IB MYP 4-5 Chemistry -Neutralisation reactions- Study Notes - New Syllabus
IB MYP 4-5 Chemistry -Neutralisation reactions- Study Notes
Key Concepts
- Neutralization Reactions and Their Applications
Neutralization Reactions and Their Applications
Neutralization Reactions and Their Applications
A neutralization reaction is a chemical reaction in which an acid reacts with a base (alkali) to form a salt and water. It is an example of a double displacement reaction.
\( \mathrm{Acid + Base \rightarrow Salt + Water} \)
During neutralization, the hydrogen ions \( \mathrm{(H^+)} \) from the acid combine with hydroxide ions \( \mathrm{(OH^-)} \) from the base to form water.
\( \mathrm{H^+ + OH^- \rightarrow H_2O} \)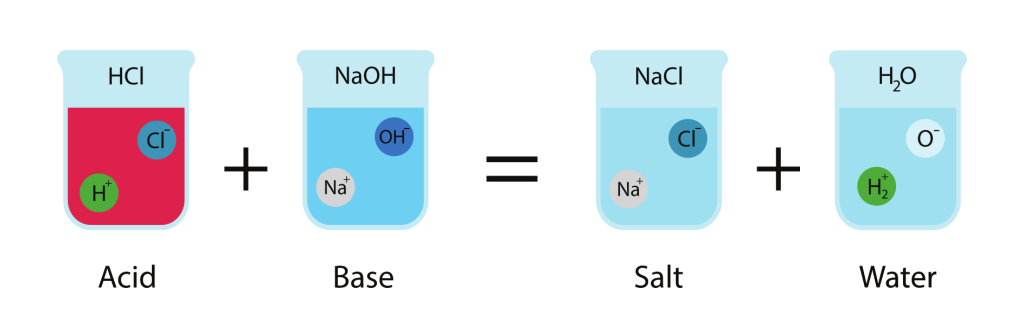
Characteristics of Neutralization
- The resulting solution is closer to neutral pH (≈ 7).
- The reaction is often exothermic — heat is released.
- The product salt depends on the acid and base used.
Examples of Neutralization Reactions
| Acid | Base | Salt Formed | Equation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrochloric acid (\( \mathrm{HCl} \)) | Sodium hydroxide (\( \mathrm{NaOH} \)) | Sodium chloride (\( \mathrm{NaCl} \)) | \( \mathrm{HCl + NaOH \rightarrow NaCl + H_2O} \) |
| Sulfuric acid (\( \mathrm{H_2SO_4} \)) | Potassium hydroxide (\( \mathrm{KOH} \)) | Potassium sulfate (\( \mathrm{K_2SO_4} \)) | \( \mathrm{H_2SO_4 + 2KOH \rightarrow K_2SO_4 + 2H_2O} \) |
| Nitric acid (\( \mathrm{HNO_3} \)) | Calcium hydroxide (\( \mathrm{Ca(OH)_2} \)) | Calcium nitrate (\( \mathrm{Ca(NO_3)_2} \)) | \( \mathrm{2HNO_3 + Ca(OH)_2 \rightarrow Ca(NO_3)_2 + 2H_2O} \) |
Ionic Equation for Neutralization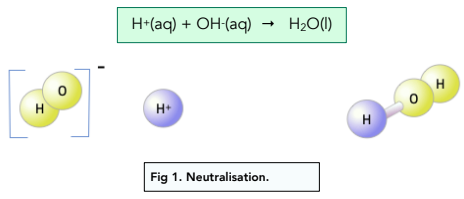
The essential reaction in all acid-base neutralizations is:
\( \mathrm{H^+(aq) + OH^-(aq) \rightarrow H_2O(l)} \)
This shows that water forms when hydrogen and hydroxide ions combine, and the remaining ions form the salt.
Applications of Neutralization in Daily Life
| Situation | Acid / Base Involved | Purpose of Neutralization |
|---|---|---|
| Indigestion relief (antacids) | Excess acid in stomach + weak base (Mg(OH)₂) | Neutralizes stomach acid and relieves discomfort |
| Soil treatment | Acidic soil + slaked lime (\( \mathrm{Ca(OH)_2} \)) | Neutralizes acidity to improve fertility |
| Treatment of acid burns | Acid spill + mild base (e.g., sodium bicarbonate) | Reduces corrosive effect of acid |
| Neutralizing factory waste | Acidic waste + alkali / basic waste + acid | Prevents environmental pollution |
| Bee sting vs. Wasp sting | Bee sting (acidic) → baking soda; Wasp sting (alkaline) → vinegar | Neutralizes the sting’s pH and reduces pain |
Energy Change During Neutralization
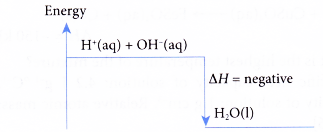
- Neutralization is usually exothermic it releases heat.
- Temperature of the solution rises slightly during the reaction.
- For strong acid–strong base reactions, the heat released per mole of water formed is nearly constant (~57 kJ/mol).
Example
Write the balanced chemical equation for the neutralization of hydrochloric acid with sodium hydroxide.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Equation: \( \mathrm{HCl + NaOH \rightarrow NaCl + H_2O} \)
Step 1: Acid provides \( \mathrm{H^+} \); base provides \( \mathrm{OH^-} \).
Step 2: \( \mathrm{H^+ + OH^- \rightarrow H_2O} \); remaining ions form salt (NaCl).
Final Answer: Sodium chloride and water are formed — neutralization reaction.
Example
Why is an antacid tablet taken after eating spicy or oily food?
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: Spicy or oily food increases hydrochloric acid in the stomach.
Step 2: Antacid tablets contain weak bases like \( \mathrm{Mg(OH)_2} \) or \( \mathrm{NaHCO_3} \).
Step 3: They neutralize excess acid:
\( \mathrm{Mg(OH)_2 + 2HCl \rightarrow MgCl_2 + 2H_2O} \)
Final Answer: Neutralization relieves acidity and heartburn by restoring stomach pH.
Example
Farmers find that continuous use of certain fertilizers makes the soil too acidic. How can this be corrected? Write a suitable equation.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: Acidic soil has excess \( \mathrm{H^+} \) ions from acid-forming fertilizers.
Step 2: Adding slaked lime (\( \mathrm{Ca(OH)_2} \)) neutralizes acidity:
\( \mathrm{2H^+ + Ca(OH)_2 \rightarrow Ca^{2+} + 2H_2O} \)
Final Answer: Lime neutralizes soil acids, improving fertility and crop yield.
