IB MYP 4-5 Chemistry -Indicators and the pH scale- Study Notes - New Syllabus
IB MYP 4-5 Chemistry -Indicators and the pH scale- Study Notes
Key Concepts
- Indicators and the pH Scale
Indicators and the pH Scale
Indicators and the pH Scale
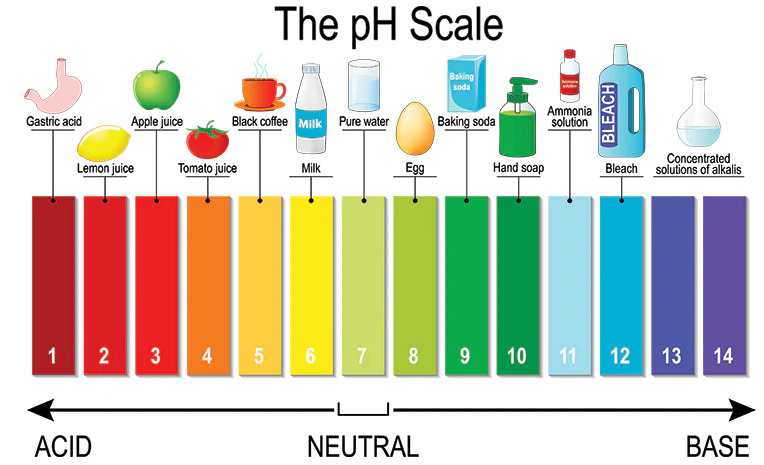
The pH scale is a numerical scale used to indicate how acidic or basic a solution is. It measures the concentration of hydrogen ions (H⁺) present in a solution.
\( \mathrm{pH = -\log[H^+]} \)
Key Idea: The pH scale helps classify substances as acidic, neutral, or basic (alkaline) and can be measured using various indicators.
The pH Scale![]()
The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14:
- pH < 7 → Acidic solution (high \( \mathrm{[H^+]} \))
- pH = 7 → Neutral solution (pure water)
- pH > 7 → Basic solution (low \( \mathrm{[H^+]} \))
Relationship between [H⁺] and pH:
- As \( \mathrm{[H^+]} \) increases → pH decreases (more acidic).
- As \( \mathrm{[H^+]} \) decreases → pH increases (more basic).
Example: If \( \mathrm{[H^+]} = 1 \times 10^{-3}\, \mathrm{mol\,dm^{-3}} \), then \( \mathrm{pH = -\log(10^{-3}) = 3} \) → acidic solution.
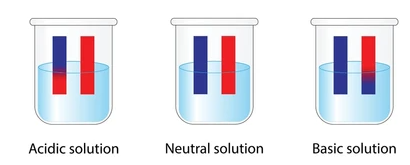
Indicators
An indicator is a substance that changes color depending on the pH of the solution it is in. Indicators help identify whether a solution is acidic, neutral, or basic.
Common Indicators and Their Color Changes
| Indicator | In Acidic Solution | In Basic Solution | Approximate pH Range |
|---|---|---|---|
Litmus | Red | Blue | 5 – 8 |
Phenolphthalein | Colorless | Pink | 8.2 – 10 |
Methyl Orange | Red | Yellow | 3.1 – 4.4 |
Universal Indicator | Red to Orange | Blue to Purple | 0 – 14 |
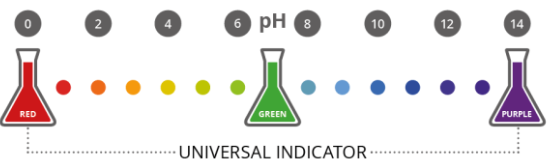
Universal Indicator and Color Chart
The universal indicator is a mixture of several indicators. It gives a range of colors that correspond to pH values, allowing more precise estimation of pH.
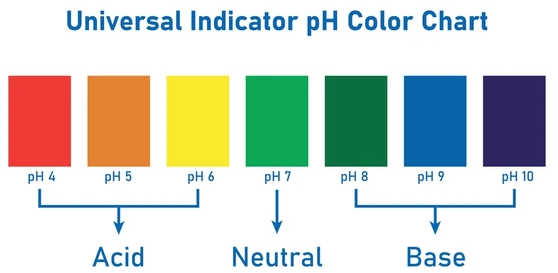
| pH Range | Type of Solution | Color (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 – 2 | Strong Acid | Red |
| 3 – 6 | Weak Acid | Orange / Yellow |
| 7 | Neutral | Green |
| 8 – 10 | Weak Base | Blue |
| 11 – 14 | Strong Base | Purple / Violet |
Measuring pH
- Indicators: Give approximate pH by color comparison.
- pH Paper: Universal indicator impregnated paper that changes color.
- pH Meter: Digital instrument that provides accurate numerical pH readings.
Everyday Examples of pH
| Substance | Approx. pH | Nature |
|---|---|---|
| Lemon juice | 2 | Strong acid |
| Vinegar | 3 | Weak acid |
| Pure water | 7 | Neutral |
| Soap solution | 9 | Weak base |
| Bleach | 12 | Strong base |
Example
A student dips red and blue litmus papers into a solution. Both papers remain unchanged. What is the likely pH of the solution?
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: If neither red nor blue litmus changes color, the solution is neutral.
Step 2: pH = 7 indicates neutrality.
Final Answer: The solution is neutral with pH ≈ 7 (like pure water).
Example
The pH of a solution is 4. How does its hydrogen ion concentration compare with a solution of pH 6?
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: Each decrease of 1 pH unit = 10× increase in \( \mathrm{[H^+]} \).
Step 2: Difference = 2 pH units → \( 10^2 = 100× \) more \( \mathrm{H^+} \).
Final Answer: The pH 4 solution is 100 times more acidic than pH 6 solution.
Example
A laboratory technician measures the pH of a solution as 9. What will be the color of phenolphthalein and methyl orange in this solution?
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: pH = 9 → basic solution.
Step 2: Phenolphthalein → turns pink in basic solutions.
Step 3: Methyl orange → turns yellow in basic solutions.
Final Answer: Phenolphthalein → pink; Methyl orange → yellow.