IB MYP 4-5 Physics- The Big Bang Theory and origin of the universe- Study Notes - New Syllabus
IB MYP 4-5 Physics-The Big Bang Theory and origin of the universe- Study Notes
Key Concepts
- The Big Bang Theory and origin of the universe
The Big Bang Theory and Origin of the Universe
Concept of the Big Bang
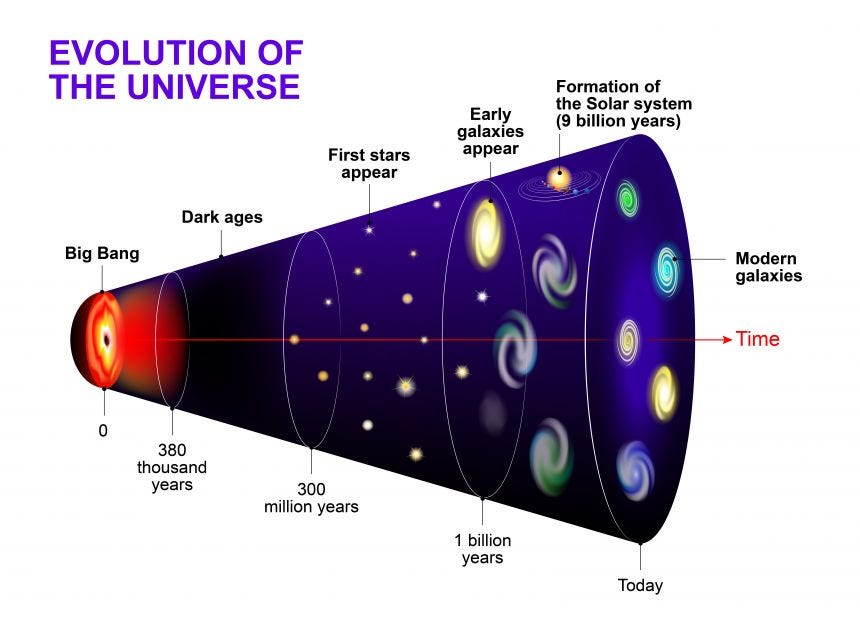
- The Big Bang Theory is the most widely accepted scientific explanation for the origin of the universe.
- It states that the universe began about 13.8 billion years ago from an extremely hot, dense, and tiny point called a singularity.
- This point expanded rapidly in an event known as the “Big Bang”.
- It was not an “explosion in space” but rather an expansion of space itself.
Early Stages of the Universe
- First second: Formation of fundamental particles (quarks, electrons, neutrinos).
- First 3 minutes: Quarks combined to form protons and neutrons. Nuclei of hydrogen, helium, and lithium were formed (known as nucleosynthesis).
- 380,000 years later: Universe cooled enough for electrons to combine with nuclei → atoms formed. This event is called recombination. Light could now travel freely (producing the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation).
- Millions of years later: Gravity pulled matter together to form stars and galaxies.
Evidence for the Big Bang
- Redshift of galaxies (Hubble’s discovery): Galaxies are moving away from us, meaning the universe is expanding.
- Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation (CMBR): Leftover “afterglow” from the Big Bang, discovered in 1965, uniform across the universe.
- Abundance of light elements: Observed hydrogen and helium proportions in the universe match Big Bang predictions.
Alternative Theories (less accepted)
- Steady State Theory: Suggested the universe has no beginning or end, and matter is continuously created. Rejected because it cannot explain CMBR.
- Oscillating/Cyclic Universe Theory: Suggests the universe goes through repeated cycles of expansion and contraction.
Current Understanding
- The Big Bang Theory, supported by strong observational evidence, remains the best model for the origin and evolution of the universe.
- Ongoing research explores mysteries like dark matter and dark energy, which influence the universe’s expansion.
Example:
How does Hubble’s observation of redshift in galaxies provide evidence for the Big Bang Theory?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Redshift shows that galaxies are moving away from us, meaning the universe is expanding. If the universe is expanding now, it must have been smaller and denser in the past, supporting the idea that it started from a single point in the Big Bang.
Example:
Why is the discovery of Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation (CMBR) considered strong evidence for the Big Bang?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
CMBR is leftover radiation from when the universe cooled enough for atoms to form and light to travel freely (about 380,000 years after the Big Bang). Its uniform presence in all directions is exactly what the Big Bang Theory predicted, making it powerful evidence.
Example:
The universe today contains mostly hydrogen and helium. How does this support the Big Bang Theory?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The Big Bang Theory predicted that the early universe was hot enough for nuclear fusion to create only light elements (hydrogen, helium, and a little lithium). Observations confirm this composition, supporting the Big Bang model.
