IB MYP 4-5 Physics- Applications of radioactivity: uses and dangers- Study Notes - New Syllabus
IB MYP 4-5 Physics-Applications of radioactivity: uses and dangers- Study Notes
Key Concepts
- Applications of radioactivity: uses and dangers
Applications of Radioactivity: Uses and Dangers
Uses of Radioactivity
Medical Applications
- Diagnosis (Tracers): Radioactive isotopes are injected into the body to trace biological processes (e.g., iodine-131 for thyroid function tests).
- Treatment (Radiotherapy): Gamma rays from isotopes like cobalt-60 are used to kill cancerous cells.
- Sterilization: Gamma rays are used to sterilize medical equipment by killing bacteria and pathogens.
Industrial Applications
- Thickness Gauging: Beta radiation is used to monitor the thickness of paper, metal sheets, or plastic films.
- Leak Detection: Radioactive tracers detect leaks in pipelines by checking for escaping radiation.
- Smoke Detectors: Americium-241 emits alpha particles, which ionize air in smoke detectors. Smoke particles interrupt this ionization and trigger the alarm.
Agricultural Applications
- Radiation is used to kill pests and insects in stored grains.
- Radioisotopes are used to study plant nutrient uptake.
Archaeological and Geological Applications
- Carbon Dating: Carbon-14 is used to determine the age of fossils and archaeological artifacts.
- Geological Dating: Uranium-238 and potassium-40 are used to find the age of rocks and minerals.
Dangers of Radioactivity

Health Hazards
- Exposure to radiation can damage living cells and DNA, leading to mutations, radiation sickness, or cancer.
- High doses can cause burns and organ failure.
Environmental Hazards
- Radioactive waste from nuclear reactors remains dangerous for thousands of years and needs secure storage.
- Nuclear accidents (e.g., Chernobyl, Fukushima) cause long-term contamination of land, water, and ecosystems.
Weapons Hazard
- Nuclear weapons release enormous energy, causing destruction, radiation poisoning, and long-lasting fallout.
Safety Precautions
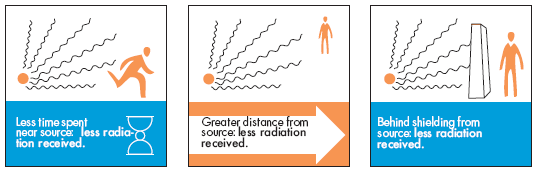
- Use shielding materials like lead or concrete to block radiation.
- Minimize exposure time and maximize distance from radioactive sources.
- Store radioactive materials in secure, shielded containers.
- Use protective clothing and monitoring devices when handling radiation.
Example:
A hospital uses cobalt-60 to treat a patient with a cancerous tumor. Explain how cobalt-60 helps in treatment, and state one possible risk of using this isotope.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Cobalt-60 emits gamma radiation, which penetrates the body and kills cancer cells by damaging their DNA, preventing them from dividing.
Risk: Healthy cells near the tumor can also be damaged, possibly leading to side effects such as fatigue, nausea, or increased cancer risk later in life.
Example:
Carbon-14 is found in a piece of wood taken from an archaeological site. Explain how scientists use carbon-14 to estimate the age of the artifact.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Carbon-14 is a radioactive isotope that decays over time with a known half-life of about 5730 years.
By measuring the remaining proportion of carbon-14 in the sample compared to living organisms, scientists can estimate how long ago the tree stopped exchanging carbon with the atmosphere.
Thus, the age of the artifact can be determined.
Example:
An industrial company uses a beta radiation source to measure the thickness of aluminum foil. Explain how the method works, and identify one danger associated with this application.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Beta particles can penetrate thin sheets of material like aluminum foil but are stopped if the foil is too thick.
A detector measures the amount of beta radiation passing through the foil. If too little radiation passes through, the foil is too thick and needs adjusting.
Danger: Workers may be exposed to beta radiation if shielding is inadequate, which can cause skin burns or tissue damage.
