IB MYP 4-5 Physics- Instruments used in astronomy- Study Notes - New Syllabus
IB MYP 4-5 Physics-Instruments used in astronomy- Study Notes
Key Concepts
- Instruments used in astronomy
Instruments Used in Astronomy
Instruments Used in Astronomy
Optical Telescopes

- Used to observe visible light from celestial objects.
- Types:
- Refracting Telescope: Uses lenses to bend light and form an image.
- Reflecting Telescope: Uses mirrors to reflect light and form an image.
- Important features:
- Aperture: Diameter of lens or mirror, determines light-gathering ability.
- Magnification: Ratio of focal length of objective to eyepiece.
- Examples: Hubble Space Telescope (uses mirrors, space-based).
Spectroscope / Spectrometer
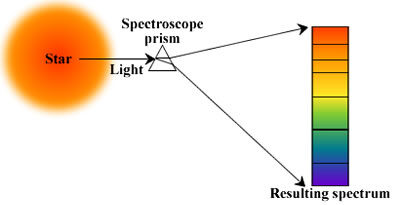
- Used to split light from stars or galaxies into its spectrum.
- Applications:
- Identify chemical composition of stars (emission and absorption lines).
- Determine redshift or blueshift, giving information about motion.
Radio Telescopes
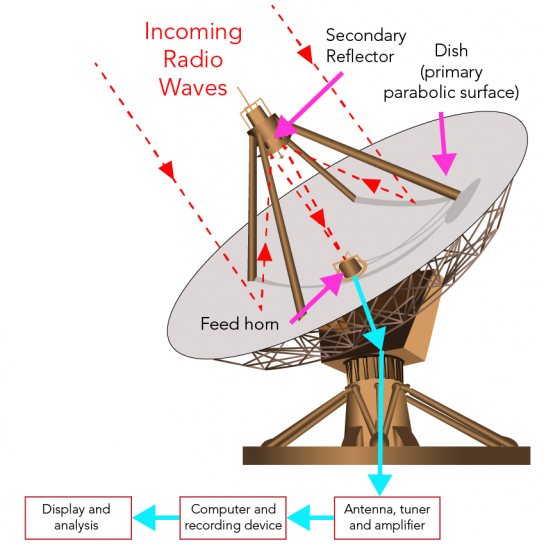
- Detect radio waves emitted by celestial objects.
- Large parabolic dishes collect weak radio signals.
- Applications:
- Study pulsars, quasars, cosmic microwave background.
- Observe through interstellar dust clouds that block visible light.
Photometers / CCD Cameras
- Measure brightness (intensity) of stars and other objects.
- CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) cameras convert light into electronic signals for imaging.
- Applications:
- Monitor variable stars, eclipsing binaries.
- Capture high-resolution images of planets, galaxies, and nebulae.
Space Telescopes
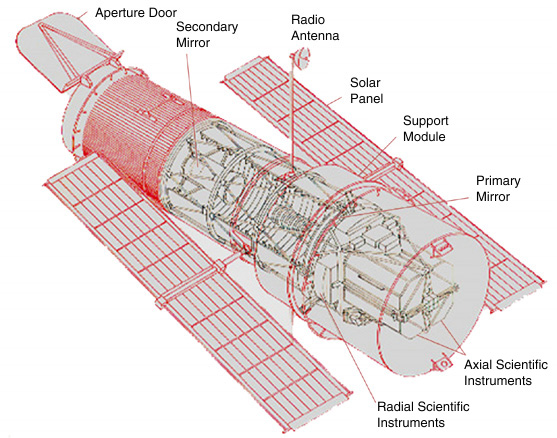
- Telescopes placed in space to avoid atmospheric distortion and absorption.
- Examples:
- Hubble Space Telescope – optical, UV, infrared observations.
- James Webb Space Telescope – infrared observations for distant galaxies.
Other Instruments
- Interferometers – combine signals from multiple telescopes to improve resolution.
- Coronagraphs – block light from the Sun to observe its corona.
- Gravitational wave detectors (e.g., LIGO) – detect ripples in spacetime from cosmic events.
Comparison Table of Astronomical Instruments
| Instrument | Type of Waves Detected | Main Use | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Refracting/Reflecting Telescopes | Visible Light | Observe planets, stars, galaxies | Hubble Space Telescope |
| Spectroscope / Spectrometer | Visible Light | Study star composition and motion | Prism or diffraction grating spectroscopes |
| Radio Telescopes | Radio Waves | Observe pulsars, quasars, dust clouds | Arecibo Observatory, VLA |
| Photometers / CCD Cameras | Visible Light | Measure brightness; take images | CCD cameras on telescopes |
| Space Telescopes | Visible, UV, IR | Avoid atmosphere; observe distant objects | Hubble, James Webb |
| Other Instruments | Various (EM waves, gravitational waves) | Special studies (resolution, corona, spacetime waves) | LIGO, Coronagraphs, Interferometers |
Example 1:
A student uses a refracting telescope with an objective lens of focal length 120 cm and an eyepiece of focal length 15 cm. Calculate the angular magnification of the telescope.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Use the formula for angular magnification of a telescope:
\( M = \dfrac{f_o}{f_e} \)
Step 2: Substitute values:
\( M = \dfrac{120}{15} = 8 \)
\(\boxed{M = 8}\)
Example 2:
A radio telescope has a parabolic dish of diameter 50 m. If the diameter is doubled, by what factor does its signal-gathering ability increase?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Signal-gathering ability ∝ area of dish:
\( \text{Area} \propto D^2 \)
Step 2: Doubling diameter increases area by:
\( 2^2 = 4 \)
\(\boxed{\text{Signal-gathering ability increases 4 times}}\)
Example 3:
An astronomer observes the spectrum of a distant star using a spectroscope. The spectral lines are shifted towards shorter wavelengths. What does this tell us about the star’s motion relative to Earth?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Shift towards shorter wavelengths is called **blueshift**.
Step 2: Blueshift indicates the star is moving **towards Earth**.
\(\boxed{\text{The star is approaching Earth}}\)
