IB MYP 4-5 Chemistry -Esterification and naming esters- Study Notes - New Syllabus
IB MYP 4-5 Chemistry -Esterification and naming esters- Study Notes
Key Concepts
- Esters — Formation, Properties, and Uses (Esterification and Naming)
Esters — Formation, Properties, and Uses (Esterification and Naming)
Esters — Formation, Properties, and Uses (Esterification and Naming)
Esters are organic compounds formed by the chemical reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol, producing an ester and water. This reaction is called esterification.
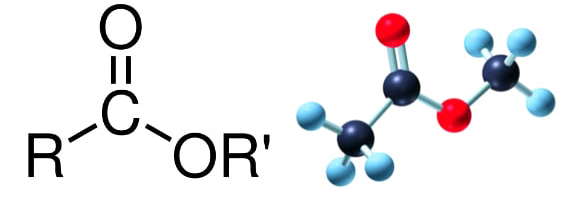
General Formula: \( \mathrm{RCOOR’} \)
- \( \mathrm{R} \) = alkyl or aryl group from the acid
- \( \mathrm{R’} \) = alkyl group from the alcohol
Functional Group: –COO– (Ester linkage)
Structure and Formation of Esters (Esterification Reaction)
Esters are formed when a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid (\( \mathrm{H_2SO_4} \)) as a catalyst.
\( \mathrm{Carboxylic\ Acid + Alcohol \xrightarrow{conc.\ H_2SO_4} Ester + Water} \)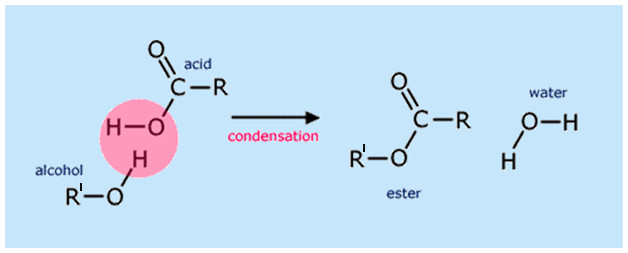
Example:
\( \mathrm{CH_3COOH + C_2H_5OH \xrightarrow{conc.\ H_2SO_4} CH_3COOC_2H_5 + H_2O} \)
Ethanoic acid + Ethanol → Ethyl ethanoate + Water
- The reaction is reversible and typically carried out by heating under reflux conditions.
- Concentrated sulfuric acid acts as a catalyst and a dehydrating agent.
Naming of Esters
Esters are named in two parts — from the alcohol and from the acid:

- The first part (prefix) comes from the alcohol → replace “-anol” with “-yl”.
- The second part (suffix) comes from the acid → replace “-ic acid” with “-oate”.
Examples:
| Carboxylic Acid | Alcohol | Ester Formed | Name of Ester |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ethanoic acid | Ethanol | \( \mathrm{CH_3COOC_2H_5} \) | Ethyl ethanoate |
| Methanoic acid | Propanol | \( \mathrm{HCOOC_3H_7} \) | Propyl methanoate |
| Butanoic acid | Methanol | \( \mathrm{C_3H_7COOCH_3} \) | Methyl butanoate |
Physical Properties of Esters
- Pleasant, fruity smell (used in perfumes and flavorings).
- Volatile liquids with lower boiling points than corresponding acids or alcohols (no hydrogen bonding between molecules).
- Sparingly soluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
Chemical Properties of Esters
- (a) Hydrolysis (Reverse of Esterification): Esters can be broken down into their parent acid and alcohol by heating with an acid or alkali.
Acid Hydrolysis:
\( \mathrm{CH_3COOC_2H_5 + H_2O \xrightarrow{H^+} CH_3COOH + C_2H_5OH} \)
Alkaline Hydrolysis (Saponification):
\( \mathrm{CH_3COOC_2H_5 + NaOH \rightarrow CH_3COONa + C_2H_5OH} \)
- (b) Combustion: Esters burn in air to form \( \mathrm{CO_2} \) and \( \mathrm{H_2O} \), releasing energy.
Uses of Esters
- Used as solvents in paints, varnishes, and adhesives.
- Used in perfumes, artificial flavors, and food essences due to their fruity smell.
- Used in the manufacture of plastics, detergents, and synthetic fibers (e.g., polyester).
- Used in pharmaceuticals and as intermediates in chemical synthesis.
Comparison Between Alcohols, Acids, and Esters
| Property | Alcohol | Carboxylic Acid | Ester |
|---|---|---|---|
| Functional Group | –OH | –COOH | –COO– |
| Nature | Neutral | Acidic | Neutral |
| Odor | Mild | Pungent | Fruity |
| Reaction with Na₂CO₃ | No reaction | Releases CO₂ gas | No reaction |
Example
Write the chemical equation for the formation of ethyl ethanoate from ethanol and ethanoic acid.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: Identify the reactants — ethanol and ethanoic acid.
Step 2: Write the reaction:
\( \mathrm{CH_3COOH + C_2H_5OH \xrightarrow{conc.\ H_2SO_4} CH_3COOC_2H_5 + H_2O} \)
Final Answer: Ethyl ethanoate and water are formed.
Example
How would you name the ester formed from methanol and propanoic acid?
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: The alcohol part is methanol → gives the prefix “methyl”.
Step 2: The acid part is propanoic acid → gives the suffix “propanoate”.
Step 3: Combine both names → Methyl propanoate.
Final Answer: The ester is called methyl propanoate.
Example
Ethyl ethanoate undergoes hydrolysis in an alkaline medium. Write the balanced chemical equation and name the products formed.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: Alkaline hydrolysis (saponification) reaction:
\( \mathrm{CH_3COOC_2H_5 + NaOH \rightarrow CH_3COONa + C_2H_5OH} \)
Step 2: Products are sodium ethanoate and ethanol.
Final Answer: On hydrolysis, ethyl ethanoate forms sodium ethanoate and ethanol.
