Question
All lengths in this question are in centimetres.
A solid metal ornament is in the shape of a right pyramid, with vertex V and square base ABCD. The centre of the base is X. Point V has coordinates (1, 5, 0) and point A has coordinates (-1, 1, 6).
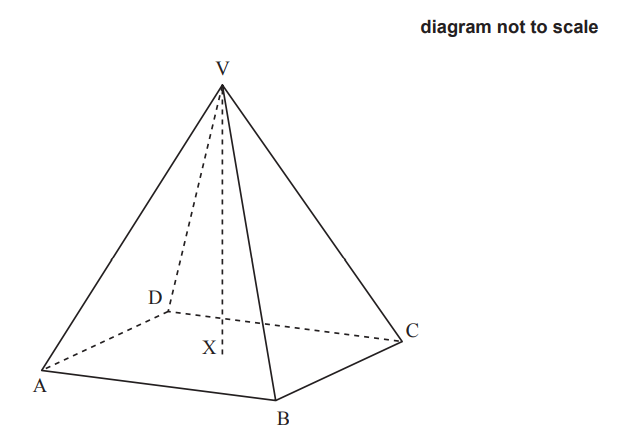
(a) Find AV.
(b) Given that \(A\hat{V}B =40^{0}\), find AB.
The volume of the pyramid is 57.2 cm3, correct to three significant figures.
(c) Find the height of the pyramid, VX.
A second ornament is in the shape of a cuboid with a rectangular base of length 2x cm, width x cm and height y cm. The cuboid has the same volume as the pyramid.
(d) The cuboid has a minimum surface area of S cm2. Find the value of S.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) attempt to use the distance formula to find AV
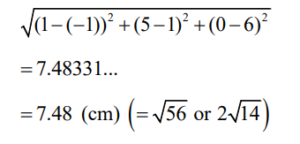
(b) METHOD 1
attempt to apply cosine rule OR sine rule to find AB

METHOD 2
Let M be the midpoint of [AB]
attempt to apply right-angled trigonometry on triangle AVM
= 2× 7.48…× sin(200)
= 5.11888…
= 5.12 (cm)
(c) METHOD 1
equating volume of pyramid formula to 57.2
\(\frac{1}{3}\times 5.11….^{2}\times h=57.2\)
h = 6.54886…
h = 6.55 (cm)
METHOD 2
Let M be the midpoint of [AB]
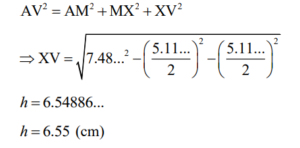
(d) V = x × 2x × y= 57.2
S = 2(2x2+xy+2xy)
Note: Condone use of A.
attempt to substitute \(y = \frac{57.2}{2x^{2}}\) into their expression for surface area
\(\left ( S(x) =\right )4x^{2}+6x\left ( \frac{57.2}{2x^{2}} \right )\)
EITHER
attempt to find minimum turning point on graph of area function
OR
\(\frac{dS}{dx}= 8x – 171.6x^{2}= 0\) OR x = 2.77849….
THEN
92.6401…
minimum surface area = 92.6(cm2)
Question:
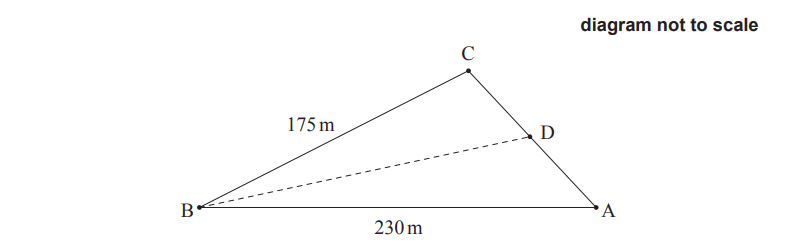
A farmer is placing posts at points A, B, and C in the ground to mark the boundaries of a triangular piece of land on his property.
From point A, he walks due west 230 metres to point B.
From point B, he walks 175 metres on a bearing of 063° to reach point C.
This is shown in the following diagram.
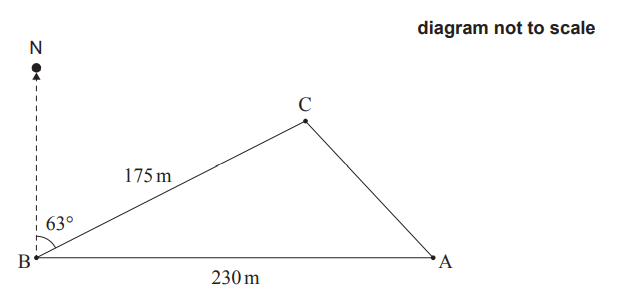
(a) Find the distance from point A to point C.
(b) Find the area of this piece of land.
(c) Find CÂB.
The farmer wants to divide the piece of land into two sections. He will put a post at point D, which is between A and C. He wants the boundary BD to divide the piece of land such that the sections have equal area. This is shown in the following diagram.
(d) Find the distance from point B to point D.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) \(A\hat{B}C = 27^{0}\)
attempt to substitute into cosine rule
1752 + 2302 – 2(175) (230) cos 270
108.62308….
AC = 109 (m)
(b) correct substitution into area formula
\(\frac{1}{2}\times 175 \times 230\times sin27^{0}\)
9136.55…
area = 9140 (m2)
(c) attempt to substitute into sine rule or cosine rule
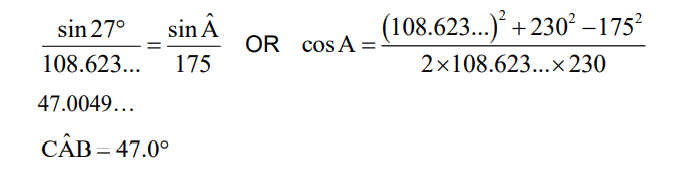
(d) METHOD 1
recognizing that for areas to be equal, AD=DC
\(AD = \frac{1}{2}AC = 54.3115…\)
attempt to substitute into cosine rule to find BD
correct substitution into cosine rule
BD2 = 2302 + 54.31152 – 2(230) (54.3115) cos 47.00490
BD = 197.009….
BD = 197 (m)
METHOD 2
correct expressions for areas of triangle BDA and triangle BCD using BD

Question:
The following diagram shows a circle with centre O and radius 5 metres.
Points A and B lie on the circle and \(A\hat{O}B\) 1.9 = radians.
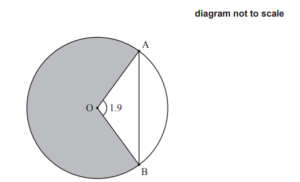
(a) Find the length of the chord [AB].
(b) Find the area of the shaded sector.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) EITHER
uses the cosine rule
AB2 = 52 + 52 -2 × 5 × 5 × cos1.9
OR
uses right-angled trigonometry
\(\frac{\frac{AB}{2}}{5}= sin 0.95\)
OR
uses the sine rule
\(\alpha = \frac{1}{2}\left ( \pi -1.9 \right )\left ( =0.6207… \right )\)
\(\frac{AB}{sin 1.9}=\frac{5}{sin 0.6207…}\)
THEN
AB = 8.13415…
AB = 8.13 (m)
(b) let the shaded area be A
METHOD 1
attempt at finding reflex angle
METHOD 2
let the area of the circle be AC and the area of the unshaded sector be AU
A = AC – AU
\(A = \pi \times 5^{2}-\frac{1}{2}\times 5^{2}\times 1.9(78.5398…-23.75)\)
= 54.7898…
= 54.8 (m2)
Question
The diagram below shows triangle PQR. The length of [PQ] is 7 cm , the length of [PR] is 10 cm , and \({\rm{P}}\widehat {\rm{Q}}{\rm{R}}\) is \(75^\circ \) .
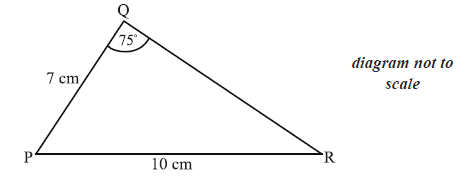
a.Find \({\rm{P}}\widehat {\rm{R}}{\rm{Q}}\) .[3]
b.Find the area of triangle PQR.[3]
Answer/Explanation
choosing sine rule (M1)
correct substitution \(\frac{{\sin R}}{7} = \frac{{\sin 75^\circ }}{{10}}\) A1
\(\sin R = 0.676148 \ldots \)
\({\rm{P}}\widehat {\rm{R}}{\rm{Q = 42}}{\rm{.5}}^\circ \) A1 N2
[3 marks]
\(P = 180 – 75 – R\)
\(P = 62.5\) (A1)
substitution into any correct formula A1
e.g. \({\text{area }}\Delta {\text{PQR}} = \frac{1}{2} \times 7 \times 10 \times \sin ({\text{their }}P)\)
\(= 31.0\) (cm2) A1 N2
[3 marks]
Question
The diagram below shows a triangle ABD with AB =13 cm and AD = 6.5 cm.
Let C be a point on the line BD such that BC = AC = 7 cm.
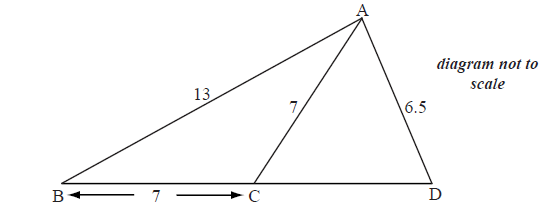
a.Find the size of angle ACB.[3]
b.Find the size of angle CAD.[5]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
METHOD 1
evidence of choosing the cosine formula (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g. \(\cos {\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{C}}{\rm{B}} = \frac{{{7^2} + {7^2} – {{13}^2}}}{{2 \times 7 \times 7}}\)
\({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{C}}{\rm{B}} = 2.38\) radians \(( = 136^\circ )\) A1 N2
METHOD 2
evidence of appropriate approach involving right-angled triangles (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g. \(\sin \left( {\frac{1}{2}{\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{C}}{\rm{B}}} \right) = \frac{{6.5}}{7}\)
\({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{C}}{\rm{B}} = 2.38\) radians \(( = 136^\circ )\) A1 N2
[3 marks]
METHOD 1
\({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{C}} {\rm{D}} = \pi – 2.381\) \((180 – 136.4)\) (A1)
evidence of choosing the sine rule in triangle ACD (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g. \(\frac{{6.5}}{{\sin 0.760 \ldots }} = \frac{7}{{\sin {\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{D}} {\rm{C}}}}\)
\({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{D}}{\rm{C}} = 0.836 \ldots \) \(( = 47.9 \ldots ^\circ )\) A1
\({\rm{C}}\widehat {\rm{A}}{\rm{D}} = \pi – (0.760 \ldots + 0.836 \ldots )\) \((180 – (43.5 \ldots + 47.9 \ldots ))\)
\( = 1.54\) \(( = 88.5^\circ )\) A1 N3
METHOD 2
\({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{B}}{\rm{C}} = \frac{1}{2}(\pi – 2.381)\) \(\left( {\frac{1}{2}(180 – 136.4)} \right)\) (A1)
evidence of choosing the sine rule in triangle ABD (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g. \(\frac{{6.5}}{{\sin 0.380 \ldots }} = \frac{{13}}{{\sin {\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{D}}{\rm{C}}}}\)
\({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{D}}{\rm{C}} = 0.836 \ldots \) \(( = 47.9 \ldots ^\circ )\) A1
\({\rm{C}}\widehat {\rm{A}}{\rm{D}} = \pi – 0.836 \ldots – (\pi – 2.381 \ldots )\) \(( = 180 – 47.9 \ldots – (180 – 136.4))\)
\( = 1.54\) \(( = 88.5^\circ )\) A1 N3
Note: Two triangles are possible with the given information. If candidate finds \({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{D}}{\rm{C}} = 2.31\) \((132^\circ )\) leading to \({\rm{C}}\widehat {\rm{A}}{\rm{D}} = 0.076\) \((4.35^\circ )\) , award marks as per markscheme.
[5 marks]
Question
The diagram below shows a quadrilateral ABCD with obtuse angles \({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{B}}{\rm{C}}\) and \({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{D}}{\rm{C}}\).
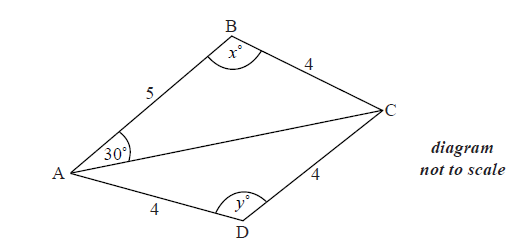
AB = 5 cm, BC = 4 cm, CD = 4 cm, AD = 4 cm , \({\rm{B}}\widehat {\rm{A}}{\rm{C}} = {30^ \circ }\) , \({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{B}}{\rm{C}} = {x^ \circ }\) , \({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{D}}{\rm{C}} = {y^ \circ }\) .
a.Use the cosine rule to show that \({\rm{AC}} = \sqrt {41 – 40\cos x} \) .[1]
b.Use the sine rule in triangle ABC to find another expression for AC.[2]
c.(i) (i) Hence, find x, giving your answer to two decimal places.
(ii) Find AC .[6]
Find y.
d(i) and (ii).(ii) Hence, or otherwise, find the area of triangle ACD.[5]
Answer/Explanation
correct substitution A1
e.g. \(25 + 16 – 40\cos x\) , \({5^2} + {4^2} – 2 \times 4 \times 5\cos x\)
\({\rm{AC}} = \sqrt {41 – 40\cos x} \) AG
[1 mark]
correct substitution A1
e.g. \(\frac{{{\rm{AC}}}}{{\sin x}} = \frac{4}{{\sin 30}}\) , \(\frac{1}{2}{\rm{AC}} = 4\sin x\)
\({\rm{AC}} = 8\sin x\) (accept \(\frac{{4\sin x}}{{\sin 30}}\)) A1 N1
[2 marks]
(i) evidence of appropriate approach using AC M1
e.g. \(8\sin x = \sqrt {41 – 40\cos x} \) , sketch showing intersection
correct solution \(8.682 \ldots \), \(111.317 \ldots \) (A1)
obtuse value \(111.317 \ldots \) (A1)
\(x = 111.32\) to 2 dp (do not accept the radian answer 1.94 ) A1 N2
(ii) substituting value of x into either expression for AC (M1)
e.g. \({\rm{AC}} = 8\sin 111.32\)
\({\rm{AC}} = 7.45\) A1 N2
[6 marks]
(i) evidence of choosing cosine rule (M1)
e.g. \(\cos B = \frac{{{a^2} + {c^2} – {b^2}}}{{2ac}}\)
correct substitution A1
e.g. \(\frac{{{4^2} + {4^2} – {{7.45}^2}}}{{2 \times 4 \times 4}}\) , \({7.45^2} = 32 – 32\cos y\) , \(\cos y = – 0.734 \ldots \)
\(y = 137\) A1 N2
(ii) correct substitution into area formula (A1)
e.g. \(\frac{1}{2} \times 4 \times 4 \times \sin 137\) , \(8\sin 137\)
area \(= 5.42\) A1 N2
[5 marks]
