IB MYP 4-5 Physics- Electric fields and field line diagrams- Study Notes - New Syllabus
IB MYP 4-5 Physics-Electric fields and field line diagrams- Study Notes
Key Concepts
- Electric fields and field line diagrams
Electric Fields
Electric Fields
An electric field is the region around a charged object where it exerts a force on other charges. It is invisible but can be represented by field lines.
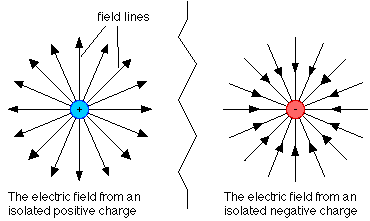
- Electric fields are created by electric charges (positive or negative).
- The strength of the field depends on the amount of charge and the distance from the charge.
- A small positive test charge is used to define the direction of the electric field.
Formula for electric field strength:
\( E = \dfrac{F}{q} \)
where
- \( E \) = electric field strength (N/C),
- \( F \) = force on the test charge (N), and
- \( q \) = magnitude of the test charge (C).
Electric Field Line Diagrams
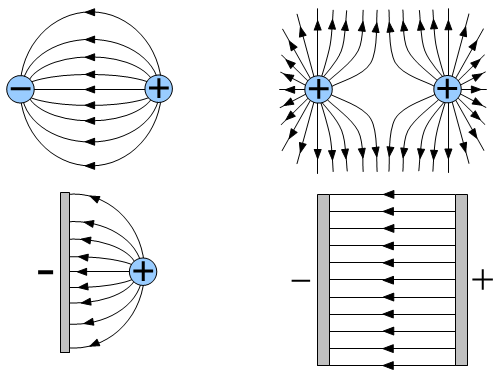
- Field lines show the direction and strength of an electric field.
- They always start from positive charges and end on negative charges.
- The closer the field lines are, the stronger the field.
- Field lines never cross each other.
Main Electric Field Patterns:
- Single Positive Charge: Lines radiate outward.
- Single Negative Charge: Lines point inward.
- Two Like Charges (repulsion): Field lines curve outward, away from each other.
- Two Unlike Charges (attraction): Field lines go from positive to negative, showing attraction.
- Uniform Field: Represented by equally spaced, parallel lines (e.g., between parallel plates).
Example:
A point charge of +2 μC creates an electric field. Describe the direction of the field lines around it.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Since the charge is positive, the electric field lines radiate outward in all directions. The field strength decreases as distance increases, so the lines spread apart with distance.
Example:
A +3 μC charge is placed near a –3 μC charge. Sketch and describe the electric field lines between them.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Field lines originate from the positive charge and terminate at the negative charge. The pattern shows straight lines between them, indicating strong attraction in the central region, with curved lines around the sides.
Example:
Two large parallel metal plates are connected to a battery, one positively charged and the other negatively charged. What does the electric field look like between the plates?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The field between the plates is uniform, represented by equally spaced, parallel, straight lines pointing from the positive plate to the negative plate. This shows the field strength is the same everywhere between the plates.
