IB MYP 4-5 Chemistry -Composition of the atmosphere- Study Notes - New Syllabus
IB MYP 4-5 Chemistry -Composition of the atmosphere- Study Notes
Key Concepts
- Composition of the Atmosphere
Composition of the Atmosphere
Composition of the Atmosphere
The atmosphere is the mixture of gases that surrounds the Earth. It extends several hundred kilometers above the surface and is essential for life, climate regulation, and protection from harmful solar radiation.
Major Components of the Atmosphere
The Earth’s atmosphere is composed mainly of nitrogen, oxygen, and trace gases. These gases are mixed together to form a stable composition in the lower atmosphere (the troposphere).
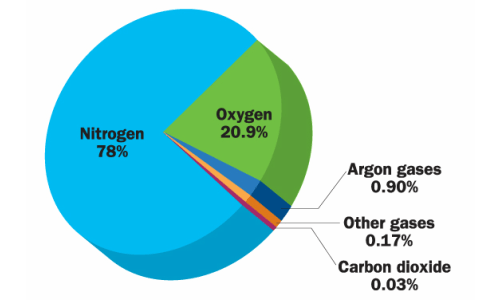
Approximate Composition by Volume:
| Gas | Symbol | Percentage by Volume (%) | Role / Importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen | \( \mathrm{N_2} \) | 78% | Maintains balance; inert gas that dilutes oxygen and prevents rapid burning. |
| Oxygen | \( \mathrm{O_2} \) | 21% | Supports respiration and combustion. |
| Argon | \( \mathrm{Ar} \) | 0.93% | Inert noble gas used in light bulbs and welding. |
| Carbon Dioxide | \( \mathrm{CO_2} \) | 0.04% | Used by plants for photosynthesis; contributes to greenhouse effect. |
| Water Vapour | \( \mathrm{H_2O (g)} \) | Variable (0–4%) | Important for weather, humidity, and cloud formation. |
| Ozone | \( \mathrm{O_3} \) | Trace | Absorbs harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation in the stratosphere. |
Layers of the Atmosphere (Overview)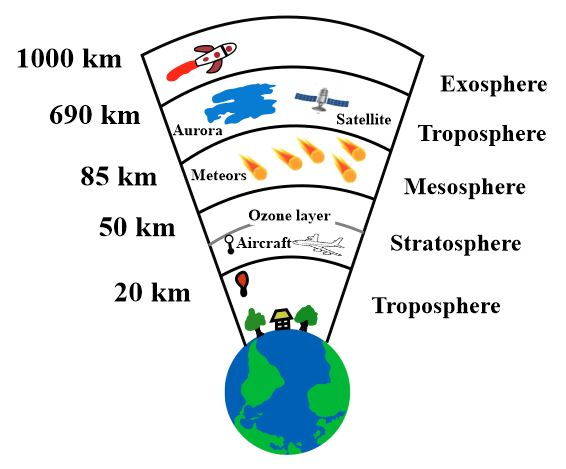
The atmosphere is divided into layers based on temperature changes:
- Troposphere: Closest to Earth; contains most air and weather phenomena.
- Stratosphere: Contains ozone layer; absorbs UV radiation.
- Mesosphere: Meteors burn here.
- Thermosphere: Very high temperature; auroras occur.
- Exosphere: Outermost layer; merges into space.
Importance of the Atmosphere
- Provides gases essential for life (oxygen and carbon dioxide).
- Protects from harmful UV rays via the ozone layer.
- Regulates temperature through greenhouse gases.
- Maintains pressure and supports weather systems.
Variation of Atmospheric Composition
The proportion of gases can vary slightly due to:
- Human activity: Combustion, deforestation, and industrial pollution increase \( \mathrm{CO_2} \) and other gases.
- Natural activity: Volcanic eruptions and respiration add \( \mathrm{CO_2} \), while photosynthesis removes it.
- Water vapour: Changes with weather, temperature, and altitude.
Greenhouse Gases and Climate
Greenhouse gases such as \( \mathrm{CO_2} \), \( \mathrm{CH_4} \), and water vapour trap heat in the atmosphere, maintaining Earth’s temperature. However, excess greenhouse gases cause global warming an enhanced greenhouse effect.
Equation (Photosynthesis):
\( \mathrm{6CO_2 + 6H_2O \xrightarrow{sunlight} C_6H_{12}O_6 + 6O_2} \)
Equation (Combustion of Fossil Fuels):
\( \mathrm{CH_4 + 2O_2 \rightarrow CO_2 + 2H_2O + Energy} \)
Summary Table: Major Gases and Functions
| Gas | Function |
|---|---|
| \( \mathrm{N_2} \) | Inert gas; prevents excessive combustion. |
| \( \mathrm{O_2} \) | Essential for respiration and burning. |
| \( \mathrm{CO_2} \) | Used in photosynthesis; traps heat in atmosphere. |
| \( \mathrm{O_3} \) | Absorbs harmful UV radiation. |
Example
Which two gases make up about 99% of the Earth’s atmosphere?
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: From composition, nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%) are the main gases.
Step 2: Combined, they make up about 99% of the atmosphere.
Final Answer: Nitrogen and oxygen.
Example
Explain why carbon dioxide is both essential and potentially harmful to life on Earth.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: Carbon dioxide is essential for photosynthesis, producing oxygen and food for living organisms.
Step 2: However, excessive \( \mathrm{CO_2} \) traps too much heat, leading to global warming and climate change.
Final Answer: \( \mathrm{CO_2} \) maintains life balance but excess levels disturb climate systems.
Example
How would the removal of the ozone layer affect living organisms on Earth? Explain scientifically.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: The ozone layer absorbs most ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun.
Step 2: Without ozone, higher levels of UV radiation would reach the surface.
Step 3: This would increase skin cancer, cataracts, and harm to crops and marine life.
Final Answer: The absence of the ozone layer would allow harmful UV rays to reach Earth, damaging living organisms and ecosystems.
