Question 2. [Maximum mark: 17]
The diagram below shows a circular clock face with centre O. The clock’s minute hand has a length of 10 cm. The clock’s hour hand has a length of 6 cm.
At 4:00 pm the endpoint of the minute hand is at point A and the endpoint of the hour hand is at point B.
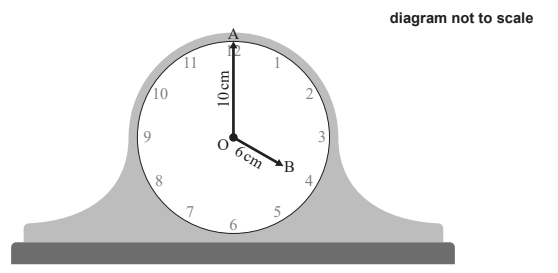
a. Find the size of angle AÔB in degrees. [2]
b. Find the distance between points A and B. [3]
Between 4:00 pm and 4:13 pm, the endpoint of the minute hand rotates through an angle, θ ,
from point A to point C. This is illustrated in the diagram.

c. Find the size of angle θ in degrees. [2]
d. Calculate the length of arc AC. [2]
e. Calculate the area of the shaded sector, AOC. [2]
A second clock is illustrated in the diagram below. The clock face has radius 10 cm with minute and hour hands both of length 10 cm. The time shown is 6:00 am. The bottom of the clock face is located 3 cm above a horizontal bookshelf.
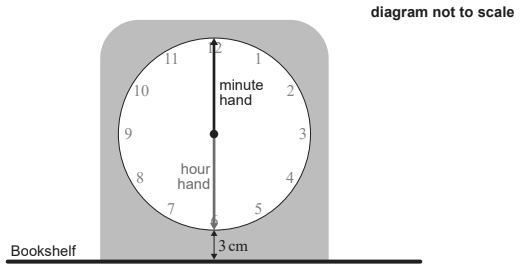
Write down the height of the endpoint of the minute hand above the bookshelf
at 6:00 am. [1]
f. The height, h centimetres, of the endpoint of the minute hand above the bookshelf is modelled by the function
h(θ ) = 10 cosθ + 13 , θ ≥ 0 ,
where θ is the angle rotated by the minute hand from 6:00 am.
g. Find the value of h when θ = 160° . [2]
The height, g centimetres, of the endpoint of the hour hand above the bookshelf is modelled by the function
g(θ ) = -10 cos \((\frac{\Theta }{12})\) + 13 , θ ≥ 0 ,
where θ is the angle in degrees rotated by the minute hand from 6:00 am.
h. Write down the amplitude of g(θ ) . [1]
The endpoints of the minute hand and hour hand meet when θ = k .
Find the smallest possible value of k . [2]
Answer/Explanation
(a) \(4\times \frac{360°\cdot }{12}OR 4\times 30° = 120°\)
(b) cosine rule \(AB^{2}= 10^{2}+6^{2}-2\times 10\times 6\times cos (120°)\)
\(AB= 14cm\)
(c) \(\Theta = 13\times 6= 78°\)
(d) arc length l= \(\frac{78}{360} \times 2\times \pi \times 10\) OR
\(l= \frac{13\pi }{30}\times 10 = 13.6cm(13.6135…,4.33\pi ,\frac{13\pi }{3})\)
(e) Area of a sector \(A= \frac{78}{360}\times \pi \times 10^{2}\) OR \( l=\frac{1}{2}\times \frac{13\pi }{30}\times 10^{2}= 68.1cm^{2}(68.0678…,21.7\pi ,\frac{65\pi }{3}\)
(f) 23
(g) correct substitution h =10cos (160 ) + 13 = 3.60 cm (3.60307…)
(h) 10 (i) EITHER 10\(\times cos(\Theta )+13 = -10\times cos(\frac{\Theta }{12})\)+13
OR  THEN k =196° (196.363…)
THEN k =196° (196.363…)
Question
Hyungmin designs a concrete bird bath. The bird bath is supported by a pedestal. This is shown in the diagram.
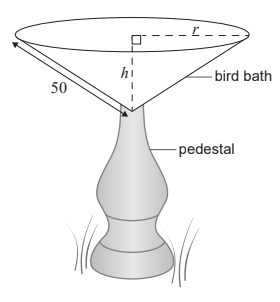
The interior of the bird bath is in the shape of a cone with radius r , height h and a constant slant height of 50 cm.
Write down an equation in r and h that shows this information. [1] Let V be the volume of the bird bath.
Show that V = \(\frac{2500\pi h}{3}-\frac{\pi h^3}{3}\) . [1]
Find \(\frac{dV}{dh}\) . [2]
Hyungmin wants the bird bath to have maximum volume.
Using your answer to part (c), find the value of h for which V is a maximum. [2]
Find the maximum volume of the bird bath. [2] To prevent leaks, a sealant is applied to the interior surface of the bird bath.
Find the surface area to be covered by the sealant, given that the bird bath has
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) \(h^{2}+r^{2}= 50^{2}\) (or equivalent)
(b)
\(\frac{1}{3}\times \pi \times (2500-h^{2})\times h \)
\( V= \frac{2500\pi h}{3}- \frac{\pi h^{3}}{3}\)
(c) \(\frac{dv}{dh}=\frac{2500\pi }{3}-\pi h^{2}\)
(d)
o= \(\frac{25000\pi }{3}-\pi h^{2}\)OR sketch of \(\frac{dv}{dh}\)
\((h= )28.9(cm)\sqrt{\frac{2500}{3}},\frac{50}{\sqrt{3}}\) \(\frac{50\sqrt{3}}{3}\), 28.8675..
(e) (V=)\(\frac{2500\times \pi 28.8675…}{3}-\frac{\pi (28.8675..)^{3}}{3}\)OR \(\frac{1}{3}\pi (40.828…)^{2}\times 28.8675\)…(v=)50400\((cm^{3})(50383.3…)\)
(f)(S=)\(\pi \times \sqrt{2500-(28.86675…)^{2}}\times 50\) (S=) \(6410(cm^{2})(6412.74….)\)
Question
Daniel wants to invest \(\$ 25\,000\) for a total of three years. There are two investment options.
Option One pays compound interest at a nominal annual rate of interest of 5 %, compounded annually.
Option Two pays compound interest at a nominal annual rate of interest of 4.8 %, compounded monthly.
An arithmetic sequence is defined as
un = 135 + 7n, n = 1, 2, 3, …
Calculate the value of his investment at the end of the third year for each investment option, correct to two decimal places.[8]
Determine Daniel’s best investment option.[1]
Calculate u1, the first term in the sequence.[2]
Show that the common difference is 7.[2]
Sn is the sum of the first n terms of the sequence.
Find an expression for Sn. Give your answer in the form Sn = An2 + Bn, where A and B are constants.[3]
The first term, v1, of a geometric sequence is 20 and its fourth term v4 is 67.5.
Show that the common ratio, r, of the geometric sequence is 1.5.[2]
Tn is the sum of the first n terms of the geometric sequence.
Calculate T7, the sum of the first seven terms of the geometric sequence.[2]
Tn is the sum of the first n terms of the geometric sequence.
Use your graphic display calculator to find the smallest value of n for which Tn > Sn.[2]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Option 1: Amount \( = 25\,000{\left( {1 + \frac{5}{{100}}} \right)^3}\) (M1)(A1)
= \(28\,940.63\) (A1)(G2)
Note: Award (M1) for substitution in compound interest formula, (A1) for correct substitution. Give full credit for use of lists.
Option 2: Amount \( = 25\,000{\left( {1 + \frac{{4.8}}{{12(100)}}} \right)^{3 \times 12}}\) (M1)
= \(28\,863.81\) (A1)(G2)
Note: Award (M1) for correct substitution in the compound interest formula. Give full credit for use of lists.[8 marks]
Option 1 is the best investment option. (A1)(ft)[1 mark]
u1 = 135 + 7(1) (M1)
= 142 (A1)(G2)[2 marks]
u2 = 135 + 7(2) = 149 (M1)
d = 149 – 142 OR alternatives (M1)(ft)
d = 7 (AG)[2 marks]
\({S_n} = \frac{{n[2(142) + 7(n – 1)]}}{2}\) (M1)(ft)
Note: Award (M1) for correct substitution in correct formula.
\( = \frac{{n[277 + 7n]}}{2}\) OR equivalent (A1)
\( = \frac{{7{n^2}}}{2} + \frac{{277n}}{2}\) (= 3.5n2 + 138.5n) (A1)(G3)[3 marks]
20r3 = 67.5 (M1)
r3 = 3.375 OR \(r = \sqrt[3]{{3.375}}\) (A1)
r = 1.5 (AG)[2 marks]
\({T_7} = \frac{{20({{1.5}^7} – 1)}}{{(1.5 – 1)}}\) (M1)
Note: Award (M1) for correct substitution in correct formula.
= 643 (accept 643.4375) (A1)(G2)[2 marks]
\(\frac{{20({{1.5}^n} – 1)}}{{(1.5 – 1)}} > \frac{{7{n^2}}}{2} + \frac{{277n}}{2}\) (M1)
Note: Award (M1) for an attempt using lists or for relevant graph.
n = 10 (A1)(ft)(G2)
Note: Follow through from their (c).[2 marks]
Question
A gardener has to pave a rectangular area 15.4 metres long and 5.5 metres wide using rectangular bricks. The bricks are 22 cm long and 11 cm wide.
The gardener decides to have a triangular lawn ABC, instead of paving, in the middle of the rectangular area, as shown in the diagram below.
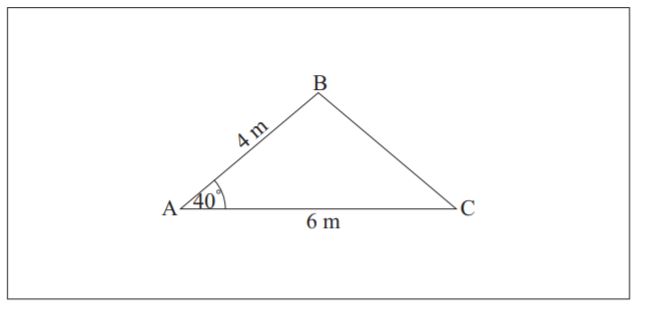
The distance AB is 4 metres, AC is 6 metres and angle BAC is 40°.
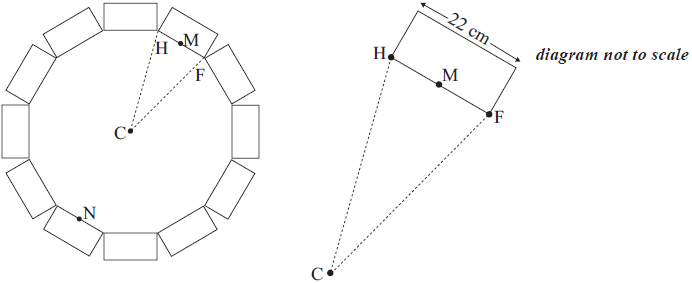
In another garden, twelve of the same rectangular bricks are to be used to make an edge around a small garden bed as shown in the diagrams below. FH is the length of a brick and C is the centre of the garden bed. M and N are the midpoints of the long edges of the bricks on opposite sides of the garden bed.
The garden bed has an area of 5419 cm2. It is covered with soil to a depth of 2.5 cm.
It is estimated that 1 kilogram of soil occupies 514 cm3.
Calculate the total area to be paved. Give your answer in cm2.[3]
Write down the area of each brick.[1]
Find how many bricks are required to pave the total area.[2]
Find the length of BC.[3]
Hence write down the perimeter of the triangular lawn.[1]
Calculate the area of the lawn.[2]
Find the percentage of the rectangular area which is to be lawn.[3]
Find the angle FCH.[2]
Calculate the distance MN from one side of the garden bed to the other, passing through C.[3]
Find the volume of soil used.[2]
Find the number of kilograms of soil required for this garden bed.[2]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
15.4 × 5.5 (M1)
84.7 m2 (A1)
= 847000 cm2 (A1)(G3)
Note: Award (G2) if 84.7 m2 seen with no working.
OR
1540 × 550 (A1)(M1)
= 847000 cm2 (A1)(ft)(G3)
Note: Award (A1) for both dimensions converted correctly to cm, (M1) for multiplication of both dimensions. (A1)(ft) for correct product of their sides in cm.[3 marks]
242 cm2 (0.0242 m2) (A1)[1 marks}
\(\frac {15.4}{0.22} = 70\) (M1)
\(\frac{5.5}{0.11} = 50\)
\(70 \times 50 = 3500\) (A1)(G2)
OR
\(\frac {847000}{242} = 3500\) (M1)(A1)(ft)(G2)
Note: Follow through from parts (a) (i) and (ii).[2 marks]
\({\text{B}}{{\text{C}}^2} = {4^2} + {6^2}-2 \times 4 \times 6 \times \cos 40^\circ \) (M1)(A1)
\({\text{BC}} = 3.90{\text{ m}}\) (A1)(G2)
Note: Award (M1) for correct substituted formula, (A1) for correct substitutions, (A1) for correct answer.[3 marks]
perimeter = 13.9 m (A1)(ft)(G1)
Notes: Follow through from part (b) (i).[1 mark]
\({\text{Area}} = \frac{1}{2} \times 4 \times 6 \times \sin 40^\circ \) (M1)
= 7.71 m2 (A1)(ft)(G2)
Notes: Award (M1) for correct formula and correct substitution, (A1)(ft) for correct answer.[2 marks]
\(\frac{{7.713}}{{84.7}} \times 100{\text{ }}\% = 9.11{\text{ }}\% \) (A1)(M1)(A1)(ft)(G2)
Notes: Accept 9.10 %.
Award (A1) for both measurements correctly written in the same unit, (M1) for correct method, (A1)(ft) for correct answer.
Follow through from (b) (iii) and from consistent error in conversion of units throughout the question.[3 marks]
\(\frac{{360^\circ }}{{12}}\) (M1)
\( = 30^\circ\) (A1)(G2)[2 marks]
\(\text{MN} = 2 \times \frac{11}{\tan 15} \) (A1)(ft)(M1)
OR
\(\text{MN} = 2 \times 11 \tan 75^\circ \)
\({\text{MN}} = 82.1{\text{ cm}}\) (A1)(ft)(G2)
Notes: Award (A1) for 11 and 2 seen (implied by 22 seen), (M1) for dividing by tan15 (or multiplying by tan 75).
Follow through from their angle in part (c) (i).[3 marks]
volume = 5419 × 2.5 (M1)
= 13500 cm3 (A1)(G2)[2 marks]
\(\frac{{13547.34 \ldots }}{{514}} = 26.4\) (M1)(A1)(ft)(G2)
Note: Award (M1) for dividing their part (d) by 514.
Accept 26.3.[2 marks]
