IB MYP 4-5 Physics- Magnetic fields - Study Notes - New Syllabus
IB MYP 4-5 Physics-Magnetic fields – Study Notes
Key Concepts
- Magnetic fields
Magnetic Fields
Magnetic Fields
A magnetic field is the region around a magnet (or moving charges like currents) where magnetic forces can be felt.
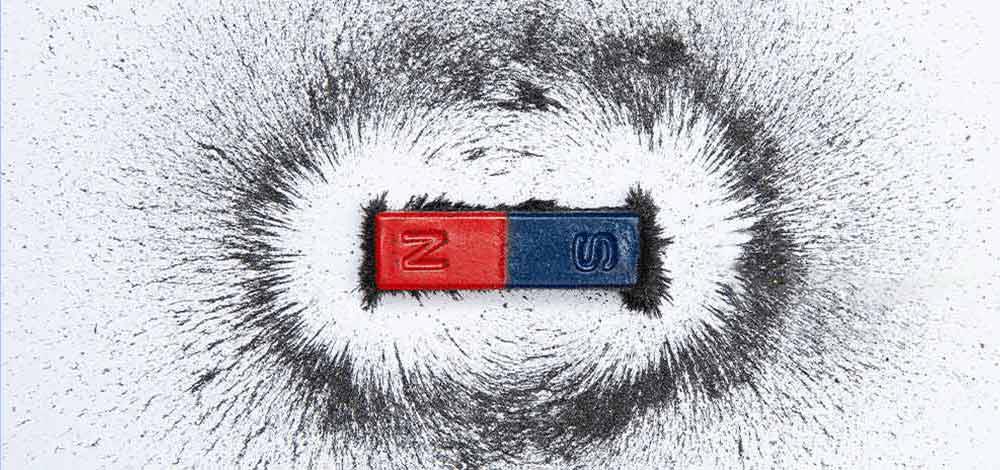

- It is represented by magnetic field lines (also called lines of flux).
- The direction of a magnetic field line is the direction a north pole of a small test magnet would point.
- The strength of the magnetic field is indicated by how close the lines are (closer lines = stronger field).
Magnetic Field Patterns
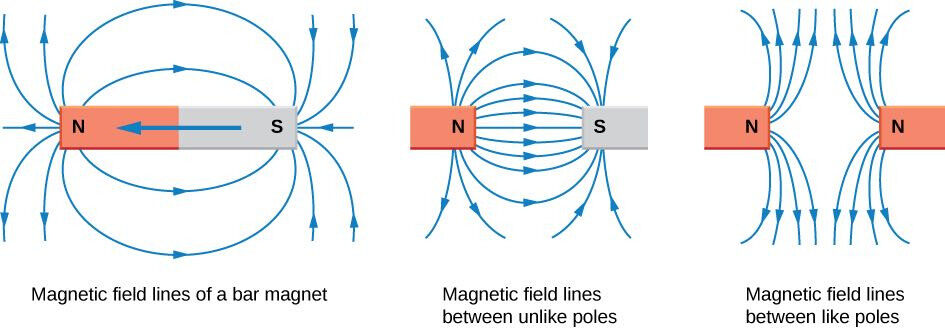
- Bar Magnet: Field lines emerge from the north pole and enter the south pole outside the magnet. Inside, they go from south to north, forming closed loops.
- Between two unlike poles: Field lines run straight from north to south, creating a strong uniform field in the middle.
- Between two like poles: Field lines repel each other, showing regions of weaker field.
Representing Magnetic Fields
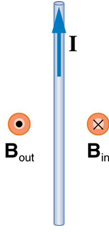
- Field into the page: represented by ✗ (tail of arrow).
- Field out of the page: represented by • (tip of arrow).
- Uniform field: represented by equally spaced, parallel straight lines.
Everyday Applications
- Magnetic compasses (navigation).
- Electromagnets in cranes, relays, doorbells.
- Magnetic storage devices (hard drives, credit cards).
- Electric motors and generators (convert electrical ↔ mechanical energy).
Example:
Draw and describe the magnetic field pattern around a bar magnet.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Field lines emerge from the north pole and curve around into the south pole.
Step 2: Inside the magnet, they run from south to north, forming closed loops.
Step 3: Field strength is strongest at the poles (lines closest together).
Final Answer: The bar magnet produces a dipole field with lines emerging from N and entering S.
Exampl:
A current flows vertically upward through a straight wire. What is the direction of the magnetic field around it?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Apply the Right-Hand Grip Rule: Thumb points in the direction of current.
Step 2: The curled fingers give the direction of magnetic field lines.
Step 3: For upward current, the field is anticlockwise around the wire.
Final Answer: The magnetic field forms anticlockwise circles around the wire.
Example:
A solenoid has current flowing through it. How is its magnetic field similar to that of a bar magnet?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Field lines inside the solenoid are nearly parallel and equally spaced → strong uniform field.
Step 2: The solenoid has two ends: one acts as a north pole, the other as a south pole.
Step 3: The external field looks just like that of a bar magnet.
Final Answer: A solenoid with current produces a bar magnet-like field with N and S poles.
