IBDP Physics- A.2 Forces and momentum- IB Style Questions For HL Paper 2 -FA 2025
Question
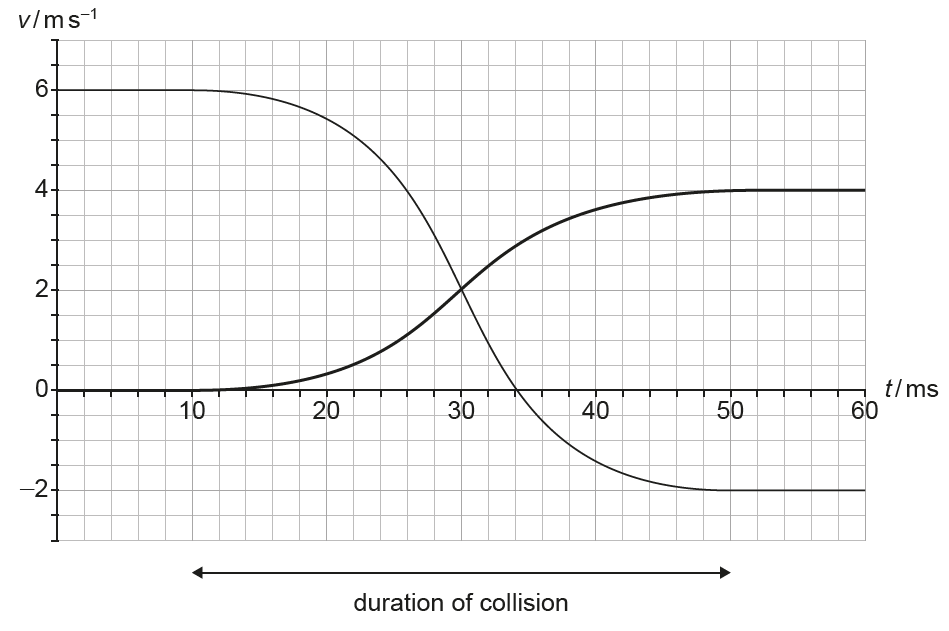
(i) the magnitude of the average force acting on trolley Y,
(ii) the average power transferred to trolley Y,
(iii) the elastic potential energy stored in the spring at \(t = 30\,ms\).
Most-appropriate topic codes (IB Physics):
• Topic A.2: Forces and momentum (Impulse and force) — part (b)(i)
• Topic A.3: Work, energy and power — part (b)(ii), (b)(iii)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)
Initial kinetic energy:
\(KE_i = \frac{1}{2}(3.0)(6.0)^2 = 54\,J\).
Final velocities from the graph are \(v_X = -2.0\,m\,s^{-1}\) and \(v_Y = 4.0\,m\,s^{-1}\).
Final kinetic energy:
\(KE_f = \frac{1}{2}(3.0)(-2.0)^2 + \frac{1}{2}(6.0)(4.0)^2 = 6 + 48 = 54\,J\).
Since the total kinetic energy is unchanged, the collision is elastic.
(b)
(i) The average force on trolley Y is given by the rate of change of its momentum:
\(F = \frac{\Delta p}{\Delta t} = \frac{6.0(4.0 – 0)}{40 \times 10^{-3}} = 6.0 \times 10^{2}\,N\).
(ii) The average power delivered to Y is the rate of increase of its kinetic energy:
\(P = \frac{48}{40 \times 10^{-3}} = 1200\,W\).
(iii) At \(t = 30\,ms\), both trolleys have a speed of \(2.0\,m\,s^{-1}\).
Total kinetic energy at this instant:
\(KE_{30} = \frac{1}{2}(3.0 + 6.0)(2.0)^2 = 18\,J\).
Using conservation of energy, the elastic energy stored in the spring is:
\(E_{spring} = 54 – 18 = 36\,J\).
