Question
A newspaper vendor in Singapore is trying to predict how many copies of The Straits Times they will sell. The vendor forms a model to predict the number of copies sold each weekday. According to this model, they expect the same number of copies will be sold each day.
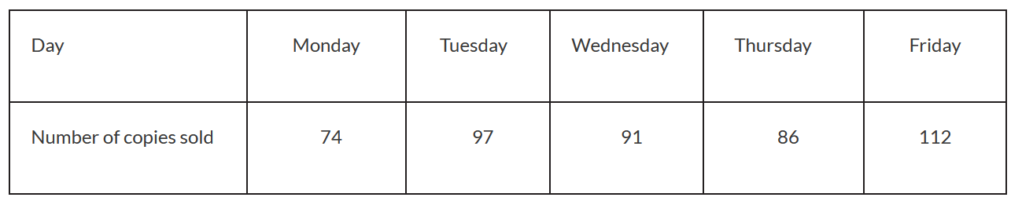
To test the model, they record the number of copies sold each weekday during a particular week. This data is shown in the table.
A goodness of fit test at the 5 % significance level is used on this data to determine whether the vendor’s model is suitable. The critical value for the test is 9.49.
a. Find an estimate for how many copies the vendor expects to sell each day. [1]
b. (i) State the null and alternative hypotheses for this test.
(ii) Write down the degrees of freedom for this test.
(iii) Write down the conclusion to the test. Give a reason for your answer. [7]
▶️Answer/Explanation
(a) \((\frac{74+97+91+86+112}{5})=92\)
(b) (i) \(H_{0}\) : The data satisfies the model \( H_{1}\) : The data does not satisfy the model (ii) 4 (iii) 2
χ2calc = 8.54 (8.54347…) OR \(p-value = 0.0736 (0.0735802…)\)
\(8.54 < 9.49\) OR \(0.0736 > 0.05\) therefore there is insufficient evidence to reject \(H_{0}\)
(i.e. the data satisfies the model)
Question
Consider the complex numbers Z1 = cos \(\frac{11\pi }{12}+sin\frac{11\pi }{12}\) and Z2 = cos \(\frac{\pi }{6}+isin\frac{\pi }{6}\)
(a) (i) Find \(\frac{Z_1}{Z_2}\)
(ii) Find \(\frac{Z_2}{Z_1}\) [3]
(b) \(\frac{Z_1}{Z_2}\) and \(\frac{Z_2}{Z_1}\) bare represented by three points O, A and B respectively on an Argand diagram. Determine the area of the triangle OAB. [2]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)
(i) \(\frac{z_{1}}{z_{2}}= cos(\frac{11\pi }{12}-\frac{\pi }{6})+i sin (\frac{11\pi }{12}-\frac{\pi }{6}) = cos \frac{3\pi }{4}+i sin \frac{3\pi }{4}\)
(ii)\(\frac{z_{2}}{z_{1}} = cos\frac{3\pi }{4}-isin \frac{3\pi }{4}\)
(b) valid attempt to calculate area of their triangle (angle between OA and OB is \(\frac{\pi }{2}\Rightarrow area (=\frac{1}{2}\times 1\times 1)=\frac{1}{2}\)
Question
If \({z_1} = a + a\sqrt 3 i\) and \({z_2} = 1 – i\), where a is a real constant, express \({z_1}\) and \({z_2}\) in the form \(r\,{\text{cis}}\,\theta \), and hence find an expression for \({\left( {\frac{{{z_1}}}{{{z_2}}}} \right)^6}\) in terms of a and i.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\({z_1} = 2a{\text{cis}}\left( {\frac{\pi }{3}} \right){\text{, }}{z_2} = \sqrt 2 {\text{ cis}}\left( { – \frac{\pi }{4}} \right)\) M1 A1 A1
EITHER
\({\left( {\frac{{{z_1}}}{{{z_2}}}} \right)^6} = \frac{{{2^6}{a^6}{\text{cis(0)}}}}{{{{\sqrt 2 }^6}{\text{cis}}\left( {\frac{\pi }{2}} \right)}}\left( { = 8{a^6}{\text{cis}}\left( { – \frac{\pi }{2}} \right)} \right)\) M1 A1 A1
OR
\({\left( {\frac{{{z_1}}}{{{z_2}}}} \right)^6} = {\left( {\frac{{2a}}{{\sqrt 2 }}{\text{cis}}\left( {\frac{{7\pi }}{{12}}} \right)} \right)^6}\) M1 A1
\( = 8{a^6}{\text{cis}}\left( { – \frac{\pi }{2}} \right)\) A1
THEN
\( = – 8{a^6}{\text{i}}\) A1
Note: Accept equivalent angles, in radians or degrees.
Accept alternate answers without cis e.g. \({\text{ = }}\frac{{8{a^6}}}{{\text{i}}}\)
[7 marks]
Question
Given that z is the complex number \(x + {\text{i}}y\) and that \(\left| {\,z\,} \right| + z = 6 – 2{\text{i}}\) , find the value of x
and the value of y .
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\(\sqrt {{x^2} + {y^2}} + x + y{\text{i}} = 6 – 2{\text{i}}\) (A1)
equating real and imaginary parts M1
\(y = – 2\) A1
\(\sqrt {{x^2} + 4} + x = 6\) A1
\({x^2} + 4 = {(6 – x)^2}\) M1
\( – 32 = – 12x \Rightarrow x = \frac{8}{3}\) A1
[6 marks]
Question
Given that \((4 – 5{\text{i}})m + 4n = 16 + 15{\text{i}}\) , where \({{\text{i}}^2} = – 1\), find m and n if
a.m and n are real numbers;[3]
b.m and n are conjugate complex numbers.[4]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
attempt to equate real and imaginary parts M1
equate real parts: \(4m + 4n = 16\); equate imaginary parts: \( -5m = 15\) A1
\( \Rightarrow m = -3,{\text{ }}n = 7\) A1
[3 marks]
let \(m = x + {\text{i}}y,{\text{ }}n = x – {\text{i}}y\) M1
\( \Rightarrow (4 – 5{\text{i}})(x + {\text{i}}y) + 4(x – {\text{i}}y) = 16 + 15{\text{i}}\)
\( \Rightarrow 4x – 5{\text{i}}x + 4{\text{i}}y + 5y + 4x – 4{\text{i}}y = 16 + 15{\text{i}}\)
attempt to equate real and imaginary parts M1
\(8x + 5y = 16,{\text{ }} -5x = 15\) A1
\( \Rightarrow x = -3,{\text{ }}y = 8\) A1
\(( \Rightarrow m = -3 + 8{\text{i}},{\text{ }}n = -3 – 8{\text{i}})\)
[4 marks]
