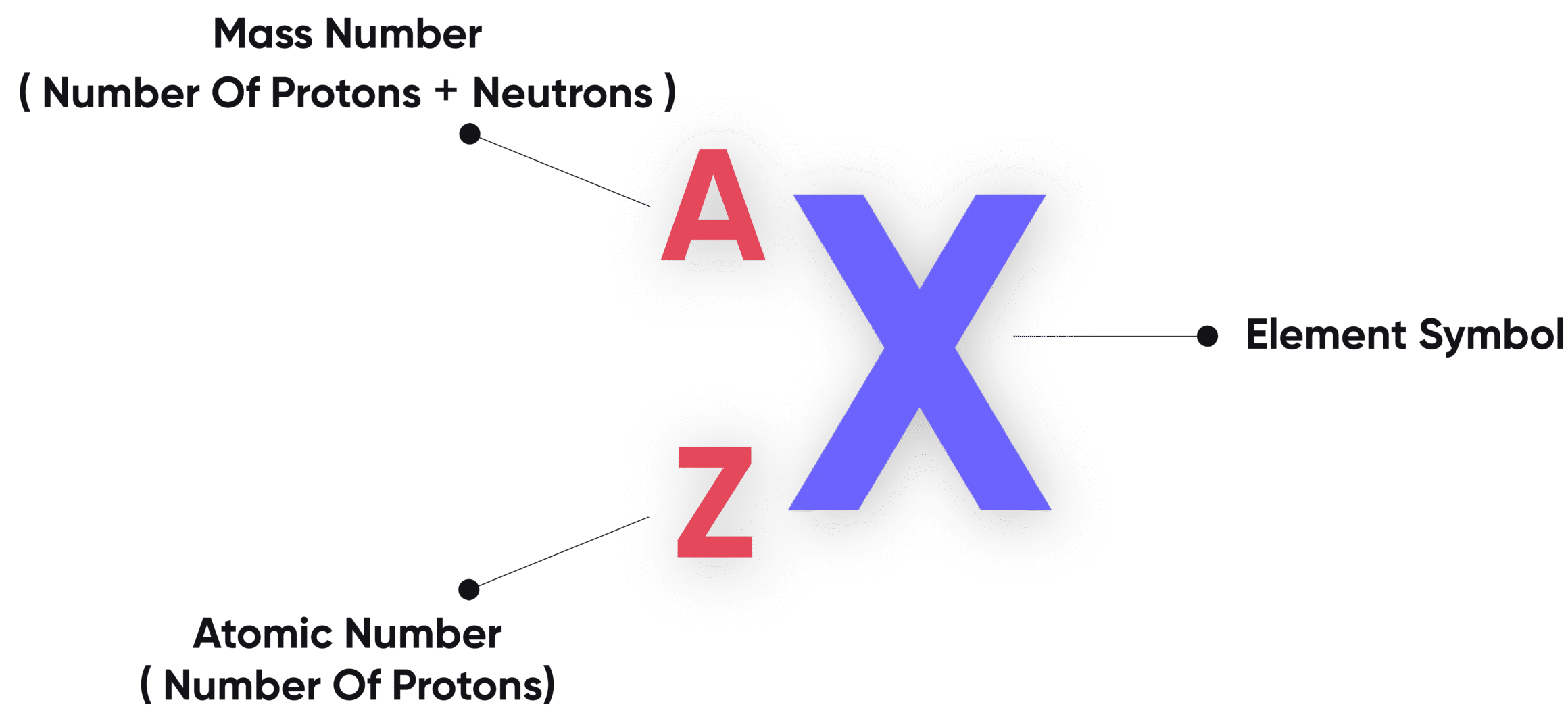
- Atomic Number (Z): Number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
- Mass Number (A): Total number of protons and neutrons in the atom’s nucleus.
\( \mathrm{A = Z + N} \), where \( \mathrm{N} \) = number of neutrons
Example: For carbon, \( \mathrm{^{12}_6C} \):
- \( \mathrm{Z = 6} \) → 6 protons
- \( \mathrm{A = 12} \) → 6 protons + 6 neutrons
Elements
An element is a pure substance made up of only one type of atom. It cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means.
![]()
- Each element is represented by a unique chemical symbol (e.g., H for hydrogen, O for oxygen).
- There are over 100 known elements arranged in the Periodic Table.
Examples:
- Hydrogen (\( \mathrm{H} \))
- Oxygen (\( \mathrm{O} \))
- Iron (\( \mathrm{Fe} \))
- Carbon (\( \mathrm{C} \))
Types of Elements
| Type | Properties | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Metals | Good conductors, shiny, malleable, form positive ions | Iron, Copper, Aluminium |
| Non-metals | Poor conductors, dull, brittle, form negative ions | Oxygen, Sulfur, Carbon |
| Metalloids | Have properties of both metals and non-metals | Silicon, Boron |
Compounds
A compound is a substance formed when two or more elements chemically combine in a fixed ratio. The resulting compound has properties different from the elements that form it.
![]()
- Formed by chemical bonds (ionic, covalent, or metallic).
- Cannot be separated by physical means.
- Have fixed composition and definite chemical formulae.
Examples:
- Water (\( \mathrm{H_2O} \)) — hydrogen and oxygen
- Carbon dioxide (\( \mathrm{CO_2} \)) — carbon and oxygen
- Sodium chloride (\( \mathrm{NaCl} \)) — sodium and chlorine
Differences Between Elements and Compounds
| Property | Element | Compound |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Single type of atom | Two or more elements chemically combined |
| Separation | Cannot be broken down chemically | Can be broken into elements by chemical reactions |
| Properties | Same as atoms forming it | Different from properties of constituent elements |
| Examples | Iron (Fe), Oxygen (O₂) | Water (H₂O), Carbon dioxide (CO₂) |
Key Note

- Atom: Smallest particle of matter that retains chemical properties.
- Element: Pure substance made of one kind of atom.
- Compound: Substance formed by chemical combination of two or more elements in fixed ratios.
- Elements combine through chemical bonds to form compounds with new properties.
Example :
Explain why water (H₂O) is a compound and not an element.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: Water is made up of two elements — hydrogen and oxygen.
Step 2: These elements are chemically combined in a fixed ratio of 2:1.
Step 3: The properties of water are completely different from those of hydrogen and oxygen.
Final Answer: Hence, water is a compound, not an element.
Example:
Carbon dioxide consists of 27.3% carbon and 72.7% oxygen by mass. Why is this percentage always the same for any sample of carbon dioxide?
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: Compounds have a fixed composition by mass.
Step 2: In carbon dioxide, one carbon atom always combines with two oxygen atoms.
Step 3: This constant ratio follows the Law of Definite Proportions.
Final Answer: Every sample of CO₂ has the same composition because it is a compound with a fixed ratio of elements.
Example :
Compare the properties of sodium, chlorine, and sodium chloride. What does this reveal about compounds?
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: Sodium is a soft, highly reactive metal; chlorine is a poisonous green gas.
Step 2: When they chemically combine, they form sodium chloride — a white, non-toxic solid used as table salt.
Step 3: The new substance has properties completely different from its elements.
Final Answer: This shows that compounds have new properties distinct from the elements that form them.
