IB MYP 4-5 Chemistry -Combustion of fuels and pollutant formation- Study Notes - New Syllabus
IB MYP 4-5 Chemistry -Combustion of fuels and pollutant formation- Study Notes
Key Concepts
- Combustion of Fuels and Pollutant Formation
Combustion of Fuels and Pollutant Formation
Combustion of Fuels and Pollutant Formation
Combustion is a chemical reaction in which a fuel reacts with oxygen to produce heat and light energy. It is an exothermic reaction, releasing energy that can be used for heating, transport, and power generation.
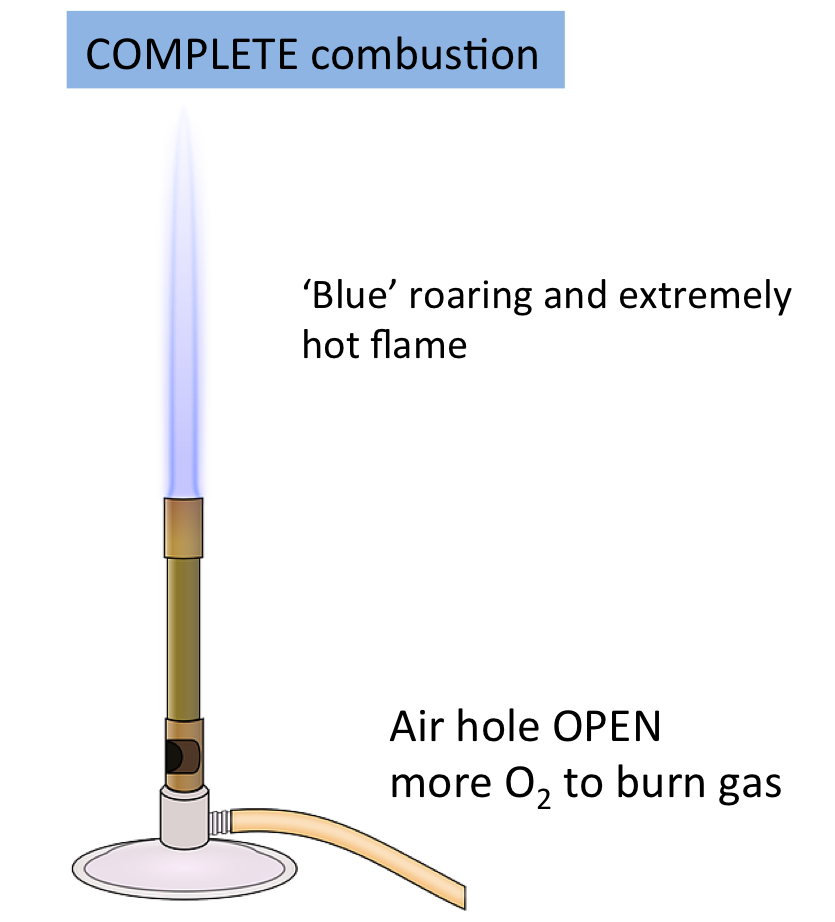
Types of Combustion
Combustion can be classified based on the availability of oxygen:
| Type of Combustion | Oxygen Supply | Main Products | Example Reaction |
|---|---|---|---|
Complete Combustion | Plentiful oxygen | Carbon dioxide and water | \( \mathrm{CH_4 + 2O_2 \rightarrow CO_2 + 2H_2O} \) |
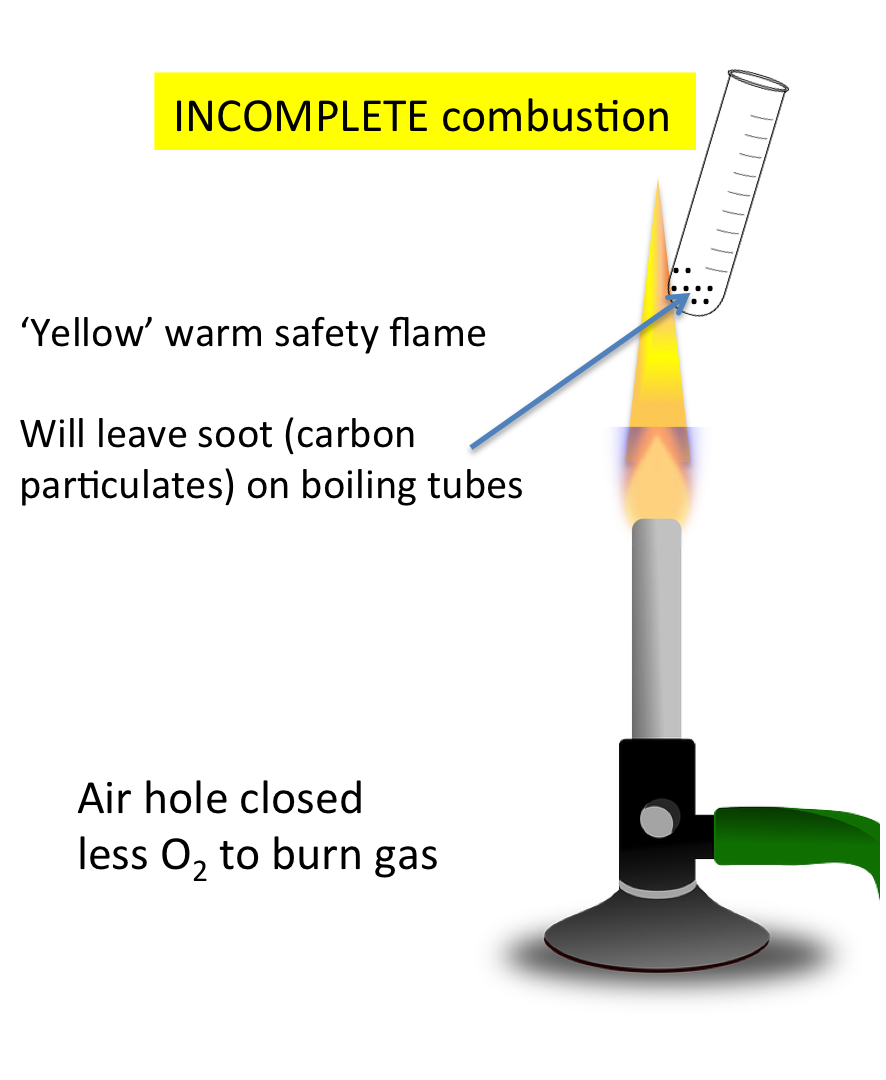
Incomplete Combustion | Limited oxygen | Carbon monoxide, carbon (soot), and water | \( \mathrm{2CH_4 + 3O_2 \rightarrow 2CO + 4H_2O} \) |
Fuels and Their Combustion
Fuels are substances that release energy when burned. Common examples include hydrocarbons such as methane, petrol, diesel, and coal.
- Hydrocarbon fuels: Contain only carbon (C) and hydrogen (H).
- Products: Carbon dioxide (\( \mathrm{CO_2} \)) and water (\( \mathrm{H_2O} \)) during complete combustion.
General Equation for Complete Combustion of a Hydrocarbon:
\( \mathrm{C_{x}H_{y} + (x + \frac{y}{4})O_{2} \rightarrow xCO_{2} + \frac{y}{2}H_{2}O} \)
Incomplete Combustion and Pollutant Formation
When there is insufficient oxygen, incomplete combustion occurs, producing harmful pollutants:
- Carbon monoxide (CO): Poisonous gas that binds to haemoglobin in blood, reducing oxygen transport.
- Carbon (C or soot): Tiny black particles causing respiratory issues and dirty surfaces.
- Unburnt hydrocarbons: Contribute to smog and air pollution.
Example (Incomplete Combustion of Methane): 
\( \mathrm{2CH_4 + 3O_2 \rightarrow 2CO + 4H_2O} \)
or \( \mathrm{CH_4 + O_2 \rightarrow C + 2H_2O} \)
Formation of Other Pollutants During Combustion
Besides CO and soot, other harmful gases form during fuel combustion:
- Nitrogen oxides (NO and NO₂): Formed when nitrogen and oxygen react at high temperatures in car engines.
- Sulfur dioxide (SO₂): Produced when sulfur-containing fuels (coal, oil) are burned.
- Carbon dioxide (CO₂): Non-toxic but contributes to the greenhouse effect and global warming.
Equations:
\( \mathrm{N_2 + O_2 \rightarrow 2NO} \)
\( \mathrm{S + O_2 \rightarrow SO_2} \)
Environmental Impact of Pollutants
| Pollutant | Source | Effect on Health/Environment | Control Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon monoxide (CO) | Incomplete combustion | Toxic; reduces oxygen transport in blood | Use catalytic converters in vehicles |
| Sulfur dioxide (SO₂) | Sulfur impurities in fuels | Causes acid rain, respiratory issues | Use low-sulfur fuels; flue gas desulfurization |
| Nitrogen oxides (NOₓ) | High-temperature engine combustion | Causes smog and acid rain | Catalytic converters; engine design control |
| Unburnt hydrocarbons | Incomplete combustion of petrol/diesel | Form photochemical smog; harmful to lungs | Efficient engine maintenance |
Prevention and Control of Pollution from Combustion
- Use catalytic converters in vehicles to remove CO, NOₓ, and hydrocarbons.
- Switch to clean fuels like natural gas, biogas, and hydrogen.
- Use low-sulfur fuels to reduce SO₂ emissions.
- Promote complete combustion by ensuring proper air supply.
Example
Write the balanced equation for the complete combustion of propane (\( \mathrm{C_3H_8} \)).
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: In complete combustion, products are \( \mathrm{CO_2} \) and \( \mathrm{H_2O} \).
Step 2: \( \mathrm{C_3H_8 + 5O_2 \rightarrow 3CO_2 + 4H_2O} \)
Final Answer: Propane burns completely to form carbon dioxide and water.
Example
What pollutant forms if there is insufficient oxygen during the combustion of methane, and why is it dangerous?
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: In limited oxygen, incomplete combustion produces carbon monoxide.
Equation: \( \mathrm{2CH_4 + 3O_2 \rightarrow 2CO + 4H_2O} \)
Step 2: CO is a toxic gas that binds to haemoglobin more strongly than oxygen.
Final Answer: Carbon monoxide forms; it is dangerous because it reduces oxygen transport in blood.
Example
Explain how the combustion of fossil fuels contributes to both acid rain and global warming.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: Fossil fuels contain sulfur compounds that form \( \mathrm{SO_2} \), which reacts with water to produce sulfuric acid — a cause of acid rain.
Equation: \( \mathrm{SO_2 + H_2O + \frac{1}{2}O_2 \rightarrow H_2SO_4} \)
Step 2: Combustion also releases \( \mathrm{CO_2} \), a greenhouse gas that traps heat in the atmosphere.
Final Answer: Combustion leads to acid rain (via \( \mathrm{SO_2} \)) and global warming (via \( \mathrm{CO_2} \)).