IBDP Physics- B.3 Gas laws- IB Style Questions For HL Paper 2 -FA 2025
Question
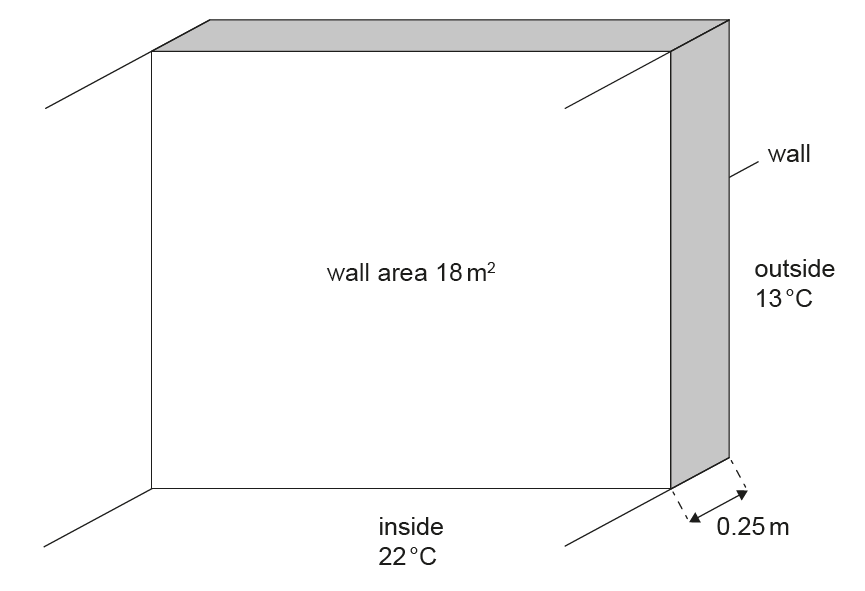
Thickness of the wall \(= 0.25\,m\)
Area of the wall \(= 18\,m^{2}\)
Thermal conductivity of the wall material \(= 1.3\,W\,m^{-1}\,K^{-1}\)
Constant temperature inside the room \(= 22^{\circ}C\)
Constant temperature outside \(= 13^{\circ}C\)
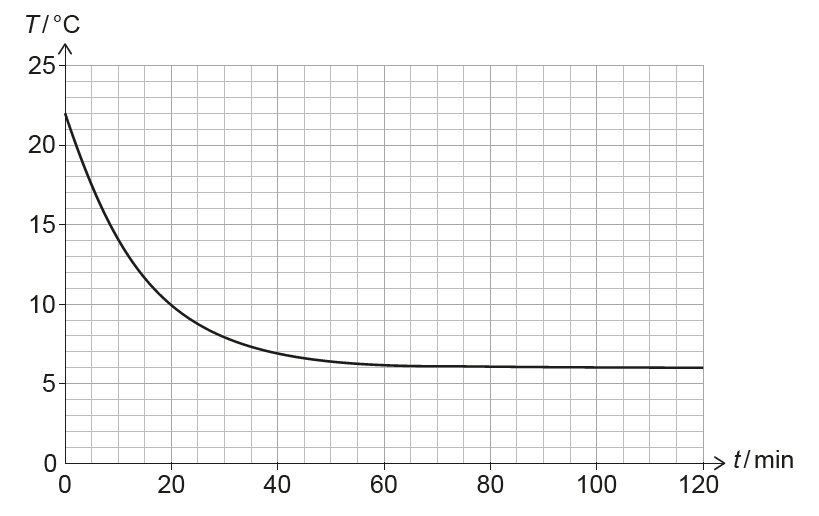
(ii) The pressure and volume of the air in the room remain constant, but the number of air molecules increases. Calculate the percentage increase in the number of air molecules in the room between \(t = 0\) and \(t = 120\,min\).
Most-appropriate topic codes (IB Physics):
• Topic B.3: Gas laws — part (c)(ii)
• Topic B.4: Thermodynamics (Entropy / Second Law) — part (d)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)
In conduction, thermal energy is transferred through collisions between neighbouring atoms or molecules. In metals, free electrons also move through the material and transfer energy by collisions.
(b)
Using \(\dfrac{\Delta Q}{\Delta t} = kA\dfrac{\Delta T}{\Delta x}\):
\[ \text{Rate} = \frac{1.3 \times 18 \times (22 – 13)}{0.25} \approx 8.4 \times 10^{2}\,W \]
(c)
(i) The rate of heat transfer depends on the temperature difference between the room and the surroundings. As the room cools, this temperature difference becomes smaller, so the rate of cooling (the gradient) decreases.
(ii) From \(PV = NkT\), with \(P\) and \(V\) constant, \(NT = \text{constant}\).
At \(t=0\): \(T_1 = 22^\circ C = 295\,K\). At \(t=120\,min\): \(T_2 = 6^\circ C = 279\,K\).
\[ \frac{N_2}{N_1} = \frac{T_1}{T_2} = \frac{295}{279} \approx 1.057 \] Percentage increase \(\approx 5.7\%\).
(d)
Thermal energy flows naturally from the warmer room to the cooler surroundings. This process increases the total entropy of the universe, in accordance with the second law of thermodynamics.
