IB MYP 4-5 Chemistry -Properties of acids and bases- Study Notes - New Syllabus
IB MYP 4-5 Chemistry -Properties of acids and bases- Study Notes
Key Concepts
- Properties of Acids and Bases
Properties of Acids and Bases
Properties of Acids and Bases
Acids and bases are two broad classes of substances that show opposite chemical properties. They can be identified by their characteristic taste, pH, reactions, and ion formation in water.
Acids
An acid is a substance that produces hydrogen ions (H⁺) when dissolved in water.
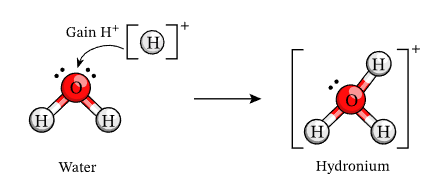
\( \mathrm{Acid \rightarrow H^+ + Anion^-} \)
Examples:
- \( \mathrm{HCl \rightarrow H^+ + Cl^-} \)
- \( \mathrm{H_2SO_4 \rightarrow 2H^+ + SO_4^{2-}} \)
- \( \mathrm{HNO_3 \rightarrow H^+ + NO_3^-} \)
General Properties of Acids:
- Have a sour taste (e.g., lemon juice, vinegar).
- Turn blue litmus red.
- React with metals to produce hydrogen gas: \( \mathrm{Zn + 2HCl \rightarrow ZnCl_2 + H_2} \)
- React with carbonates to produce carbon dioxide: \( \mathrm{CaCO_3 + 2HCl \rightarrow CaCl_2 + CO_2 + H_2O} \)
- Conduct electricity in aqueous solution (contain free ions).
Bases
A base is a substance that produces hydroxide ions (OH⁻) when dissolved in water.
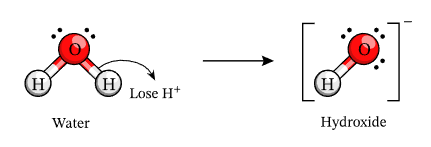
\( \mathrm{Base \rightarrow Cation^+ + OH^-} \)
Examples:
- \( \mathrm{NaOH \rightarrow Na^+ + OH^-} \)
- \( \mathrm{KOH \rightarrow K^+ + OH^-} \)
- \( \mathrm{Ca(OH)_2 \rightarrow Ca^{2+} + 2OH^-} \)
General Properties of Bases:
- Have a bitter taste and soapy feel.
- Turn red litmus blue.
- React with acids to form salt and water (neutralization): \( \mathrm{NaOH + HCl \rightarrow NaCl + H_2O} \)
- Can be corrosive and irritant (especially strong alkalis).
- Conduct electricity in aqueous solution (contain free ions).
Acids and Bases — Comparison Table
| Property | Acids | Bases |
|---|---|---|
| Ions Produced in Water | \( \mathrm{H^+} \) | \( \mathrm{OH^-} \) |
| Taste | Sour | Bitter |
| Effect on Litmus | Turns blue → red | Turns red → blue |
| Electrical Conductivity | Good (due to ions) | Good (due to ions) |
| Reaction with Metals | Produces hydrogen gas | Usually no reaction |
| Neutralization Reaction | React with bases to form salt and water | React with acids to form salt and water |
Strength of Acids and Bases (Qualitative)
- Strong acids: Completely ionize in water (e.g., \( \mathrm{HCl, HNO_3, H_2SO_4} \)).
- Weak acids: Partially ionize (e.g., \( \mathrm{CH_3COOH} \)).
- Strong bases: Completely dissociate (e.g., \( \mathrm{NaOH, KOH} \)).
- Weak bases: Partially dissociate (e.g., \( \mathrm{NH_3} \)).
pH Scale (Overview):
- Acidic → pH < 7
- Neutral → pH = 7
- Basic → pH > 7
Example
What happens when magnesium reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid?
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: Magnesium is a reactive metal that reacts with acids to form hydrogen gas.
Step 2: \( \mathrm{Mg + 2HCl \rightarrow MgCl_2 + H_2} \)
Final Answer: Hydrogen gas is evolved, and magnesium chloride solution is formed.
Example
What will happen when an acid reacts with a carbonate compound? Explain using an equation.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: Acids react with carbonates to produce salt, water, and carbon dioxide gas.
Step 2: Example: \( \mathrm{CaCO_3 + 2HCl \rightarrow CaCl_2 + CO_2 + H_2O} \)
Final Answer: Fizzing occurs due to CO₂ gas, confirming acidic nature.
Example
A student mixes equal volumes of 1 M \( \mathrm{NaOH} \) and 1 M \( \mathrm{HCl} \). Predict the products and describe the resulting solution.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: Reaction: \( \mathrm{NaOH + HCl \rightarrow NaCl + H_2O} \)
Step 2: Equal moles of acid and base neutralize each other completely.
Step 3: Resulting solution contains neutral salt (NaCl) and water.
Final Answer: pH = 7 (neutral solution).
