IB MYP 4-5 Chemistry -Greenhouse gases and global warming- Study Notes - New Syllabus
IB MYP 4-5 Chemistry -Greenhouse gases and global warming- Study Notes
Key Concepts
- Greenhouse Gases and Global Warming
Greenhouse Gases and Global Warming
Greenhouse Gases and Global Warming
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are gases in the Earth’s atmosphere that trap heat and keep the planet warm enough to support life. However, an excess of these gases causes global warming the gradual increase in Earth’s average surface temperature due to the enhanced greenhouse effect.
The Greenhouse Effect
The greenhouse effect is the natural process by which certain gases trap heat in the atmosphere, preventing it from escaping into space.
Process:
- Solar radiation (shortwave energy) from the Sun passes through the atmosphere and warms the Earth’s surface.
- The Earth emits this energy as infrared radiation (longwave).
- Greenhouse gases absorb and re-radiate some of this heat back to the surface, maintaining a suitable temperature for life.
Without this effect, Earth’s average temperature would be about -18°C instead of +15°C.
Major Greenhouse Gases and Their Sources
| Greenhouse Gas | Chemical Formula | Main Sources | Approximate Contribution (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Dioxide | \( \mathrm{CO_2} \) | Burning fossil fuels, deforestation, industrial processes | 60% |
| Methane | \( \mathrm{CH_4} \) | Cattle farming, rice fields, landfills, fossil fuel extraction | 20% |
| Nitrous Oxide | \( \mathrm{N_2O} \) | Fertilizers, animal waste, industrial emissions | 6% |
| Water Vapour | \( \mathrm{H_2O (g)} \) | Evaporation from oceans, lakes, and rivers | Varies (natural feedback) |
| Ozone | \( \mathrm{O_3} \) | Photochemical reactions in the atmosphere | Small but significant |
| Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) | \( \mathrm{CFCl_3, CF_2Cl_2} \) | Aerosols, refrigeration, foam manufacturing | Less than 1%, but very strong heat-trapping effect |
The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect
The enhanced greenhouse effect occurs when human activities increase the concentration of greenhouse gases, trapping more heat and causing a rise in global temperatures.
![]()
Major Causes:
- Burning fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas)
- Deforestation (reduces \( \mathrm{CO_2} \) absorption by plants)
- Industrial emissions and agriculture
- Landfills releasing methane
Effects of Global Warming
Environmental Effects: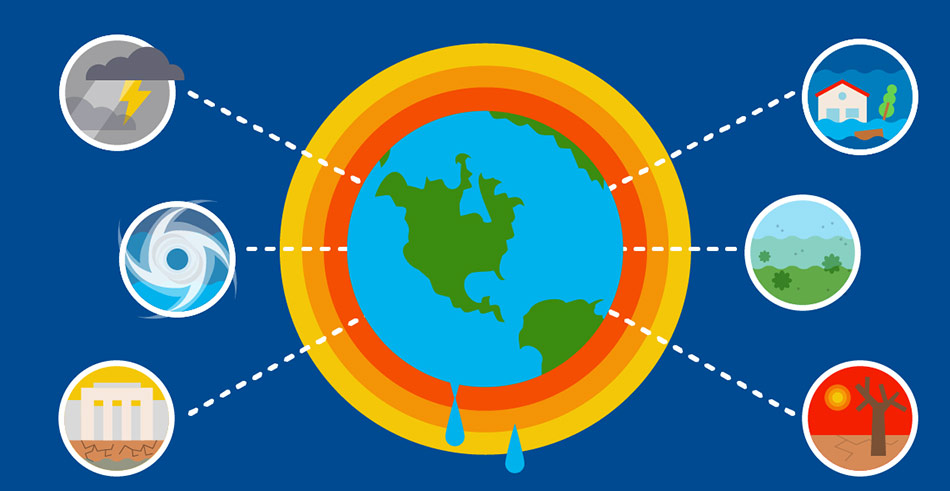
- Melting of glaciers and polar ice caps → rising sea levels
- Increased frequency of floods, droughts, and heatwaves
- Disturbance of ecosystems and loss of biodiversity
- Ocean acidification due to \( \mathrm{CO_2} \) absorption
Human and Economic Effects:
- Reduced crop yield and food security
- Spread of vector-borne diseases (e.g., malaria)
- Damage to infrastructure due to extreme weather
- Increased energy demand for cooling
Equations Involving Greenhouse Gases
Combustion (CO₂ release):
\( \mathrm{CH_{4} + 2O_{2} \rightarrow CO_{2} + 2H_{2}O + Energy} \)
Photosynthesis (CO₂ removal):
\( \mathrm{6CO_{2} + 6H_{2}O \xrightarrow{sunlight} C_{6}H_{12}O_{6} + 6O_{2}} \)
Decomposition / Methane formation:
\( \mathrm{C + 2H_2 \rightarrow CH_4} \)
Methods to Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions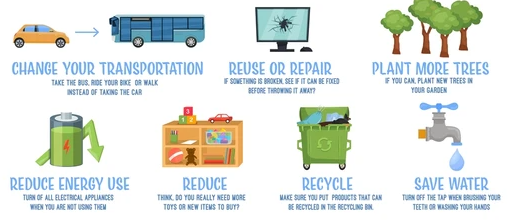
- Switch to renewable energy: Solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal power.
- Energy efficiency: Reduce fossil fuel use in transportation and industry.
- Afforestation: Plant more trees to absorb \( \mathrm{CO_2} \).
- Carbon capture and storage (CCS): Trap and store \( \mathrm{CO_2} \) emissions underground.
- Reduce waste and recycling: Less landfill methane production.
Example
Name two major greenhouse gases and their sources.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: \( \mathrm{CO_2} \) — formed from burning fossil fuels and deforestation.
Step 2: \( \mathrm{CH_4} \) — released from cattle farming and landfills.
Final Answer: Carbon dioxide (energy use) and methane (agriculture and waste) are major greenhouse gases.
Example
Explain how deforestation contributes to global warming.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: Trees absorb \( \mathrm{CO_2} \) during photosynthesis.
Step 2: Cutting trees reduces \( \mathrm{CO_2} \) absorption.
Step 3: Burning or decay of trees releases stored carbon back as \( \mathrm{CO_2} \).
Final Answer: Deforestation increases atmospheric \( \mathrm{CO_2} \), enhancing the greenhouse effect and causing warming.
Example
Discuss how the increased concentration of greenhouse gases affects global climate patterns.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: Higher GHG concentrations trap more heat in the atmosphere.
Step 2: This causes uneven heating → changes in wind patterns, rainfall, and ocean currents.
Step 3: Leads to extreme weather events, melting glaciers, and sea-level rise.
Final Answer: Increasing greenhouse gases disturb natural climate systems, leading to global climate change and environmental instability.
