IB Mathematics AA SL Local maximum and minimum values Study Notes - New Syllabus
IB Mathematics AA SL Local maximum and minimum values Study Notes
LEARNING OBJECTIVE
- Local maximum and minimum points.
Key Concepts:
- Local Maximum and Minimum Points
- Optimization
- Points of Inflexion
- IBDP Maths AA SL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 1
- IBDP Maths AA SL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 2
- IB DP Maths AA HL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 1
- IB DP Maths AA HL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 2
- IB DP Maths AA HL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 3
Local Maximum and Minimum Points
Local Maximum and Minimum Points
Concept:
- A local maximum occurs when a function changes from increasing to decreasing.
- A local minimum occurs when a function changes from decreasing to increasing.
- Use the first derivative test or second derivative test to identify them.
-

Important Rules:
- If \( f'(x) = 0 \) and \( f”(x) > 0 \), there is a local minimum.
- If \( f'(x) = 0 \) and \( f”(x) < 0 \), there is a local maximum.
Example
Find the local maximum and minimum points of the function:
\( f(x) = x^3 – 3x^2 + 4 \)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
\( f'(x) = 3x^2 – 6x \)
Set \( f'(x) = 0 \) ⇒ \( x(x – 2) = 0 \) ⇒ \( x = 0 \), \( x = 2 \)
Second derivative: \( f”(x) = 6x – 6 \)
\( f”(0) = -6 \) ⇒ maximum at \( x = 0 \)
\( f”(2) = 6 \) ⇒ minimum at \( x = 2 \)
Local maximum: \( f(0) = 4 \)
Local minimum: \( f(2) = 0 \)
Optimization
Optimization
Concept:
- Used to find maximum or minimum values in real-world problems.
- Applications: maximize area, minimize cost, maximize profit, etc.
Steps:
- Write the quantity to optimize.
- Use constraints to reduce variables.
- Differentiate and solve \( f'(x) = 0 \).
- Use the second derivative test or endpoints to confirm.
Example
A rectangle is to be drawn with a fixed perimeter of 40 cm. Find the dimensions that give the maximum area.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Let width = \( x \), then length = \( 20 – x \) (since perimeter = 2(x + length))
Area = \( A = x(20 – x) = 20x – x^2 \)
Derivative: \( A'(x) = 20 – 2x \)
Set to zero: \( A'(x) = 0 \Rightarrow x = 10 \)
So length = 10, width = 10
Maximum area: when rectangle is a square (10 × 10 cm)
Example
A company sells a product for $20 per unit. The cost to produce x units is given by \( C(x) = 5x + 100 \). Find the number of units that must be sold to maximize profit.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Revenue \( R(x) = 20x \)
Cost \( C(x) = 5x + 100 \)
Profit \( P(x) = R(x) – C(x) = 20x – (5x + 100) = 15x – 100 \)
Derivative: \( P'(x) = 15 \)
Since derivative is constant, profit increases with more units. No maximum within a restricted domain, but check context limits.
If the question had a domain (e.g., 0 ≤ x ≤ 50), you’d check endpoints.
Example
A closed cylindrical can is to be made with a fixed surface area of 600 cm². Find the dimensions (radius and height) that give the maximum volume.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Let radius = \( r \), height = \( h \)
Surface area: \( 2\pi r^2 + 2\pi rh = 600 \)
Solve for \( h \): \( h = \frac{600 – 2\pi r^2}{2\pi r} \)
Volume: \( V = \pi r^2 h \)
Substitute \( h \):
\( V = \pi r^2 \cdot \frac{600 – 2\pi r^2}{2\pi r} = \frac{r(600 – 2\pi r^2)}{2} \)
Differentiate and solve \( V'(r) = 0 \) to find max volume.
This leads to optimal ratio when height = 2 × radius.
Conclusion: For maximum volume, the height equals the diameter (i.e., \( h = 2r \))
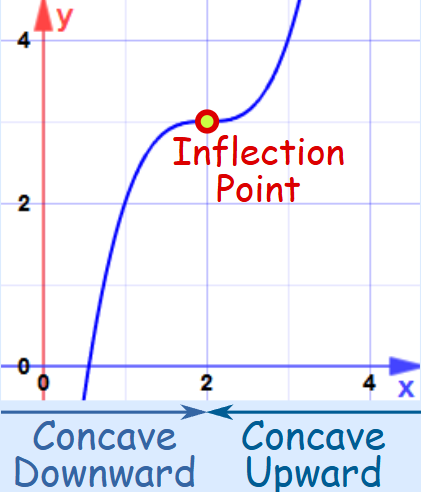
Points of Inflexion
Points of Inflexion
Concept:
- A point where the graph changes concavity (from concave up to down or vice versa).
- Occurs when \( f”(x) = 0 \) and changes sign.
- \( f”(x) = 0 \) alone is not sufficient – sign change is necessary.

Concavity Terms:
- “Concave up” when \( f”(x) > 0 \)
- “Concave down” when \( f”(x) < 0 \)
Example
Determine the point of inflexion for the function \( f(x) = x^3 \).
▶️ Answer/Explanation
\( f'(x) = 3x^2 \),
\( f”(x) = 6x \)
Set \( f”(x) = 0 \):
\( 6x = 0 \Rightarrow x = 0 \)
Test sign of \( f”(x) \):
\( f”(-1) = -6 \),
\( f”(1) = 6 \) ⇒ sign changes
So, point of inflexion at \( x = 0 \),
Coordinates: \( (0, 0) \)