IB MYP 4-5 Physics- Characteristics of the Sun and planets- Study Notes - New Syllabus
IB MYP 4-5 Physics-Characteristics of the Sun and planets- Study Notes
Key Concepts
- Characteristics of the Sun and planets
Characteristics of the Sun and planets
Surface Temperatures
The surface temperature of a planet or star depends mainly on its distance from the Sun and atmospheric conditions.
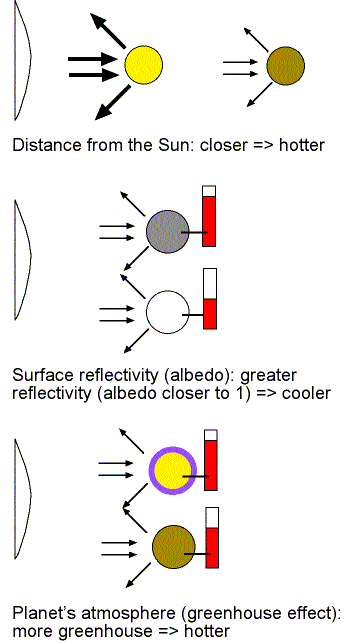
- The Sun: Surface temperature is about \( 5,500^\circ \, C \) (photosphere), with the core reaching about \( 15 \times 10^6 \, ^\circ C \).
- Mercury: Extreme variation: daytime about \( 430^\circ C \), night about \( -180^\circ C \) because it has no atmosphere.
- Venus: About \( 465^\circ C \), hotter than Mercury due to thick carbon dioxide atmosphere (greenhouse effect).
- Earth: Average \( 15^\circ C \), suitable for life because of balanced greenhouse effect and liquid water.
- Outer planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune) are much colder, with temperatures below freezing due to their great distance from the Sun.
Example:
Mercury has no atmosphere, while Venus has a thick atmosphere of carbon dioxide. Which one has a higher average surface temperature?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Venus has a much higher average temperature than Mercury despite being farther from the Sun.
This is because its thick CO₂ atmosphere traps heat through the greenhouse effect.
Thus, Venus is the hottest planet in the solar system.
Example:
Compare the temperatures of Neptune and Earth. Why is Neptune much colder?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Earth is about 150 million km from the Sun, while Neptune is about 4.5 billion km away.
Because Neptune receives much less solar radiation, its surface is extremely cold (around -200 °C).
Earth, being closer, maintains moderate temperatures that allow life.
Numbers of Moons
Moons are natural satellites that orbit planets.
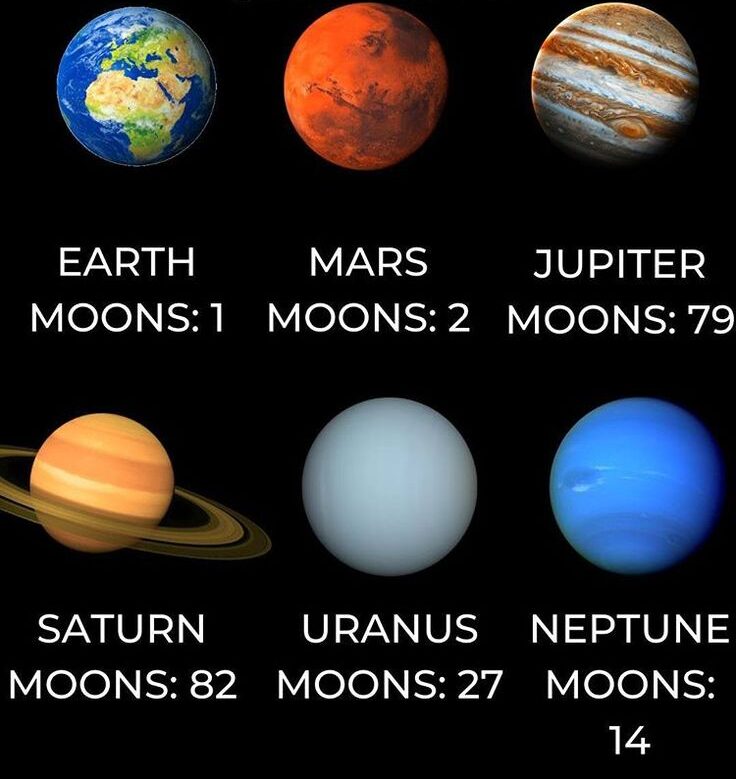
- Earth: Has 1 moon, which affects tides and stabilizes Earth’s tilt.
- Mars: Has 2 small moons (Phobos and Deimos).
- Jupiter: Has the largest number of moons (at least 92 confirmed), including the largest moon in the solar system, Ganymede.
- Saturn: Over 80 moons, including Titan (larger than Mercury).
- Mercury and Venus: Have no moons.
Example:
Why does Jupiter have more moons than Earth?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Jupiter has a much larger mass, which gives it stronger gravity.
This allows it to capture and hold many more natural satellites in orbit compared to Earth.
Example:
Mars has 2 small moons (Phobos and Deimos). Explain how they are different from Earth’s Moon.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Phobos and Deimos are irregularly shaped, much smaller, and likely captured asteroids.
Earth’s Moon is spherical and much larger compared to Mars’ moons, making it more stable in orbit.
Distances from the Sun
Planets’ distances determine how much sunlight and heat they receive.
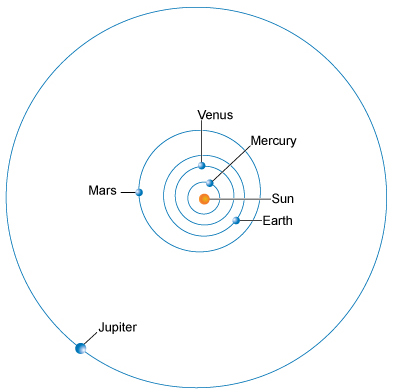
- Mercury: Closest planet, average distance about \( 58 \times 10^6 \, \text{km} \).
- Earth: Average distance \( 150 \times 10^6 \, \text{km} \) (1 Astronomical Unit, AU).
- Jupiter: About \( 778 \times 10^6 \, \text{km} \) from the Sun.
- Neptune: Farthest planet, about \( 4.5 \times 10^9 \, \text{km} \) away.
- The farther a planet, the less energy it receives, so outer planets are very cold.
Example:
Why does Mercury experience more extreme heating than Earth?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Mercury is much closer to the Sun (58 million km compared to Earth’s 150 million km).
It receives more intense solar radiation, causing higher daytime temperatures.
Example:
Why does Pluto (a dwarf planet) take much longer to orbit the Sun compared to Earth?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Pluto is much farther from the Sun (5.9 billion km).
This gives it a longer orbital path and weaker gravitational pull from the Sun, leading to a much slower orbit (248 Earth years).
Orbital Properties
All planets orbit the Sun in an elliptical path (Kepler’s First Law), nearly circular in most cases.
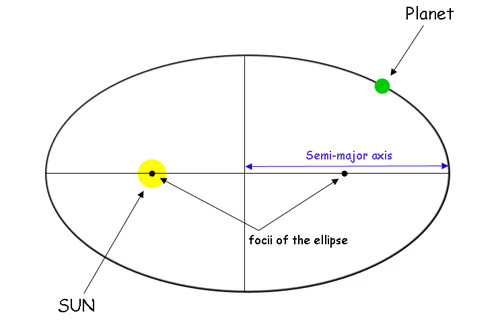
- Mercury: Has the shortest orbital period (88 Earth days).
- Earth: Orbital period is 365 days (1 year).
- Jupiter: Orbital period is about 12 Earth years.
- Neptune: Orbital period is about 165 Earth years.
- Planets farther from the Sun move more slowly due to weaker gravitational pull.
Example:
Earth takes 365 days to orbit the Sun. Jupiter takes about 12 years. Explain why.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Jupiter is much farther from the Sun, so its orbit is much larger.
The weaker gravitational pull also makes it move more slowly, giving it a longer orbital period.
Example:
Mercury has the shortest orbital period (88 days). Why is it so short?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Mercury is the closest planet to the Sun, with the strongest gravitational pull from it.
This causes Mercury to move very quickly around the Sun, completing its orbit in just 88 days.
Masses
Mass determines the strength of a planet’s gravity and ability to hold an atmosphere.

- Sun: Mass is about \( 2 \times 10^{30} \, \text{kg} \), making up about 99.8% of the total mass of the solar system.
- Earth: Mass about \( 6 \times 10^{24} \, \text{kg} \), with surface gravity of \( 9.8 \, \text{m/s}^2 \).
- Jupiter: Largest planet, mass about \( 1.9 \times 10^{27} \, \text{kg} \), over 300 times Earth’s mass.
- Mercury: Smallest planet, mass about \( 3.3 \times 10^{23} \, \text{kg} \).
- Larger mass means stronger gravity, which is why gas giants can hold thick atmospheres and many moons.
Example:
Why does Jupiter have stronger gravity compared to Earth?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Jupiter is about 318 times more massive than Earth.
Greater mass increases its gravitational pull, allowing it to attract more moons and gas.
Example:
Explain why Earth has stronger gravity than Mars despite both being rocky planets.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Earth has a greater mass than Mars (about 10 times larger).
This gives Earth stronger gravity, which allows it to hold a thicker atmosphere compared to Mars’ thin one.
