IB MYP 4-5 Chemistry -Preparing soluble and insoluble salts- Study Notes - New Syllabus
IB MYP 4-5 Chemistry -Preparing soluble and insoluble salts- Study Notes
Key Concepts
- Preparing Soluble and Insoluble Salts
Preparing Soluble and Insoluble Salts
Preparing Soluble and Insoluble Salts
A salt is an ionic compound formed when the hydrogen ions \( \mathrm{(H^+)} \) of an acid are replaced by metal ions or ammonium ions \( \mathrm{(NH_4^+)} \).
![]()
Salts can be soluble or insoluble in water. Different preparation methods are used depending on the solubility of the salt formed.
Solubility Rules for Common Salts
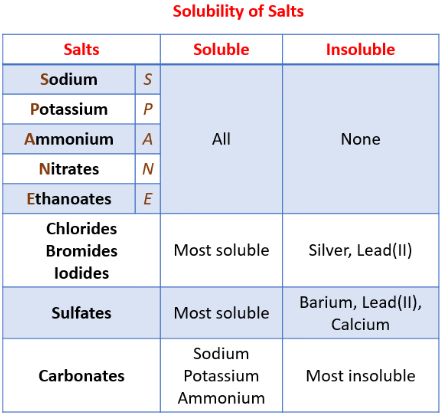
| Type of Salt | Solubility in Water |
|---|---|
| All nitrates (\( \mathrm{NO_3^-} \)) | Soluble |
| All sodium, potassium, ammonium salts | Soluble |
| Chlorides | Soluble (except \( \mathrm{AgCl, PbCl_2} \)) |
| Sulfates | Soluble (except \( \mathrm{BaSO_4, PbSO_4, CaSO_4} \)) |
| Carbonates | Insoluble (except \( \mathrm{Na_2CO_3, K_2CO_3, (NH_4)_2CO_3} \)) |
Methods for Preparing Soluble Salts
There are three main laboratory methods for preparing soluble salts, depending on the reactivity and solubility of reactants.
A. Acid + Metal Reaction (for soluble salts of reactive metals)
General Equation:
\( \mathrm{Acid + Metal \rightarrow Salt + Hydrogen\ gas} \)
Example: \( \mathrm{Zn + H_2SO_4 \rightarrow ZnSO_4 + H_2} \)
- Add excess metal to ensure all acid reacts.
- Filter out unreacted metal.
- Evaporate filtrate to obtain crystals.
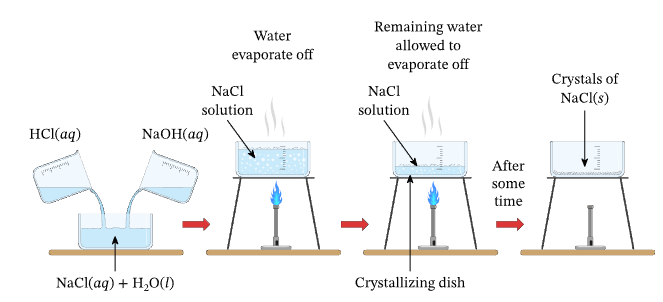
B. Acid + Base (or Alkali) Reaction (Neutralization)
General Equation:
\( \mathrm{Acid + Base \rightarrow Salt + Water} \)
Example: \( \mathrm{HCl + NaOH \rightarrow NaCl + H_2O} \)
- Use titration to find exact proportions when both reactants are soluble.
- Evaporate solution to crystallization point and cool to form crystals.
C. Acid + Carbonate Reaction (for insoluble bases that react slowly)
General Equation:
\( \mathrm{Acid + Carbonate \rightarrow Salt + Water + CO_2} \)
Example: \( \mathrm{CuCO_3 + 2HCl \rightarrow CuCl_2 + H_2O + CO_2} \)
- Add carbonate until no more effervescence occurs.
- Filter off unreacted solid.
- Evaporate filtrate slowly to obtain crystals.
Method for Preparing Insoluble Salts (Precipitation Method)
When two soluble salts are mixed and an insoluble salt (precipitate) forms, the reaction is called precipitation.
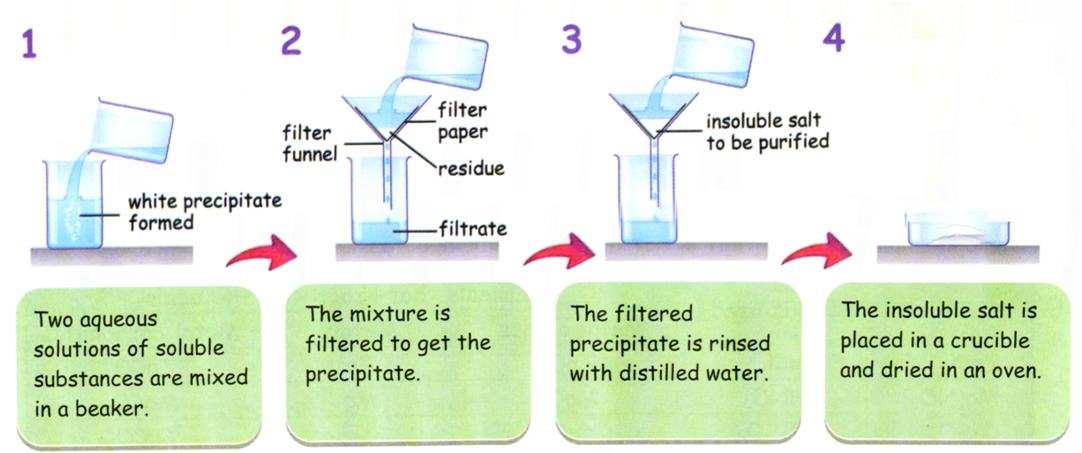
General Equation:
\( \mathrm{Solution\ A + Solution\ B \rightarrow Insoluble\ Salt + Soluble\ Salt} \)
Example: \( \mathrm{BaCl_2(aq) + Na_2SO_4(aq) \rightarrow BaSO_4(s) + 2NaCl(aq)} \)
- Mix two soluble salt solutions.
- Filter to separate the insoluble precipitate.
- Wash the precipitate with distilled water.
- Dry between filter papers or in a drying oven.
Choosing the Correct Method
| Type of Salt | Method of Preparation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Soluble salt (acid + insoluble base) | Add excess base, filter, evaporate, crystallize | \( \mathrm{CuO + H_2SO_4 \rightarrow CuSO_4 + H_2O} \) |
| Soluble salt (acid + alkali) | Titration (neutralization) | \( \mathrm{NaOH + HCl \rightarrow NaCl + H_2O} \) |
| Insoluble salt | Precipitation | \( \mathrm{Pb(NO_3)_2 + 2KI \rightarrow PbI_2 + 2KNO_3} \) |
Example
Describe how you would prepare a pure, dry sample of copper(II) sulfate crystals from copper(II) oxide.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: Add copper(II) oxide to warm dilute sulfuric acid until no more dissolves.
Step 2: Filter off excess black solid (CuO).
Step 3: Evaporate filtrate gently to crystallization point, then cool.
Equation: \( \mathrm{CuO + H_2SO_4 \rightarrow CuSO_4 + H_2O} \)
Final Answer: Blue crystals of copper(II) sulfate are obtained.
Example
Write the ionic equation for the formation of barium sulfate from barium chloride and sodium sulfate solutions, and describe how you would isolate the solid.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: \( \mathrm{BaCl_2(aq) + Na_2SO_4(aq) \rightarrow BaSO_4(s) + 2NaCl(aq)} \)
Ionic Equation: \( \mathrm{Ba^{2+}(aq) + SO_4^{2-}(aq) \rightarrow BaSO_4(s)} \)
Step 2: Filter off the white precipitate, wash with water, and dry between filter papers.
Final Answer: White barium sulfate precipitate is obtained.
Example
Explain how you could prepare pure ammonium nitrate crystals starting from ammonia solution and nitric acid.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: Both reactants are soluble — use titration method.
Equation: \( \mathrm{NH_3(aq) + HNO_3(aq) \rightarrow NH_4NO_3(aq)} \)
Step 2: Use an indicator (e.g., methyl orange) to find neutralization point.
Step 3: Repeat the reaction without indicator, then evaporate gently to form crystals.
Final Answer: Colorless ammonium nitrate crystals are obtained after crystallization.
