IB MYP 4-5 Physics- Density- Study Notes - New Syllabus
IB MYP 4-5 Physics-density- Study Notes
Key Concepts
- Density
Density
Density
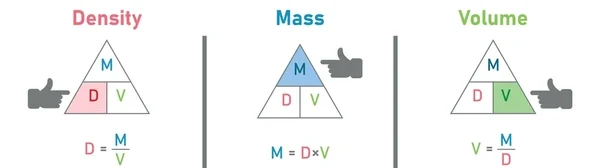
Density is defined as the mass per unit volume of a substance.
Formula:
\( \rho = \dfrac{m}{V} \)
- Where:
- \( \rho \): density (kg/m³ or g/cm³)
- \( m \): mass (kg or g)
- \( V \): volume (m³ or cm³)
SI Unit: \( \text{kg/m}^3 \)
Other units: \( \text{g/cm}^3 \) (commonly used in lab)
Important Conversion:
\( 1\,\text{g/cm}^3 = 1000\,\text{kg/m}^3 \)
How to Measure Density (Step-by-Step)
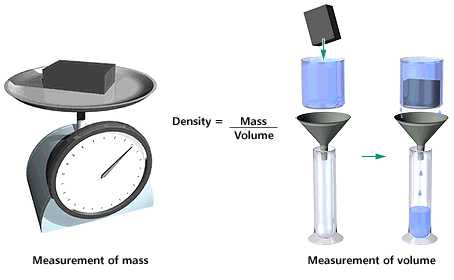
- Measure the mass of the object using a digital balance.
- Measure the volume:
- Use dimensions if the object is regular.
- Use the displacement method in a measuring cylinder if irregular.
- Calculate density using \( \rho = \dfrac{m}{V} \)
Example:
How can you determine the volume of an irregularly shaped metal stone using a measuring cylinder?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
To find the volume of an irregular object like a stone, use the displacement method:
- Fill a measuring cylinder with a known volume of water, say \( V_1 \).
- Gently place the stone into the cylinder.
- Record the new volume, \( V_2 \).
- The volume of the stone is the difference:
\( V = V_2 – V_1 \)
This method works because the object displaces its own volume of water.
Final Answer: \( \boxed{V = V_2 – V_1} \)
Example:
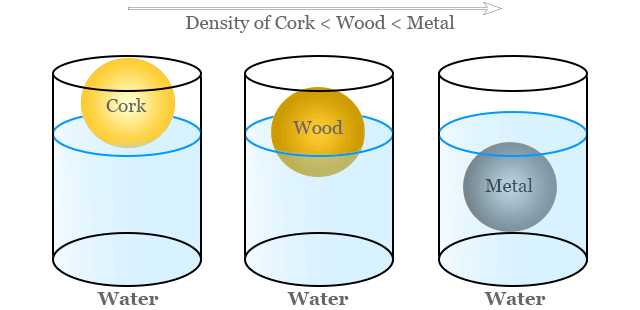
Object A has a density of \( 2.7\,\text{g/cm}^3 \) and Object B has a density of \( 1.0\,\text{g/cm}^3 \). Which one is likely to float in water, and why?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Water has a density of approximately \( 1.0\,\text{g/cm}^3 \).
Objects with a density less than water will float, and those with greater density will sink.
Here, Object B has the same density as water, so it will be neutrally buoyant (may just float or remain suspended).
Object A has a higher density than water, so it will sink.
Final Answer: \( \boxed{\text{Object B will float or remain suspended}} \)
Example:
A block of wood has a mass of \( 300\,\text{g} \) and a volume of \( 400\,\text{cm}^3 \). Calculate its density in \( \text{g/cm}^3 \).
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Use the formula:
\( \rho = \dfrac{m}{V} = \dfrac{300}{400} = 0.75\,\text{g/cm}^3 \)
Since the density is less than water’s, this block would float.
Final Answer: \( \boxed{0.75\,\text{g/cm}^3} \)
