IB DP Biology- B2.1 Membranes and membrane transport - IB Style Questions For SL Paper 1A -FA 2025
Question
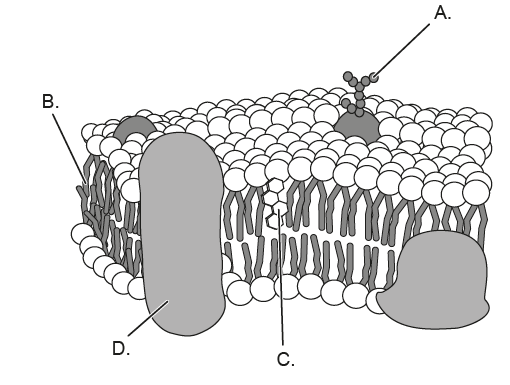
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Label A points to a glycoprotein with an attached carbohydrate chain. These carbohydrate side groups act as identification markers on the cell surface and are essential for cell recognition and communication. Therefore, the structure that enables recognition between cells is A.
✅ Answer: (A)
Question
A number of different proteins are involved in nerve function. Which of the following does not require a membrane protein?
A. Active transport of sodium
B. Diffusion of K+ into the cell
C. Diffusion of the neurotransmitter across the synapse
D. Binding of the neurotransmitter to the post-synaptic membrane
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Answer: C. Diffusion of the neurotransmitter across the synapse
Explanation: 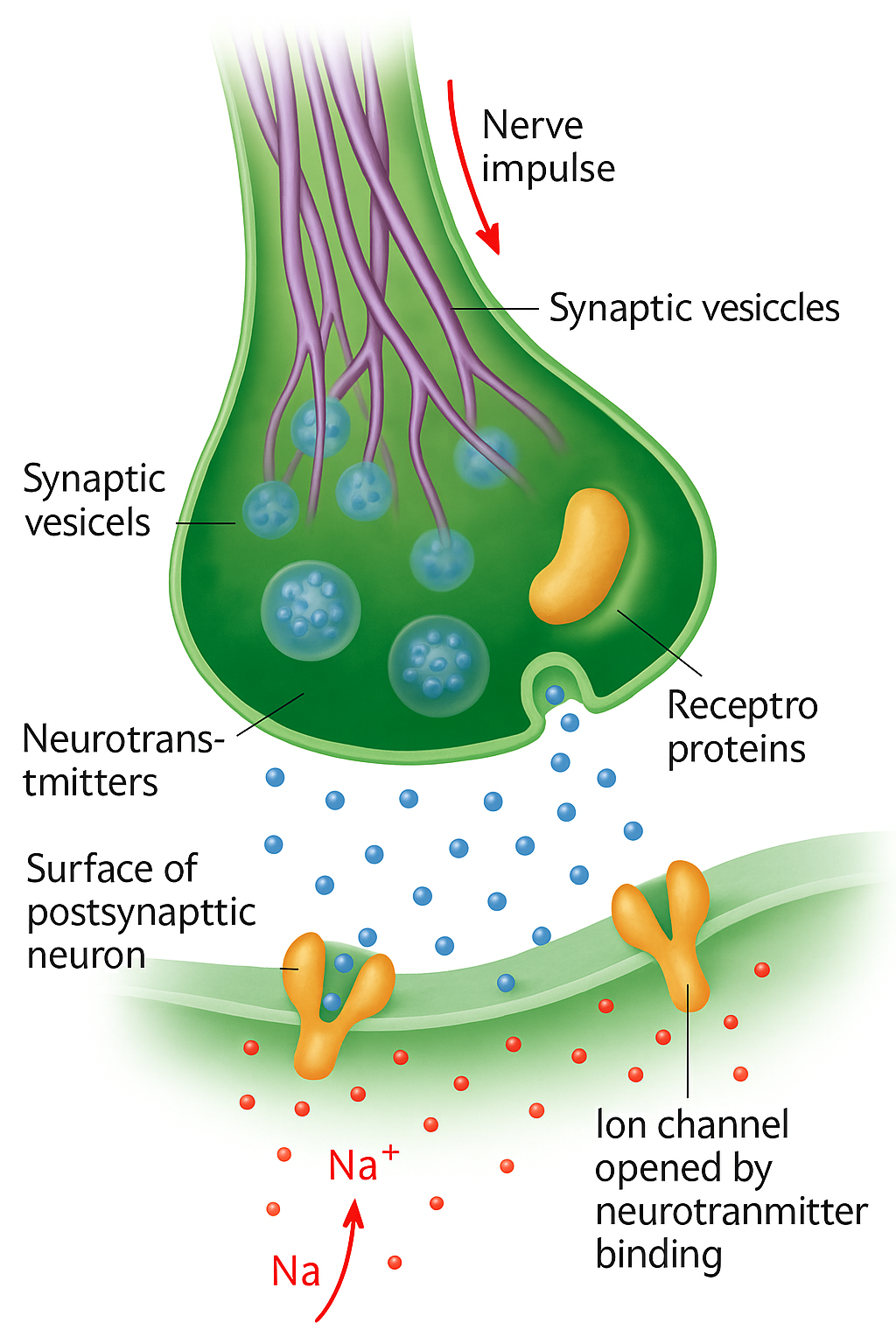
Membrane proteins play key roles in active transport, facilitated diffusion, receptor binding, and cell signaling. However, simple diffusion of small molecules—such as neurotransmitters crossing the synaptic cleft—does not require a membrane protein. The synaptic cleft is a fluid-filled gap between neurons where neurotransmitters move passively by diffusion.
Evaluating the options:
A. Incorrect – Active transport of sodium (e.g., sodium–potassium pump) requires membrane proteins because ions move against their concentration gradient using ATP.
B. Incorrect – Diffusion of K⁺ into the cell occurs through potassium channels, which are membrane proteins. Although the process is passive, ions cannot cross the lipid bilayer unaided.
C. Correct – Diffusion of the neurotransmitter across the synapse is a passive process through the extracellular fluid of the synaptic cleft. No membrane proteins are needed for this movement.
D. Incorrect – Binding of the neurotransmitter to the post-synaptic membrane involves receptor proteins embedded in the membrane, which detect and respond to the neurotransmitter.
Question
The diagram shows protein channels involved in the passive movement of a substance into the cell across the cell membrane.

What describes this movement?
A. Energy of ATP is used to transport substances into the cell.
B. Substances can move from areas of low to areas of high concentration.
C. The proteins ensure that movement of substances is only in one direction.
D. Net movement occurs until the concentrations in and out of the cell are equal.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Answer: D. Net movement occurs until the concentrations in and out of the cell are equal.
Explanation:
The diagram shows protein channels embedded in a cell membrane that help substances move into the cell from the extracellular space to the intracellular space.
This type of movement is known as passive transport (specifically, facilitated diffusion), and it has the following key features:
- No energy (ATP) is required for this process.
- Substances move from high to low concentration, following the concentration gradient.
- Movement continues until concentrations are equal on both sides, a state called equilibrium.
- The proteins do not control direction—movement depends on concentration differences.
- Movement from low to high concentration would require energy (i.e., active transport), not shown here.
Option Analysis:
A. Incorrect – Passive transport does not require ATP.
B. Incorrect – Movement from low to high concentration requires energy (active transport).
C. Incorrect – Proteins in passive transport do not force one-way movement; it is driven by concentration differences.
D. Correct – In diffusion, net movement continues until concentrations inside and outside the cell reach equilibrium.
