IB Mathematics AHL 3.12 Concept of a vector AA HL Paper 3- Exam Style Questions
Question
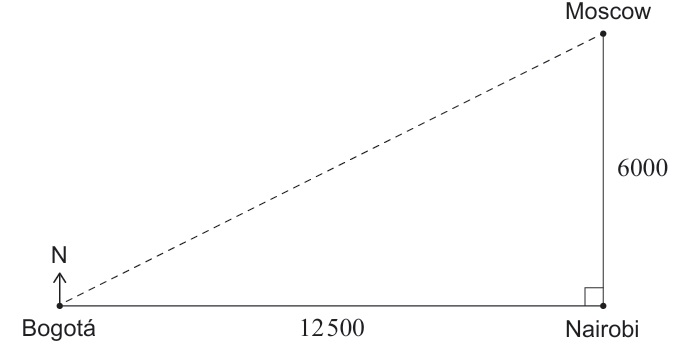
In the Euclidean (flat) model, the locations are defined as follows:
- Nairobi is situated \(6000\) km directly south of Moscow.
- Bogotá is situated \(12\,500\) km directly west of Nairobi.
Most‑appropriate topic codes (IB Mathematics AA AHL):
• AHL 3.13: Scalar product of two vectors; properties of the scalar product; angle between two vectors.
• AHL 3.16: Vector product of two vectors; properties of the vector product; geometric interpretation.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) (i)
Distance = \(\sqrt{6000^2 + 12500^2}\)
Distance = \(\sqrt{36,000,000 + 156,250,000} = \sqrt{192,250,000}\)
Distance \(\approx 13865.4\) km
Answer: 13900 km (to 3 significant figures).
(a) (ii)
Let Moscow be at (0, 6000) and Nairobi at (0, 0). Bogotá is at (-12500, 0).
The angle \(\alpha\) from the North-South line satisfies \(\tan \alpha = \frac{12500}{6000}\).
\(\alpha = \arctan(2.0833…) \approx 64.36^\circ\).
Bearing = 064.4°.
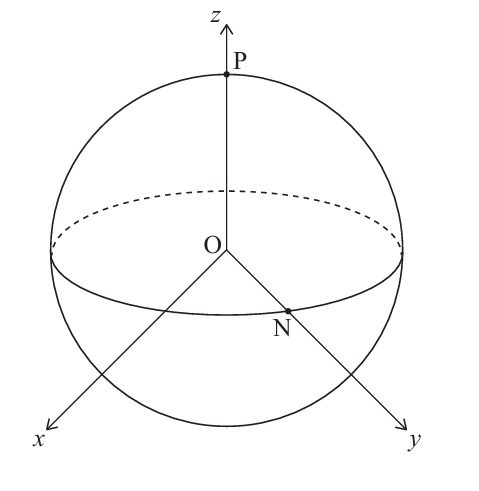
(b) (i)
Using \(\mathbf{p} \cdot \mathbf{n} = |\mathbf{p}| |\mathbf{n}| \cos \theta\):
\(\begin{pmatrix} 0 \\ 0 \\ 6 \end{pmatrix} \cdot \begin{pmatrix} 0 \\ 6 \\ 0 \end{pmatrix} = (0)(0) + (0)(6) + (6)(0) = 0\).
\(36 \cos \theta = 0 \implies \cos \theta = 0\).
Angle = 90° (or \(\pi/2\) radians).
(b) (ii)
Distance = \(r \theta\).
Distance = \(6000 \times \frac{\pi}{2} = 3000\pi\) km.
(c) (i)
\(\mathbf{a} \times \mathbf{p} = \begin{vmatrix} \mathbf{i} & \mathbf{j} & \mathbf{k} \\ 6 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 6 \end{vmatrix} = \mathbf{i}(0-0) – \mathbf{j}(36-0) + \mathbf{k}(0-0) = \begin{pmatrix} 0 \\ -36 \\ 0 \end{pmatrix}\).
(c) (ii)
\(\mathbf{a} \times \mathbf{n} = \begin{vmatrix} \mathbf{i} & \mathbf{j} & \mathbf{k} \\ 6 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 6 & 0 \end{vmatrix} = \mathbf{i}(0-0) – \mathbf{j}(0-0) + \mathbf{k}(36-0) = \begin{pmatrix} 0 \\ 0 \\ 36 \end{pmatrix}\).
Let \(\phi\) be the angle at vertex A.
\(\cos \phi = \frac{(\mathbf{a} \times \mathbf{p}) \cdot (\mathbf{a} \times \mathbf{n})}{|\mathbf{a} \times \mathbf{p}| |\mathbf{a} \times \mathbf{n}|} = \frac{0 + 0 + 0}{36 \times 36} = 0\).
\(\phi = 90^\circ\).
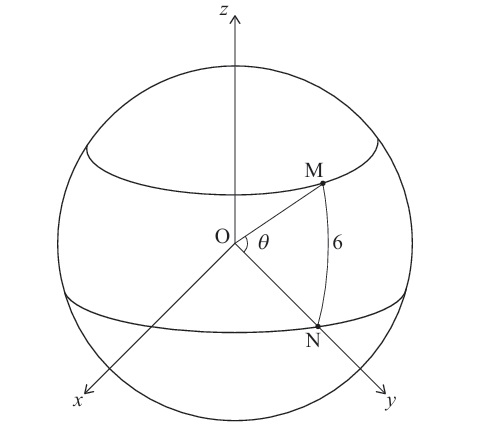
(d)
Arc length MN = 6000 km.
Angle between \(\mathbf{m}\) and \(\mathbf{n}\) is \(\theta_{MN} = \frac{\text{Arc}}{\text{Radius}} = \frac{6000}{6000} = 1\) radian.
Using \(\mathbf{m} \cdot \mathbf{n} = |\mathbf{m}| |\mathbf{n}| \cos \theta_{MN}\):
\(\begin{pmatrix} 0 \\ 6\cos\theta \\ 6\sin\theta \end{pmatrix} \cdot \begin{pmatrix} 0 \\ 6 \\ 0 \end{pmatrix} = 36\cos\theta_{MN}\).
\(36\cos\theta = 36\cos(1)\).
\(\theta = 1\) radian \(\approx 57.2958^\circ\).
\(\theta = 57.3^\circ\) (to 3 s.f.).
(e)
The angle \(\psi\) between \(\mathbf{b}\) and \(\mathbf{m}\) is found via \(\mathbf{b} \cdot \mathbf{m}\):
\(\mathbf{b} \cdot \mathbf{m} = (6\sin 120^\circ)(0) + (6\cos 120^\circ)(6\cos \theta) + (0)(6\sin \theta)\).
\(\mathbf{b} \cdot \mathbf{m} = 36(-\frac{1}{2})\cos(1) \approx -18(0.5403…) \approx -9.7254\).
\(\cos \psi = \frac{-9.7254}{36} \approx -0.27015\).
\(\psi = \arccos(-0.27015) \approx 1.844\) radians.
Distance = \(6000 \times 1.844 \approx 11064\) km.
Answer: 11100 km (to 3 s.f.).
(f)
Bearing is the angle between \(\mathbf{b} \times \mathbf{p}\) and \(\mathbf{b} \times \mathbf{m}\).
\(\mathbf{b} \times \mathbf{p} = \begin{pmatrix} -18 \\ -18\sqrt{3} \\ 0 \end{pmatrix}\).
\(\mathbf{b} \times \mathbf{m} = \begin{pmatrix} (6\cos 120^\circ)(6\sin\theta) – 0 \\ 0 – (6\sin 120^\circ)(6\sin\theta) \\ (6\sin 120^\circ)(6\cos\theta) – 0 \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} -18\sin 1 \\ -18\sqrt{3}\sin 1 \\ 18\sqrt{3}\cos 1 \end{pmatrix}\).
Dot product \(= (-18)(-18\sin 1) + (-18\sqrt{3})(-18\sqrt{3}\sin 1) + 0 = 324\sin 1 + 972\sin 1 = 1296\sin 1 \approx 1090.5\).
\(|\mathbf{b} \times \mathbf{p}| = 36\).
\(|\mathbf{b} \times \mathbf{m}| = \sqrt{(-18\sin 1)^2 + (-18\sqrt{3}\sin 1)^2 + (18\sqrt{3}\cos 1)^2} \approx 34.66\).
\(\cos(\text{bearing}) = \frac{1090.5}{36 \times 34.66} \approx 0.874 \implies \text{Bearing} \approx 29.1^\circ\).
Answer: 029.1°.